Abstract
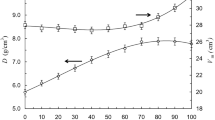
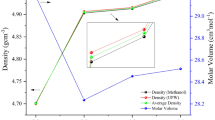
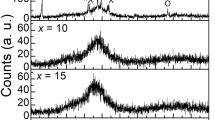
Density, electrical conductivity and optical properties of xNaF⋅(100–x)TeO2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 75 mol%) glasses and glass–ceramics have been investigated. Density and molar volume decrease with increasing NaF content. The change of free volume is a primary factor in changing molar volume as well as the conductivity. Na+ ions are assumed as the main charge carriers in these glasses and glass–ceramics. The conductivity was found to have a limited change because of decreasing in free volume and the association between Na and F. Energy gap and Urbach energy decrease with increasing NaF content up to NaF ≤ 40 mol%, while refractive index increases. After that, these quantities remain nearly constant for further additions of NaF. These changes are due to the structural changes that occur with modifying the network by NaF. For NaF ≤ 10 mol%, the entire NaF content enters the structure to convert TeO4 units into TeO3/2F and Na+[TeO3+1]– units; whereas, it starts to form its own matrix beside modifying the tellurite network, for NaF > 10 mol%. Molar refractivity and metallization criterion decrease with increasing NaF content. This shows an insulating behavior.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.B.A. Devi, S. Mahamuda, M. Venkateswarlu, K. Swapna, A.S. Rao, G.V. Prakash, Dy3+ ions doped single and mixed alkali fluoro tungsten tellurite glasses for LASER and white LED applications. Opt. Mater. (Amst) 62, 569–577 (2016)
L. Huang, S. Shen, A. Jha, Near infrared spectroscopic investigation of Tm3+-Yb3+ co-doped tellurite glasses. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 345, 349–353 (2004)
H. Desirena, A. Schülzgen, S. Sabet, G. Ramos-Ortiz, E. la Rosa, N. Peyghambarian, Effect of alkali metal oxides R2O (R= Li, Na, K, Rb and Cs) and network intermediate MO (M= Zn, Mg, Ba and Pb) in tellurite glasses. Opt. Mater. (Amst) 31, 784–789 (2009)
S.H. Kim, T. Yoko, S. Sakka, Linear and nonlinear optical properties of TeO2 glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 76, 2486–2490 (1993)
R.A.H. El-Mallawany, Tellurite Glasses Handbook: Physical Properties and Data (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2011).
A.E. Ersundu, M. Çelikbilek, S. Aydin, A Review of Scanning Electron Microscopy Investigations in Tellurite Glass Systems, Curr. Microsc. Contrib. Adv. Sci. Technol. (A. Méndez-Vilas, Ed.). (2012).
L.M.S. El-Deen, M.S. Al Salhi, M.M. Elkholy, IR and UV spectral studies for rare earths-doped tellurite glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 465, 333–339 (2008)
S. Neov, I. Gerasimova, V. Kozhukharov, M. Marinov, The structure of glasses in the TeO2–P2O5 system. J. Mater. Sci. 15, 1153–1166 (1980)
J.M. Rojo, P. Herrero, J. Sanz, B. Tanguy, J. Portier, J.M. Reau, Relationship between microstructure and ionic conduction properties in oxyfluoride tellurite glass-ceramics. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 146, 50–56 (1992)
P. Balaya, C.S. Sunandana, Crystallization studies of 30Li2O:70TeO2 glass. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 162, 253–262 (1993)
J.M. Rojo, J. Sanz, J.M. Reau, B. Tanguy, Influence of ion distribution on the ionic conductivity of lithium tellurite glasses (Li2O–TeO2 and LiF–TeO2). J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 116, 167–174 (1990)
W. Vogel, H. Burger, G. Zerge, B. Muller, K. Forkel, G. Winterstein, A. Boxberger, H. Romhild, Halogenid-und sulfathaltige telluritglaser. Silikattechnelk 25, 207 (1974)
N. Elkhoshkhany, S.Y. Marzouk, S. Shahin, Synthesis and optical properties of new fluoro-tellurite glass within (TeO2–ZnO–LiF–Nb2O5–NaF) system. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 472, 39–45 (2017)
E.F. El Agammy, H. Doweidar, K. El-Egili, R. Ramadan, M. Jaremko, A.H. Emwas, Structure of NaF–TeO2 glasses and glass-ceramics. Ceram. Int. 46, 18551–18561 (2020)
E.F. El Agammy, H. Doweidar, K. El-Egili, R. Ramadan, Structure of PbF2–TeO2 glasses and glass-ceramics. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 4016–4024 (2020)
H. Doweidar, Density of CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 glasses with (CaO/Al2O3)≥ 1; the hidden factors. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 471, 344–348 (2017)
H. Doweidar, K. El-Egili, A. Altawaf, Structural units and properties of BaF2–PbF2–B2O3 glasses. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 464, 73–80 (2017)
K. El-Egili, H. Doweidar, R. Ramadan, A. Altawaf, Role of F− ions in the structure and properties of BaF2–B2O3 glasses. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 449, 83–93 (2016)
H. Doweidar, G. El-Damrawi, E.F. El Agammy, Structural correlations in BaO–PbO–B2O3 glasses as inferred from FTIR spectra. Vib. Spectrosc. 73, 90–96 (2014)
H. Doweidar, G. El-Damrawi, E.F. El Agammy, FTIR investigation and mixed cation effect of Li2O–BaO–B2O3 glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 207, 259–270 (2018)
H. Doweidar, Density and molar volume of Li2O–SiO2 glasses in relation to their microstructure. Phys. Chem. Glas. 39, 286–289 (1998)
