Abstract
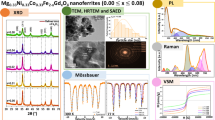
In this study, lanthanum La-doped Mg0.33Ni0.33Co0.33Fe2-xLaxO4 (0.00 ≤ x ≤ 0.08) nanoferrites were synthesized using the co-precipitation method. The physical properties of the samples were examined using X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), selected area electron diffraction (SAED), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The XRD results confirmed the formation of a single-phase spinel ferrite. Upon increasing the La3+ ions concentration, crystallite and particle sizes decreased as revealed from XRD and TEM analysis, respectively. The values of the lattice parameter estimated from the SAED are in harmony with those obtained from XRD patterns. The appearance of two bands in the FTIR spectra, mainly in the range of 592–595 and 387–422 cm−1, confirms the formation of the spinel structure. Furthermore, the red shift in A1g Raman mode, observed in La-doped nanoferrites, was attributed to the active motion of Fe3+ towards the A sites. The samples demonstrated a ferromagnetic behavior with a reducing saturation magnetization from 31.87 to 12.99 emu/g as x increased from 0.00 to 0.08, respectively. Different forms of the law of approach to saturation (LAS) were employed to fit M–H hysteresis curves of experimental data. Moreover, different parameters were investigated, including the exchange field, anisotropy field, Bohr magneton, and magnetocrystalline anisotropy. These parameters were further analyzed to check the accuracy of the fitting and the best-suited model.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
V. Manikandan, A. Mirzaei, S. Vigneselvan, S. Kavita, R.S. Mane, S.S. Kim, J. Chandrasekaran, Role of ruthenium in the dielectric, magnetic properties of nickel ferrite (Ru–NiFe2O4) nanoparticles and their application in hydrogen sensors. ACS Omega 4, 12919–12926 (2019)
M.F. Al-Hilli, S. Li, K.S. Kassim, Structural analysis, magnetic and electrical properties of samarium substituted lithium–nickel mixed ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 873–879 (2012)
M. Abdellatif, A. Azab, M. Salerno, Effect of rare earth doping on the vibrational spectra of spinel Mn-Cr ferrite. Mater. Res. Bull. 97, 260–264 (2018)
S. Kumar, T.J. Shinde, P.N. Vasambekar, Microwave synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline Mn-Zn ferrites, Advanced. Mater. Lett. 4, 373–377 (2013)
M.N. Akhtar, A. Sulong, M. Akhtar, M.A. Khan, Systematic study of Ce3+ on the structural and magnetic properties of Cu nanosized ferrites for potential applications. J. Rare Earths 36, 156–164 (2018)
Y. Dasan, B. Guan, M. Zahari, L. Chuan, Influence of La3+ substitution on structure, morphology and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni-Zn ferrite. PLoS ONE 12, e0170075 (2017)
H. Ghorbani, M. Eshraghi, A.S. Dodaran, Structural and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles doped with cadmium. Physica B 634, 413816 (2022)
P. Sowjanya, N.P. Kumar, A. Chelvane, M.R. Reddy, Synthesis and analysis of low field high magnetostrictive Ni–Co ferrite for magneto-electric energy harvesting applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 279, 115674 (2022)
N. Abinaya, M.C. Robert, N. Srinivasan, S. Saravanakumar, Electron density mapping and bonding in Mn doped CoFe2O4 using XRD, and its correlation with room temperature optical and magnetic properties, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, (2023) 170938.
S. Bhandare, R. Kumar, A. Anupama, M. Mishra, R.V. Kumar, V. Jali, B. Sahoo, Effect of Mg-substitution in Co–Ni-Ferrites: cation distribution and magnetic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 251, 123081 (2020)
X. Zeng, Z. Hou, J. Ju, L. Gao, J. Zhang, Y. Peng, The cation distributions of Zn-doped normal spinel MgFe2O4 ferrite and its magnetic properties. Materials 15, 2422 (2022)
R. Rosnan, Z. Othaman, R. Hussin, A.A. Ati, A. Samavati, S. Dabagh, S. Zare, Effects of Mg substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of Co0.5Ni0.5−xMgxFe2O4 nanoparticle ferrites, Chinese Physics B, 25 (2016) 047501.
