Abstract
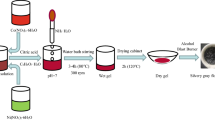
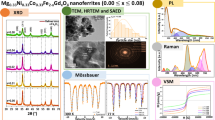
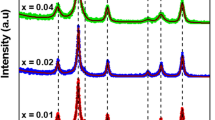
In this study, magnesium–cobalt nanoferrites (MCNF) doped with La3+ ions were prepared by sol–gel method. The chemical formula of the samples prepared was Mg0.2Co0.8Fe2-xLaxO4 (x = 0.0, x = 0.025, x = 0.05, x = 0.075, x = 0.1). The crystal structure of the samples and the successful doping of La3+ ions can be obtained by X-ray diffraction (XRD). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) reflects the information of absorption bands and functional groups in a certain range. According to the position of different absorption bands, it can be judged that the chemical reaction has been completed in the preparation process. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images showed that the sample is spherical, the particle size distribution is narrow, and the sample size is uniform. Energy dispersion spectroscopy (EDS) was used to characterize the specific elements in the samples and confirmed that the elements in the samples were Mg, Co, Fe, La, and O. There were no other impurities in the samples. Vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) is used primarily to analyze the magnetic properties of samples. The results demonstrate that the doping of La3+ ions can change the crystal properties of the samples, and Mg0.2Co0.8Fe2-xLaxO4 has a cubic spinel structure. The coercivity of the sample is between 611.24 and 779.43 Oe, and it has the properties of hard magnetic materials.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.F. Huq, D.K. Sah, R. Ahmed, Z.H. Mahmood, Ni–Cu–Zn ferrite research: a brief review. J. Sci. Res. 216, 215–233 (2013)
B. Coehi-Eromosele, S. Eejiweala, Palanawe, Magneto-structural properties of Ni–Zn nanoferrites synthesized by the low-temperature auto-combustion method. B. Mater Sci. 1465, 1465–1472 (2015)
P. Thakura, R. Sharma, M. Kumar, S.C. Katyal, P.B. Barman, V. Sharma, P. Sharma, Structural, morphological, magnetic and optical study of co-precipitated Nd3+ doped Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 317, 317–325 (2019)
P.V. Gaikwad, R.J. Kamble, S.J. Mane-Gavade, S.R. Sabale, P.D. Kamble, Magneto-structural properties and photocatalytic performance of sol–gel synthesized cobalt substituted Ni–Cu ferrites for degradation of methylene blue under sunlight. Physica B. 79, 79–85 (2019)
N. Feltin, M.P. Pileni, New Technique for Synthesizing Iron Ferrite Magnetic Nanosized Particles. Langmuir 3927, 3927–3933 (1997)
W. Wernsdorfer, E. Bonet Orozco, K. Hasselbach, A. Benoit, D. Mailly, O. Kubo, H. Nakano, B. Barbara, Macroscopic quantum tunneling of magnetization of single ferrimagnetic nanoparticles of barium ferrite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 4014, 4014–4017 (1997)
K. Gwang-Hee, D.S. Hwang, Magnetic-field dependence of macroscopic quantum tunneling and coherence of ferromagnetic particles. Phys. Rev. B 55, 8918–8917 (1997)
Z Ahmada, S Atiqa, S. Kumail Abbasa, Shahid Mahmood Ramayb, Saira Riaza, Shahzad Naseem, Structural and complex impedance spectroscopic studies of Mg-substituted CoFe2O4. Ceram. Int. 1, 0272–8842 (2016)
C.O. Ehi-Eromosele, B.I. Ita, E.E.J. Iweala, Low-temperature combustion synthesis of cobalt magnesium ferrite magnetic nanoparticles: effects of fuel-to-oxidizer ratio and sintering temperature. J. Sol-Gel Sci Techn. 2, 0928–1707 (2015)
