Abstract
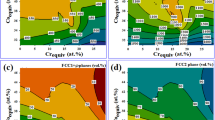
A set of novel Co-free high-entropy alloys CrxFeNi(3-x)Al (x = 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.25, 1.5) were fabricated by non-self-consumable vacuum melting method, and their solidification microstructures as well as compression properties were investigated. The research results firstly demonstrate that the solidification microstructures of Cr-0.25, Cr-0.5 and Cr-0.75 are composed of primary B2 phase and (FCC + B2) eutectic structure; Secondly, there are primary B2 phase and (FCC + B2) eutectic structure in the solidification microstructure of Cr-1, with a tiny amount of BCC phase distributing on the matrix of primary phase B2; In addition, as a “sunflower-like" structure of BCC phase and B2 phase, the solidification microstructure of Cr-1.25 is identified. Also, the core of the sunflower is B2 phase, and the petals are alternately arranged by BCC phase and B2 phase; Last but not least, it is a fine BCC phase and B2 dual-phase structure that form the solidification microstructure of Cr-1.5. Among the phases mentioned above, the FCC phase is abundant in Ni and Fe elements, the B2 phase is abundant in Ni and Al elements, and the BCC phase is abundant in Cr element. With the ascending trend of Cr content, the strength of CrxFeNi(3-x)Al high-entropy alloy descends initially and then climbs, during which the primary reasons for the rise of strength are solid solution strengthening, fine crystal strengthening and precipitation of BCC phase. The compressive strengths of Cr-1.25 and Cr-1.5 alloys are 2111.5 and 1985.3 MPa, respectively, and the compressibility can attain to 41.36 and 49.87%, respectively, manifesting comprehensive mechanical properties.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin et al., Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6(5), 299 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200300567
B. Cantor, I. Chang, P. Knight et al., Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 375, 213 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.10.257
Z.A. Yong, A. Ttz, T.B. Zhi et al., Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater Sci. 61, 1 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2013.10.001
A.D.B.M. Bons, A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Materialia 122, 448 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.08.081
Z.P. Liu et al., An assessment on the future development of high-entropy alloys: Summary from a recent workshop. Intermetallics 66, 67 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2015.06.021
J.-W. Yeh, Alloy Design Strategies and Future Trends in High-Entropy Alloys. JOM 65, 1759 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-013-0761-6
M.H. Chuang, M.H. Tsai, W.R. Wang et al., Microstructure and wear behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy high-entropy alloys. Acta Materialia 59(16), 6308 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2011.06.041
Y. Zou, H. Ma, R. Spolenak, Ultrastrong ductile and stable high-entropy alloys at small scales. Nat. Commun. 6, 7748 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8748
Y.D. Wu, Y.H. Cai, T. Wang et al., A refractory Hf25Nb25Ti25Zr25 high-entropy alloy with excellent structural stability and tensile properties. Mater. Lett. 130, 277 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.05.134
Y. Deng, C. Tasan, K. Pradeep et al., Design of a twinning-induced plasticity high entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 94, 124 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2015.04.014
D. Li, C. Li, T. Feng et al., High-entropy Al03CoCrFeNi alloy fibers with high tensile strength and ductility at ambient and cryogenic temperatures. Acta Materialia 123, 285 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.10.038
B. Gludovatz, A. Hohenwarter, D. Catoor et al., A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 345(6201), 1153 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254581
Z. Tang, T. Yuan, C. Tsai et al., Fatigue behavior of a wrought Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi two-phase high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 99, 247 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2015.07.004
M.A. Hemphill, T. Yuan, G.Y. Wang et al., Fatigue behavior of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloys. Acta Materialia 60(16), 5723 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2012.06.046
Y. Lu, Y. Dong, S. Guo et al., A promising new class of high-temperature alloys: eutectic high-entropy alloys. Rep 4, 6200 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06200
I.S. Wani, T. Bhattacharjee, S. Sheikh et al., Tailoring nanostructures and mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high entropy alloy using thermo-mechanical processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 675, 99 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.08.048
A. Ib, A. Mw, B. Zw, Eutectic/eutectoid multi-principle component alloys: a review. Mater. Charact. 147, 545 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2018.07.030
X. Ye et al., A new infinite solid solution strategy to design eutectic high entropy alloys with B2 and BCC structure. Scripta Materialia. 199, 74128 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113886.