Y. Jiang, A. Sun, X. Huang, J. Wang, Study on the crystal structure and magnetic properties of Zn-Cu–Co nano ferrite doped with Yb3+. J. Alloy. Compd. 931, 167527 (2023)
N. Suo, A. Sun, L. Yu, Z. Zuo, X. Zhao, W. Zhang, Y. Zhang, L. Shao, T. Yu, Preparation and study of lattice structure and magnetic properties of Bi3+ ion-doped Ni–Mg–Co ferrites by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 95, 360–374 (2020)
L. Shao, A. Sun, Y. Zhang, L. Yu, N. Suo, Z. Zuo, Comparative study on the structure and magnetic properties of Ni-Mg-Co ferrite doped with Al and rare earth elements. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 5339–5352 (2021)
O. Hemeda, A. Tawfik, M. Mostafa, M. Zaki, M. Abd El Ati, Structural and magnetic properties of nano ferrite for magnetoelectric applications, Journal of Physics: Conference Series, IOP Publishing, 2019, pp. 012026.
N. Suo, A. Sun, Y. Zhang, L. Yu, L. Shao, Z. Zuo, Magnetic transformation of Ni–Mg–Zn ferrite substituted by the Co2+ ions from soft magnetic to hard magnetic. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 3286–3302 (2021)
H.-S. Guo, L. Zhang, Y.-L. Yan, J. Zhang, J. Wang, S.-Y. Wang, L.-Z. Li, X.-H. Wu, Effect of lanthanum substitution on structural, magnetic, and electric properties of Ni–Zn–Co ferrites for radio frequency and microwave devices. Ceram. Int. 48, 22557–22563 (2022)
K. Sakthipandi, K. Kannagi, A. Hossain, Effect of lanthanum doping on the structural, electrical, and magnetic properties of Mn0.5Cu0.5LaxFe2−xO4 nanoferrites, Ceramics International, 46 (2020) 19634–19638.
A. Aslam, A.U. Rehman, N. Amin, M.A. un Nabi, Q. ul ain Abdullah, N. Morley, M.I. Arshad, H.T. Ali, M. Yusuf, Z. Latif, Lanthanum doped Zn0.5Co0.5LaxFe2−xO4 spinel ferrites synthesized via co-precipitation route to evaluate structural, vibrational, electrical, optical, dielectric, and thermoelectric properties, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 154 (2021) 110080.
H. Basma, J. Al Boukhari, M. Abd Al Nabi, A. Aridi, R. Sayed Hassan, D. Naoufal, M. Roumie, R. Awad, Enhancement of the magnetic and optical properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles by ruthenium doping, Appl. Phys. A, 128 (2022) 409.
H.L. Andersen, C. Granados-Miralles, M. Saura-Múzquiz, M. Stingaciu, J. Larsen, F. Søndergaard-Pedersen, J.V. Ahlburg, L. Keller, C. Frandsen, M. Christensen, Enhanced intrinsic saturation magnetization of ZnxCo1−xFe2O4 nanocrystallites with metastable spinel inversion. Mater. Chem. Front. 3, 668–679 (2019)
M. Kamran, M. Anis-ur-Rehman, Influence of La3+ substitutions on structural, dielectric and electrical properties of spinel cobalt ferrite. Ceram. Int. 49, 7017–7029 (2023)
C.C. Naik, A. Salker, Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Dy3+ and Sm3+ substituted Co–Cu ferrite. Mater. Res. Express 6, 066112 (2019)
M.M. Roni, K. Hoque, T.C. Paul, M. Khan, M.E. Hossain, Synthesis of La-doped Mn0.6Zn0.4LaxFe2-xO4 and the study of its structural, electrical and magnetic properties for high frequency applications, Results Mater. 11 (2021) 100215.