S.F. Mansour, O.M. Hemeda, S.I. El-Dek, B.I. Salem, Influence of La doping and synthesis method on the properties of CoFe2O4 nanocrystals. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 7, 7–8 (2016)
M.I.A. Abdel Maksoud, G.S. El-Sayyad, A. Abokhadra, L.I. Soliman, H.H. El-Bahnasawy, A.H. Ashour, J. Mater. Sci-Mater. El. 2599, 2598–2616 (2020)
S.E. Jacobo, P.G. Bercoff, Structural and electromagnetic properties of yttrium-substituted Ni–Zn ferrites. Ceram. Int. 7664, 7664–7668 (2016)
R. Jasrotia, Virender Pratap Singh, Rajesh Kumar, Kirti Singha, Monika Chandel, Mahavir Singh, Analysis of Cd2+and In3+ions doping on microstructure, optical, magnetic and mössbauer spectral properties of sol-gel synthesized BaM hexagonal ferrite based nanomaterials. Results Phys. 1933, 1933–1941 (2019)
Muhammad Farooq Warsi, Ayesha Iftikhar, Muhammad Asif Yousuf, Muhammad Ilyas Sarwar, Sheraz Yousaf, Sajjad Haider, Mohamed F. Aly Aboud, Imran Shakir, Sonia Zulfiqar, Erbium substituted nickel–cobalt spinel ferrite nanoparticles: Tailoring the structural, magnetic and electrical parameters. Ceram. Int. 24194, 24194–24203 (2020)
S.M. Kabbur, U.R. Ghodake, R.C. Kambale, S.D. Sartale, L.P. Chikhale, S.S. Suryavanshi, Magnetic Electric and Optical Properties of Mg-Substituted Ni–Cu–Zn Ferrites. J. Electron. Mater. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5616-4
M.K. Shobana, Wonjong Nam, Heeman Choe, Yttrium-Doped Cobalt Nanoferrites Prepared by Sol-Gel Combustion Method and Its Characterization. J. Nanosci. Nanotechno. 3535, 3535–3538 (2013)
Y. Xuan, Q. Li, G. Yang, Synthesis and magnetic properties of Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 464, 464–469 (2007)
M. Anis-ur-Rehman ·MA Malik, M. Akram · M. Kamran · K Khan, A Maqsood, Structural and Magnetic Properties of Nanocrystalline Mg–Co Ferrites. J Supercond Nov Magn. 2693:2691–2696 (2012)
Z.K. Heiba, M.B. Mohamed, A.M. Wahba, L. Arda, Magnetic and Structural Properties of Nanocrystalline Cobalt-Substituted Magnesium–Manganese Ferrite. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3069-7 (2015)
L.-Z. Li, X.-X. Zhong, R. Wang, Tu. Xiao-Qiang, L. Peng, Structural and magnetic properties of Co-substituted NiCu ferrite nanopowders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 98, 98–103 (2017)
B. Rajesh Babu, M.S.R. Prasad, K.V. Ramesh, Y. Purushotham, Structural and Magnetic properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5AlxFe2-xO4 nano ferrite system. Mater. Chem. Phys. 586, 585–591 (2014)
S. Karimi, P. Kameli, H. Ahmadvand, H. Salamati, Effects of Zn-Cr-substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of Ni1-xZnxFe2-xCrxO4 ferrites. Ceram. Int. 16948, 16948–16955 (2016)
N. Yadav, A. Kumar, P.S. Rana, D.S Rana, M. Arora, R.P. Pant, Finite size effect on Sm3þdoped Mn0.5Zn0.5SmxFe2-xO4 (0≤x≤0.5) ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 8623, 8623–8629 (2015)
A.B. Gadkari, T.J. Shinde, P.N. Vasambekar, Structural analysis of Sm3+doped nanocrystalline Mg–Cd ferrites prepared by oxalate co-precipitation method. Mater. Charact. 1328, 1328–1333 (2008)
L. Wang, B.K. Rai, S.R. Mishra, Structural and magnetic study of Al3+doped Ni0.75Zn0.25Fe2-xAlxO4 nanoferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 813, 183–194 (2015)
A.M. Roy, Formation and stability of nanosized, undercooled propagating intermediate melt duringβ→δphase transformation in HMX nanocrystal. 1, 56001 (2021)
