Abstract
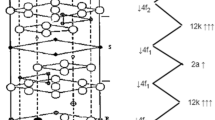
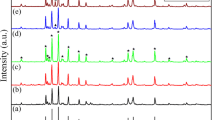
In this research project a series of chromium substituted barium hexa-ferrites with formula BaCrxFe(12-x)O19 (x = 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6) have been synthesized using powder metallurgy route, sintered at 1100 °C for 2 h. The structural, functional analysis, surface morphology, magnetic and ferroelectric properties have been investigated using X-ray diffractometer, Fourier infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, vibrating sample magnetometer, and ferroelectric technique, respectively. The structural analysis reveals the formation of barium hexaferrite structure with minor secondary phase of Hematite α- Fe2O3 in first five samples. Surface morphology shows that all grains have definite grains shape and grain boundaries. VSM analysis revealed the antiferromagnetic loops due to existence of hematite phase in (x = 0 to x = 0.5) samples, whereas the sample (x = 0.6) shows the ferro-magnetic behavior. Ferroelectric measurement shows centrosymmetric and non-centrosymmetric orientation and maximum remnant polarization due to presence of more Fe2+ ions in (x = 0.1–0.5) so that not proper closing of first five samples enhanced the magnetoelectric (ME) coupling.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.O. Pillai, Solid State Physics, New Age International (P) Ltd, New Delhi, 6th edition, (2004).
B.D.Cullity, C.D. Graham Jr., Introduction to Magnetic Materials, Graham school edition of Wiley publication, IEEE Press, 2nd edition (2009).
C. Kittle, Introduction to solid state physics, John Willey & sons Inc., ISBN: 8126510455, 9788126510450, 7th edition (2007).
V. Rajendran, Materials science (Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 2004)
C.B. Certer, M. Norton, Grant Ceramic Materials Science and Engineering, Springer, pp. 212–15, ISBN 0-387-462470-8 (2007).
I. Ali, M.U. Islam, M.S. Awan, M. Ahmad, Effects of Ga-Cr substituted on structural and magnetic properties of hexaferrites synthesized by sol gel method. J Alloys Compound 547 (2013), 118–125 (2012)
M. Pieper, A. Morel, F. Kool’s, Ferroic and Multiferroics, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 242, 1480 (2002).
J. Li, T.M.GR, R. Sinclair, S.S. Rosenblu, Advances in nanoscale Magnetism: proceeding of international conference, J. Mater. Res. 9, 1499 (1994).
K. Tanwar, D. S. Gyan, P. Gupta, S. Pandey, OmParkash: Investigation of crystal structure microstructure and low temperature magnetic behavior of Ce4+ and Zn2+ co-doped barium hexaferrites (BaFe12O19). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. (2018).
V. Kostishyn, L. Panina, A. Balagurov, Thermal evolutions of exchange interactions in lightly doped barium hexaferrites. J. Magn. Mater. 426, 554–562 (2017).
Y. Yang, F. Wang, X. Liu, J. Shao, Magnetic and microstructural properties of Al substituted M-Type Ca-Sr hexaferrites. J. Magn. Mater. 421, 349–354 (2017).
M.N. Ashiq, M.J. Iqbal, I.H. Gul: Effect of Al-Cr doping on the structural magnetic and dielectric properties of strontium hexaferrites nanomaterials. J. Magn. Mater. 323, 259–263 (2011).
V. N. Dhage. M.L. Mane, M.K. Barbrekar, C.M. Kale, Influence of chromium substituted on structural and magnetic properties of BaFe12O19 powder prepared by sol-gel auto combustion method. J Alloys Compounds 509 (2011) 4394–4398, (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.01.040
V.C Chavan, S.E. Shirsath, M.L. Mane, R.H. Kadam, S.S. More: Transformation of mixed hexagonal spinel structure and magnetic properties of Co2+ substituted BaFe12O19. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. (2016).
S. Mandizadeh, F. Soofivand, S. Bagheri, M. Salavati-Niasari, SrCrxFe12-xO19 nanoceramics as an effective catalyst for desulfurization of liquid fuels; Green sol-gel synthesis, characterization, magnetic and optical properties. PLos One J 0162891 (2017).
T. R. Wagner, preparation and crystal structure analysis of Magneto-Plumbite type BaGaFe12O19. Solid State Chem. (1998).
R.C. Alange, P. P. Khirade, S. D. Birajdar, Influence of Al-Cr co substituted on physical properties of strontium hexaferrite nanoparticle’s synthesized by sol-gel auto combustion method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 407–417 (2017).
J. Brame, C. Griggs, Surface area analysis using the brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) method. US Army Corps of Engineers, Engraining and Research Center (2016).
S. Kumar, S. Supriya, M. Kar: Effect of lattice strain on structural and magnetic properties of Ca substituted barium hexaferrite, DAE solid state physics Symposium 2017, AIP conf. 1942, 130040–1–130040–4 (2018).