M. Hashim, S.E. Shirsath, S. Kumar, R. Kumar, A.S. Roy, J. Shah, R. Kotnala, Preparation and characterization chemistry of nano-crystalline Ni–Cu–Zn ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 549, 348–357 (2013)
V. Chaudhari, S.E. Shirsath, M. Mane, R. Kadam, S. Shelke, D. Mane, Crystallographic, magnetic and electrical properties of Ni0.5Cu0.25Zn0.25LaxFe2−xO4 nanoparticles fabricated by sol–gel method, J. Alloys Compounds, 549 (2013) 213–220.
P. Thakur, R. Sharma, V. Sharma, P. Barman, M. Kumar, D. Barman, S. Katyal, P. Sharma, Gd3+ doped Mn-Zn soft ferrite nanoparticles: superparamagnetism and its correlation with other physical properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 432, 208–217 (2017)
T. Poudel, B. Rai, S. Yoon, D. Guragain, D. Neupane, S. Mishra, The effect of gadolinium substitution in inverse spinel nickel ferrite: Structural, Magnetic, and Mössbauer study. J. Alloy. Compd. 802, 609–619 (2019)
B.P. Jacob, S. Thankachan, S. Xavier, E. Mohammed, Effect of Gd3+ doping on the structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni–Cd mixed ferrite. Phys. Scr. 84, 045702 (2011)
Z. Xueyun, Y. Dongsheng, Z. Liling, Improved cut-off frequency in gd/la doped niznco ferrites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 272, 115334 (2021)
X. Zhou, Y. Zhou, L. Zhou, J. Wei, J. Wu, D. Yao, Effect of Gd and La doping on the structure, optical and magnetic properties of NiZnCo ferrites. Ceram. Int. 45, 6236–6242 (2019)
P. Thakur, R. Sharma, M. Kumar, S. Katyal, N. Negi, N. Thakur, V. Sharma, P. Sharma, Superparamagnetic La doped Mn–Zn nano ferrites: dependence on dopant content and crystallite size. Mater. Res. Express 3, 075001 (2016)
D. Ravinder, M. Hashim, A. Upadhyay, M.M. Ismail, S. Kumar, R. Kumar, S.S. Meena, A. Khalilullah, Investigation of structural and magnetic properties of La doped Co–Mn ferrite nanoparticles in the presence of α-Fe2O3 phase. Solid State Commun. 342, 114629 (2022)
R. Tholkappiyan, K. Vishista, Combustion synthesis of Mg–Er ferrite nanoparticles: cation distribution and structural, optical, and magnetic properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 40, 631–642 (2015)
S.M. Suryawanshi, D.S. Badwaik, B.S. Shinde, K.D. Gaikwad, M. Shkir, K.V. Chandekar, S. Gundale, A comprehensive study on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Ni0.3Cu0.3Zn0.4Fe1.8Cr0.2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel auto combustion route, J. Mol. Struct. 1272 (2023) 134173.
