Abstract
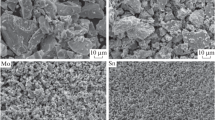
New Ti-based alloys have recently attracted great attention in biomedical implementations due to their high strength, good biocompatibility, shape memory feature, low density and corrosion resistance. In this study, Ti-16 at% Nb-4 at% Sn alloy was produced by powder metallurgy for use as a biomaterial. In addition, the effects of sintering temperature and sintering time on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the alloy were investigated. The results indicated that β phase was dominate and α phase was seen as secondly phase in the microstructures of the sintered samples. As sintering temperature and sintering time increase, the porosity decreases, and compressive strength raised depending on decreasing porosity. Elastic modules of samples produced via powder metallurgy (PM) are close to that of natural bone; hence, the samples do not cause bone abrasion when combined with bone.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Kaya, F. Yakuphanoğlu, A study on microstructure of porous TiNbZr alloy produced as biomaterial. Materialwiss. Werkstofftech. 50, 742–746 (2019)
M. Kaya, F. Yakuphanoglu, E. Elibol Annac, M. Köm, Microstructure characterization and biocompatibility behaviour of TiNbZr alloy fabricated by powder metallurgy. Mater. Res. Express. 6, 1–12 (2019)
N. Masahashi, Y. Mori, H. Tanaka, A. Kogure, H. Inoue, K. Ohmura, Y. Kodama, M. Nishijima, E. Itoi, S. Hanada, Bioactive TiNbSn alloy prepared by anodization in sulfuric acid electrolytes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 98, 753–763 (2019)
M. Kaya, O. Cakmak, Shape memory behavior of porous NiTi Alloy. Mater. Trans. A. 47A, 1499–1503 (2016)
P. Li, X. Ma, D. Wang, H. Zhang, Microstructural and mechanical properties of β-Type Ti–Nb–Sn biomedical alloys with low elastic modulus. Metal. 9, 1–16 (2019)
M. Eskil, The effect of aging temperature on transformation parameters of porous NiTi shape memory alloy fabricated by SHS. Russ. J. Non-Ferr. Met. 54, 104–111 (2012)
S.L. Zhu, X.J. Yang, F. Hu, S.H. Deng, Z.D. Cui, Precessing of porous NiTi shape memory alloy from elemental powders by Ar-sintering. Mater. Lett. 58, 2369–2373 (2004)
J. Xiong, Y. Li, P.D. Hodgson, C. Wen, Nanohydroxyapatite coating on a titanium–niobium alloy by a hydrothermal process. Acta Biomater. 6, 1584–1590 (2010)
T. Kunii, Y. Mori, H. Tanaka, A. Kogure, M. Kamimura, N. Mori, S. Hanada, N. Masahashi, E. Itoi, Improved osseointegration of a TiNbSn alloy with a low young’s modulus treated with anodic oxidation. Sci. Rep. 9, 1–10 (2019)
E. Yılmaz, A. Gökçe, F. Findik, H.O. Gülsoy, Characterization of biomedical Ti-16Nb-(0–4)Sn alloys produced by powder injection molding. Vacuum 142, 164–174 (2017)
N. Sumitomo, K. Noritake, T. Hattori, K. Morikawa, S. Niwa, K. Sato, M. Niinomi, Experiment study on fracture fixation with low rigidity titanium alloy: Plate fixation of tibia fracture model in rabbit. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 19, 1581–1586 (2008)
T.F. Azevedo, T.N. Lima, M.D. Macedo, J.G. Blas, S. Griza, The mechanical behavior of TiNbSn alloys according to alloying contents, cold rolling and aging. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 75, 33–40 (2017)
L.C. Zhang, L.Y. Chen, A review on biomedical titanium alloys: Recent progress and prospect. Adv. Eng. Mater. 21, 1–29 (2019)
H. Matsumoto, S. Watanable, S. Hanada, Beta TiNbSn alloys with low young’s modulus and high strength. Mater. Trans. 46, 1070–1078 (2005)
R.P. Kolli, A. Devaraj, A review of metastable beta titanium alloys. Metals 506, 1–41 (2018)
T.K. Jung, H.S. Lee, S. Semboshi, N. Masahashi, T. Abumiya, S. Hanada, Mechanical properties graded Ti alloy implants for orthopedic applications. Mater. Sci. Forum. 631, 205–2010 (2009)
X. Rao, C.L. Chun, Y.Y. Zheng, Phase composition, microstructure, and mechanical properties of porous Ti–Nb–Zr alloys prepared by a two-step foaming powder metallurgy method. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 34, 27–36 (2014)
P.E.L. Moraes, R.J. Contieri, E.S.N. Lopes, A. Robin, R. Caram, Effects of Sn addition on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of Ti–Nb–Sn alloys. Mater. Charact. 96, 273–281 (2014)