C. Kittel, P. McEuen, P. McEuen, Introduction to Solid State Physics (Wiley, New York, 1996).
P. Wesołowski, W. Jakubowski, J.L. Nowiński, Electrical properties of superionic silver-borate glasses doped with AgI. Phys. Status Solidi. 115, 81–86 (1989)
H.A.A. Sidek, S. Rosmawati, Z.A. Talib, M.K. Halimah, W.M. Daud, Synthesis and optical properties of ZnO–TeO2 glass system. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 6, 1489 (2009)
E.A. Davis, N.F. Mott, Conduction in non-crystalline systems V. Conductivity, optical absorption and photoconductivity in amorphous semiconductors. Philos. Mag. 22, 903–922 (1970)
W.S. AbuShanab, E.B. Moustafa, A.H. Hammad, R.M. Ramadan, A.R. Wassel, Enhancement the structural, optical and nonlinear optical properties of cadmium phosphate glasses by nickel ions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 18058–18064 (2019)
M.M. Hivrekar, D.B. Sable, M.B. Solunke, K.M. Jadhav, Different property studies with network improvement of CdO doped alkali borate glass. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 491, 14–23 (2018)
S.Y. Marzouk, R. Seoudi, D.A. Said, M.S. Mabrouk, Linear and non-linear optics and FTIR characteristics of borosilicate glasses doped with gadolinium ions. Opt. Mater. (Amst) 35, 2077–2084 (2013)
M.R. Sahar, N. Noordin, Oxychloride glasses based on the TeO2–ZnO–ZnCl2 system. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 184, 137–140 (1995)
E.A. Davis, N.F. Mott, Electronic Processes in Non-Crystalline Materials (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1971).
W. Stambouli, H. Elhouichet, M. Ferid, Study of thermal, structural and optical properties of tellurite glass with different TiO2 composition. J. Mol. Struct. 1028, 39–43 (2012)
M.S. Malik, C.A. Hogarth, The effect of chloride ions on the optical properties of TeO2–CuO–CuCl2 glasses. J. Mater. Sci. 25, 116–120 (1990)
V. Dimitrov, S. Sakka, Electronic oxide polarizability and optical basicity of simple oxides. I. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 1736–1740 (1996)
I. Jlassi, H. Elhouichet, M. Ferid, Thermal and optical properties of tellurite glasses doped erbium. J. Mater. Sci. 46, 806–812 (2011)
S.L.S. Rao, G. Ramadevudu, M. Shareefuddin, A. Hameed, M.N. Chary, M.L. Rao, Optical properties of alkaline earth borate glasses. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 4, 25–35 (2012)
F. Nawaz, M.R. Sahar, S.K. Ghoshal, A. Awang, I. Ahmed, Concentration dependent structural and spectroscopic properties of Sm3+/Yb3+ co-doped sodium tellurite glass. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 433, 89–95 (2014)
M. Abdel-Baki, F. El-Diasty, F.A.A. Wahab, Optical characterization of xTiO2−(60–x) SiO2–40Na2O glasses: II. Absorption edge, Fermi level, electronic polarizability and optical basicity. Opt. Commun. 261, 65–70 (2006)
S. Sherman, S. Wagner, R.A. Gottscho, Correlation between the valence-and conduction-band-tail energies in hydrogenated amorphous silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 3242–3244 (1996)
S. Kasap, P. Capper, Springer Handbook of Electronic and Photonic Materials (Springer, Berlin, 2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Agammy, E.F., Doweidar, H., El-Egili, K. et al. Physical and optical properties of NaF–TeO2 glasses and glass–ceramics. Appl. Phys. A 127, 42 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04153-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04153-6