H. Yao, X. Ning, H. Zhao, A. Hao, M. Ismail, Effect of Gd-doping on structural, optical, and magnetic properties of NiFe2O4 as-prepared thin films via facile sol–gel approach. ACS Omega 6, 6305–6311 (2021)
M. Islam, A.A. Hossain, M. Ahsan, M. Bally, M.S. Ullah, S. Hoque, F. Khan, Structural characteristics, cation distribution, and elastic properties of Cr3+ substituted stoichiometric and non-stoichiometric cobalt ferrites. RSC Adv. 12, 8502–8519 (2022)
H. Anwar, A. Maqsood, Enhancement of electrical and magnetic properties of Cd2+ doped Mn–Zn soft nanoferrites prepared by the sol–gel autocombustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 333, 46–52 (2013)
A.S. Fawzi, A. Sheikh, V. Mathe, Structural, dielectric properties and AC conductivity of Ni(1–x)ZnxFe2O4 spinel ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 502, 231–237 (2010)
Y. Peng, C. Xia, M. Cui, Z. Yao, X. Yi, Effect of reaction condition on microstructure and properties of (NiCuZn)Fe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized via co-precipitation with ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 71, 105369 (2021)
S.B. Somvanshi, M.V. Khedkar, P.B. Kharat, K. Jadhav, Influential diamagnetic magnesium (Mg2+) ion substitution in nano-spinel zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4): thermal, structural, spectral, optical and physisorption analysis. Ceram. Int. 46, 8640–8650 (2020)
S.B. Somvanshi, S.A. Jadhav, M.V. Khedkar, P.B. Kharat, S. More, K. Jadhav, Structural, thermal, spectral, optical and surface analysis of rare earth metal ion (Gd3+) doped mixed Zn–Mg nano-spinel ferrites. Ceram. Int. 46, 13170–13179 (2020)
T. Dippong, E.A. Levei, O. Cadar, Investigation of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of MFe2O4 (M= Co, Ni, Zn, Cu, Mn) obtained by thermal decomposition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 8483 (2022)
A.M. Wahba, M.B. Mohamed, N. Imam, Correlating structural, magnetic, and luminescence properties with the cation distribution of Co0.5Zn0.5+xFe2–xO4 nanoferrite, J. Mag. Magnetic Mater. 408 (2016) 51–59.
R. Yassine, A. Abdallah, R.S. Hassan, N. Yaacoub, R. Awad, Z. Bitar, Prospecting the structural and magnetic features of (x) CuO/(1-x) CdFe2O4 nanocomposite system (0.0≤ x≤ 1.0), J. Nanoparticle Res. 25 (2023) 90.
F. Naaz, H.K. Dubey, C. Kumari, P. Lahiri, Structural and magnetic properties of MgFe2O4 nanopowder synthesized via co-precipitation route. SN Appl. Sci. 2, 808 (2020)
P. Raji, K.B. Kumar, Structural, elastic and magnetic properties of Ca doped copper ferrite nanoparticles. Physica B 632, 413759 (2022)
A. Anupama, V. Rathod, V. Jali, B. Sahoo, Composition dependent elastic and thermal properties of LiZn ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 728, 1091–1100 (2017)
S. Naik, A. Salker, S. Yusuf, S. Meena, Influence of Co2+ distribution and spin–orbit coupling on the resultant magnetic properties of spinel cobalt ferrite nanocrystals. J. Alloy. Compd. 566, 54–61 (2013)
R. Jain, S. Gulati, Influence of Fe2+ substitution on FTIR and Raman spectra of Mn ferrite nanoparticles. Vib. Spectrosc. 126, 103540 (2023)
A. Subha, M.G. Shalini, B. Sahu, S.C. Sahoo, Structural transformation and magnetic properties of copper ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 20790–20799 (2018)
B. Nandan, M. Bhatnagar, S.C. Kashyap, Cation distribution in nanocrystalline cobalt substituted nickel ferrites: X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopic investigations. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 129, 298–306 (2019)
R. Jasrotia, V.P. Singh, R. Kumar, M. Singh, Raman spectra of sol-gel auto-combustion synthesized Mg–Ag–Mn and Ba–Nd–Cd-In ferrite based nanomaterials. Ceram. Int. 46, 618–621 (2020)
L.I. Granone, A.C. Ulpe, L. Robben, S. Klimke, M. Jahns, F. Renz, T.M. Gesing, T. Bredow, R. Dillert, D.W. Bahnemann, Effect of the degree of inversion on optical properties of spinel ZnFe2O4. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20, 28267–28278 (2018)
Z. Yan, J. Gao, Y. Li, M. Zhang, M. Guo, Hydrothermal synthesis and structure evolution of metal-doped magnesium ferrite from saprolite laterite. RSC Adv. 5, 92778–92787 (2015)
H. Ghorbani, M. Eshraghi, A.S. Dodaran, P. Kameli, S. Protasowicki, D. Vashaee, Effect of Yb doping on the structural and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 147, 111642 (2022)
M.K. Manglam, M. Kar, Effect of Gd doping on magnetic and MCE properties of M-type barium hexaferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 899, 163367 (2022)
A.U. Rehman, N. Morley, N. Amin, M.I. Arshad, M.A. un Nabi, K. Mahmood, A. Ali, A. Aslam, A. Bibi, M.Z. Iqbal, Controllable synthesis of La3+ doped Zn0.5Co0.25Cu0.25Fe2−xLaxO4 (x= 0.0, 0.0125, 0.025, 0.0375, 0.05) nano-ferrites by sol-gel auto-combustion route, Ceramics Int., 46 (2020) 29297–29308.