A. Yolun, M. Simsek, M. Kaya, E.E. Annac, M. Kom, O. Cakmak, Fabrication, characterization, and in vivo biocompatibility evaluation of titanium-niobium implants. Proc IMechE Part H: J Engineering in Medicine 235(1), 99–108 (2021)
T.K. Jung, S. Semboshi, N. Masahashi, S. Hanada, Mechanical properties and microstructures of beta Ti-25Nb-11Sn ternary alloy for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 33, 1629–1635 (2013)
K. Miura, N. Yamada, S. Hanada, T.K. Jung, E. Itoi, The bone tissue compatibility of a new Ti-Nb-Sn alloy with a low young’s modulus. Acta Biomater. 7, 2320–2326 (2011)
A.J. Varkey, Antibacterial properties of some metals and alloys in combating coliforms in contaminated water. Sci. Res. Essays. 5(24), 3834–3839 (2010)
M.K. Ibrahim, E. Hamzah, S.N. Saud, Microstructure, Phase Transformation, Mechanical Behavior, Bio-corrosion and Antibacterial Properties of Ti-Nb-xSn (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5 and 1.5) SMAs. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 28, 382–393 (2019)
S.M. Amininezhad, A. Rezvani, M. Amouheidari, S.M. Amininejad, S. Rakhshani, The antibacterial activity of SnO2 nanoparticles Against escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus. Zahedan J. Res. Med. Sci. 17(9), 1–5 (2015)
E. Yılmaz, A. Gökçe, F. Findik, H.O. Gülsoy, Powder metallurgy processing of Ti–Nb based biomedical alloys. Acta Phys. Pol. A. 134, 278–280 (2018)
X. Wang, Y. Chen, L. Xu, Z. Liu, K.-D. Woo, Effects of Sn content on the microstructure, mechanical properties and biocompatibility of Ti–Nb–Sn/hydroxyapatitebiocomposites synthesized by powder metallurgy. Mater. Des. 49, 511–519 (2013)
T.F. Azevedo, T.N. Lima, M.D. Macedo, J.G. de Blas, S. Griza, Fracture mechanics behavior of TiNbSn alloys as a function of alloy content, cold working and aging. Eng. Fracture Mech. 229, 106946 (2020)
W.N.S.W. Nawai, N.A. Kasani, R. Nordin, Z. Arifin, S. Shamsuddin, Effect of sintering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-Nb-Sn-HA composites produced by powder metallurgy. App. Mech. Mater. 625, 180–183 (2014)
M. Kaya, Ö. Çakmak, B. Gülenç, K.C. Atlı, Thermomechanical cyclic stability of porous NiTi shape memory alloy. Mater. Res. Bull. 95, 243–247 (2017)
M. Mour, D. Das, T. Winkler, E. Hoenig, G. Mielke, M.M. Morlock, A.F. Schilling, Advances in porous biomaterials for dental and orthopaedic applications. Mater. 3(5), 2947–2974 (2010)
G. Ryan, A. Pandit, D.P. Apatsidis, Fabrication methods of porous metals for use in orthopaedic applications. Biomater. 27(13), 2651–2670 (2006)
O. Khalifa, E. Wahab, A. Tilp, The effect of Sn and TiO2 nano particles added in electroless Ni-P plating solution on the properties of composite coatings. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 5(6), 136–144 (2011)
S. Ehtemam-Haghighi, H. Attar, I.V. Okulov, M.S. Dargusch, D. Kent, Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of bulk and porous low-cost TieMoeFe alloys produced by powder metallurgy. J. Alloys Compd. 853, 156768 (2021)
K.A. Nazari, A. Nouri, T. Hilditcz, Mechanical properties and microstructure of powder metallurgy Ti–xNb–yMo alloys for implant materials. Mater. Des. 88, 1164–1174 (2015)
A. Nouri, P.D. Hodgson, C.E. We, Effect of process control agent on the porous structure and mechanical properties of a biomedical Ti–Sn–Nb alloy produced by powder metallurgy. Acta Biomater. 6, 1630–1639 (2010)
M. Kaya, A. Yolun, O. Çakmak, F. Yakuphanoğlu, E. Elibol, M. Köm, M. Güvenç, Production of titanium based porous TiNb alloy for biomedical applications. Nev. Bil. Tekn. Der. 7, 49–59 (2018)
O. Cakmak, “Investigation of Biocompatibility Property and Production of TiNbSn Alloys by Powder Metallurgy,” Msc Thesis. Adıyaman University, (2017).
O. Cakmak, M. Kaya, Thermodynamics of Smart Materiel Shape Memory Alloys. Nev. Bil. Tekn. Der. 6(2), 541–555 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Scientific Research Projects Coordination of Adıyaman University for Master thesis (Project No: MÜFLTP/2017-0001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çakmak, Ö., Kaya, M. Effect of sintering procedure on microstructure and mechanical properties of biomedical TiNbSn alloy produced via powder metallurgy. Appl. Phys. A 127, 561 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04678-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04678-4