J. Xi, Z. Yang, Z. Lu et al., A novel Fe20Co20Ni41Al19 eutectic high entropy alloy with excellent tensile properties-ScienceDirect. Mater. Lett. 216, 144 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.01.017
S. Vrtnik, S. Guo, S. Sheikh et al., Magnetism of CoCrFeNiZrx eutectic high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 93, 122 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2017.11.017
Q. Wu, Z. Wang, T. Zheng et al., A casting eutectic high entropy alloy with superior strength-ductility combination[J]. Mater. Lett. 253, 268 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.06.067
Y. Dong, Z. Yao, X. Huang et al., Microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCoxCrFeNi3-x eutectic high-entropy-alloy system. J. Alloys Compounds 823, 153886 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.153886
X. Jin, Y. Zhou, L. Zhang et al., A new pseudo binary strategy to design eutectic high entropy alloys using mixing enthalpy and valence electron concentration. Mater. Des. 143, 49 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2018.01.057
A. Shafiei, S. Rajabi, A cobalt-rich eutectic high-entropy alloy in the system Al–Co–Cr–Fe–Ni. Appl. Phys. A 125, 11 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3084-9
J. Xi, J. Bi, Z. Lu et al., A new CrFeNi2Al eutectic high entropy alloy system with excellent mechanical properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 770, 655 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.08.176
G. Sheng, C. Ng, L. Jian et al., Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 109(10), 213 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3587228
X. Yong Dong, YLu. Gao et al., A multi-component AlCrFe2Ni2 alloy with excellent mechanical properties. Mater. Lett. 169, 62 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.01.096
C. Zhang, Z. Fan, S. Chen et al., Computational thermodynamics aided high-entropy alloy design,. JOM: J. Minerals Metals Mater. Soc. 64(7), 839 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-012-0365-6
A. Subramaniam Anil et al., On the formation of disordered solid solutions in multi-component alloys. J. Alloys Compounds: Interdiscipl. J. Mater. Sci. Solid-state Chem. Phys. 587, 113 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.10.133
Q.W. Tian, G.J. Zhang et al., Homogenization of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys with improved corrosion resistance. Mater. Charact. 151, 302 (2019)
D.B. Miracle, Overview No. 104 the physical and mechanical properties of NiAl. Acta Metallurgica Et Materialia 41(3), 649 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-7151(93)90001-9
W.H. Liu, J.Y. He, H.L. Huang et al., Effects of Nb additions on the microstructure and mechanical property of CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 60, 1 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2015.01.004
M. Yue, B. Jiang, C. Li et al., The BCC/B2 morphologies in AlxNiCoFeCr high-entropy alloys. Metals-Open Access Metall. J. 7(2), 57 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/met7020057
B.S. Li, Y.P. Wang, M.X. Ren et al., Effects of Mn Ti and V on the microstructure and properties of AlCrFeCoNiCu high entropy alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 498(1–2), 482 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2008.08.025
Z. Xuerou, L. Yukun, S. Tuo, Advances in the study of phase formation theory of high entropy alloys. Mater. Guide 33(7), 1174 (2019)
Y, Zhang, et al., Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 10(6), 534 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200700240
P. Jinsheng, Q. Jianmin, T. Minbo, Fundamentals of materials science (Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, 2006)
Y.P. Lu, H. Jiang, S. Guo et al., A new strategy to design eutectic high-entropy alloys using mixing enthalpy. Intermetallics 91, 124 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2017.09.001
X. Yang, Y. Zhang, Prediction of high-entropy stabilized solid-solution in multi-component alloys-ScienceDirect. Mater. Chem. Phys. 132(2), 233 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.11.021
Dong Yong. Fundamental study on microstructure and mechanical properties in multi-phase Al-Cr-Fe-Ni-M high entropy alloys, (2016).
Acknowledgements
The research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51604161), Yichang Key Laboratory of Graphite Additive Manufacturing Program (Nos. YKLGAM202001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Ye, X., Xu, D. et al. Microstructures and properties of CrxFeNi(3-x)Al high-entropy alloys. Appl. Phys. A 128, 1 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05118-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05118-z