X. Zhou, J. Wang, D. Yao, Effect of rare earth doping on magnetic and dielectric properties of NiZnMn ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 935, 167777 (2023)
X. Huang, A. Sun, Y. Jiang, J. Wang, Y. Zhang, L. Shao, Influence of La3+ ions doping on morphology and magnetic properties of Mg–Co ferrites. Appl. Phys. A 127, 1–11 (2021)
S. Chakrabarty, A. Dutta, M. Pal, Enhanced magnetic properties of doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles by virtue of cation distribution. J. Alloy. Compd. 625, 216–223 (2015)
M.J. Iqbal, Z. Ahmad, Y. Melikhov, I.C. Nlebedim, Effect of Cu–Cr co-substitution on magnetic properties of nanocrystalline magnesium ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 1088–1094 (2012)
A. Abdallah, R. Awad, Mixed magnetic behavior in gadolinium and ruthenium co-doped nickel oxide nanoparticles. Phys. Scr. 97, 015802 (2022)
S. Mazen, N. Abu-Elsaad, A. Khadour, A comparative study of the structural and magnetic properties for Zn2+ and Ge4+ ions substituted nickel ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 491, 165562 (2019)
A. Aslinjensipriya, R.S. Reena, R. Ragu, S.G. Infantiya, G. Mangalam, C.J. Raj, S.J. Das, Exploring the influence of tin in micro-structural, magneto-optical and antimicrobial traits of nickel oxide nanoparticles. Surfaces and Interfaces 28, 101605 (2022)
R. Melo, P. Banerjee, A. Franco, Hydrothermal synthesis of nickel doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: optical and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 14657–14667 (2018)
E.C. Devi, I. Soibam, Law of approach to saturation in Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 32, 1293–1298 (2019)
A. Abdallah, R. Awad, Influence of Ru dopants on the structural, optical, and magnetic properties of nickel oxide nanoparticles. Physica B 629, 413651 (2022)
S. Khene, Critical Currents and Superconductivity: Ferromagnetism Coexistence in High-Tc Oxides, CRC Press2016.
M.J.N. Isfahani, M.J. Fesharaki, V. Šepelák, Magnetic behavior of nickel–bismuth ferrite synthesized by a combined sol–gel/thermal method. Ceram. Int. 39, 1163–1167 (2013)
S. Komogortsev, R. Iskhakov, Law of approach to magnetic saturation in nanocrystalline and amorphous ferromagnets with improved transition behavior between power-law regimes. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 440, 213–216 (2017)
Acknowledgements
All authors acknowledge the Specialized Materials Science Laboratory and the Advanced Nanomaterials Laboratory in Beirut Arab University (BAU) for promoting this work. The authors also express their gratitude for researchers at Alexandria university that helped in the experimental measurements.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AMA and AA data curation, formal analysis and writing MR sample preparation and characterization, RMMR measurements and data analysis, RA conceptualization, review and editing, supervision, project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdallah, A.M., Aridi, A., Rabaa, M. et al. Tailored physical and magnetic properties by La3+ dopants in Mg–Ni–Co nanoferrites: insight into the law of approach to saturation. Appl. Phys. A 129, 770 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07040-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07040-y