A.M. Roy, Energetics and kinematics of undercooled nonequilibrium interfacial molten layer in cyclotetramethylene-tetranitramine crystal. Physica B. 1, 412986 (2021)
W.R. Agami, Effect of neodymium substitution on the electric and dielectric properties of Mn–Ni–Zn ferrite. Physica B. 534, 17–21 (2018)
M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M. Behpour, A. Sobhani-Nasab, S.M. Hosseinpour-Mashkani, ZnFe2–xLaxO4 nanostructure: synthesis, characterization, and its magnetic properties. J. Multidiscip. Sci. 26, 9776–9781 (2015)
N.S. Kumar, K.V. Kumar, Synthesis and structural properties of bismuth doped cobalt nanoferrites prepared by sol-gel combustion method. World 5, 140–151 (2015)
W. Wang, Z. Ding, X. Zhao, S. Wu, F. Li, M. Yue, J. P. Liu, Microstructure and magnetic properties of MFe2O4 (M = Co, Ni, and Mn) ferrite nanocrystals prepared using colloid mill and hydrothermal method. J. Appl. Phys. 117, 17A328 (2015)
N. Suo, A. Sun, Y. Zhang, Yu. Lichao, L. Shao, Z. Zuo, Magnetic transformation of Ni–Mg–Zn ferrite substituted by the Co2+ ions from soft magnetic to hard magnetic. J. Mater. Sci. 2390(32), 3286–3302 (2021)
A.B. Gadkaria, T.J. Shinde, P.N. Vasambekar, Structural analysis of Y3+-doped Mg–Cd ferrites prepared by oxalate co-precipitation method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 508, 505–510 (2009)
L. Yu, A. Sun, N. Suo, Z. Zuo, X. Zhao, W. Zhang, Structural, morphological and magnetic properties of Ni–Cu–Co ferrites by the Sm3+ions substitution. Mod. Phys. Lett. B. 10, 2050236 (2020)
V. Vinayak, P.P. Khirade, S.D. Birajdar, D.B. Sable, K.M. Jadhav, Structural, Microstructural, and Magnetic Studies on Magnesium (Mg2+)-Substituted CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 1026, 1025–1032 (2016)
Mi. Yan, X. Peng, Fundamentals of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials (Zhejiang University Press, Zhejiang, 2006), p. 10
S. Bhukal, T. Namgyal, S. Mor, S. Bansal, S. Singhal, Structural, electrical, optical and magnetic properties of chromium substituted Co–Zn nanoferrites Cu0.6Zn0.4CrxFe2-xO4 (0≤x≤1.0) prepared via sol-gel Au-to-combustion method. J. Mol Struct. 1012, 12–167 (2012)
P.A. Shaikh, R.C. Kambale, A.V. Rao, Y.D. Kolekar, Effect of Ni doping on structural and magnetic properties of Co1–xNixFe1.9Mn0.1O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 718–726 (2010)
J.M.D. Coey, Rare-Earth Iron Permanent Magnets, vol. 45 (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1996), p. 5526
J.M.D. Coey, Rare earth-iron permanent magnets. J. Cheminformatics. 23 (2010)
V. Chaudhari, S.E. Shirsath, M.L. Mane, R.H. Kadam, S.B. Shelke, D.R. Mane, Crystallographic, magnetic and electrical properties of Ni0.5Cu0.25Zn0.25LaxFe2-xO4 nanoparticles fabricated by sol–gel method. J. Alloy. Compd. 549, 213–220 (2013)
R. Jasrotia, Virender Pratap Singh, Rajesh Kumar, Kirti Singha, Monika Chandel, Mahavir Singh, Analysis of Cd2+ and In3+ ions doping on microstructure, optical, magnetic and mössbauer spectral properties of sol–gel synthesized BaM hexagonal ferrite based nanomaterials. Results Phys. 1938, 1933–1941 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Sun, A., Jiang, Y. et al. Influence of La3+ ions doping on morphology and magnetic properties of Mg–Co ferrites. Appl. Phys. A 127, 926 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05054-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05054-y