S. Asiri, S. Guner, A.D. Korkmaz, M.D. Amir, K.M. Batoo: Magneto- optical properties of BaCryFe12-yO19 (0.0≤y≤1.0) hexaferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 451(2018), 463–472 (2017).
W.J. Zhang, B. Verstegen, Alloy Compound. 546, 234–238 (2013).
W. Wangi, X. Song, L. Shuai Jiangi, Influence of iron Content on Microstructure and magnetic properties of Sr0.3 La0.4Ca0.3 n (Fe2O3) Co0.4, journal of superconductivity and novel magnetism (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4190-6.
A. Moitra, S. Kim, S. Kim, S-G Kim, Defect formation energy and magnetic properties of aluminum-substituted M-type barium hexaferrite. Comput. Condensed Matter. 1, 45e50 (2014).
S.V. Trukhanov, A.V. Trukhanova, V.G. Kostishyan, Thermal evolution of exchange interaction in high doped barium hexaferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426(2017), 554–562 (2016)
A.V. Trukhanov, S. Trukhanov, L. V. Panena, Strong correlation between magnetic and electrical subsystems in diamagnetically substituted hexaferrites ceramics. Ceram. Int. 43, 5635–5641 (2017).
S. Anjum, F. Sehar, MS. Awan, R. Zia, Role of Bi3+ substitution on structural, magnetic and optical properties of spinel ferrite. Appl. Phys. A. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9798-z (2016).
S. Anjum, F. Sehar, Z. Mustafa, M.S. Awan, Enhancement of structural and magnetic properties of M-type hexaferrite permanent magnet based on synthesis temperature. Appl. Phys. A 124, 49 (2018).
T. Ben Ghzaiel, W. Dhaoui, Effect of non-magnetic and magnetic trivalent ion substitutions on BaM- Ferrites properties synthesized by hydrothermal method, Hall archives- ouvertes, HAL Id: 01316630 (2016).
C. P. Joshi, International journal of scientific and research publications, vol (4), (2014).
A. Mohammedi, A. Ataie, S. Sheibani, Chromium (VI) ions absorption onto barium hexaferrite magnetic nano-absorbent. Adv. Mater. Lett. 7(7), 579–586 (2016).
S. Guner, S. Asiri, H. Gungunes, K.M. Batoo, Magneto-optical properties of BaFe(12-y) CryO19 hexaferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 451(2018), 453–472 (2017)
G. H. Jonker, J. H. Van Santen, Ferromagnetic compounds of manganese with perovskite structure. Physica, 16–337 (1950).
L. Peng-Ting, Z. Li. La-doped BiFeO3: synthesis and Multiferroic property study. Chin. Phys. B 23(4), 047701 (2014).
N. Tran, H.S. Kim, Electronic structure and magnetic properties of Ba1-xSrxCoFe11O19 hexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 44(2018), 12132–12136 (2018)
A. Srinivas, M. Manivel Raja, Enhanced ferroelectricity and magnetoelectricity in 0.75BaTiO3–0.25BaFe12O19 by spark plasma sintering. Process. Appl. Ceram. 7(1), 29–35. https://doi.org/10.2298/PAC1301029S.
S. Waseem, S. Anjum, L. Mustafa, Effect of Cr and Fe co doping on structural, optical, electrical and magnetic properties of titanium dioxide (TiO2). Mater. Sci. Poland 33(3), 508–514 (2015).
W. Dhaoui, T. Ben Ghzaiel, Non-magnetic and magnetic trivalent ion substitutions on BaM- Ferrites properties synthesized by hydrothermal method, Hall archives- ouvertes, HAL Id: 01316630, (2016).
S. Katlakunta, Sher Singh Meena: improved magnetic properties of Cr3+ doped SrFe12O19 synthesized via microwave hydrothermal route. Mater. Res. Bull. 63(2015), 58–66 (2014)
I. Ali, M.U. Islam, Effects of Ga-Cr substituted on structural and magnetic properties of hexaferrites synthesized by sol gel method. J. Alloys Compound 547(2013), 118–125 (2012).
X. Chen, G. Tan: Multiferroic properties of BaFe12O19 ceramics, Science foundation of Hubei Province (2010CDA078), Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China (2010).
S. Kumar, S. Supriya, PVDF, Barium hexaferrites and rGO nanocomposite for high energy density Capacitor. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2018.2853040
V.G. Kostishyn, L.V. Panina, Synthesis of hexagonal BaFe12O19 and SrFe12O19 ferrite ceramics with Multiferroic properties. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S207511331505007X
A.V. Trukhanov, S.V. Trukhanov, Multiferroic properties and structural features of M-Type Al- S substituted Barium hexaferrites. Phys. Solid State (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783417040308
G. Tan, Magnetodielectric coupling response in La- Modified M-type strontium Hexaferrite. Phys. Status Solid (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/PSSA.201800295
T.-J. Park, G.C. Papaefthymiou, A.J. Viesca, Y. Lee, H. Zhou, S.S. Wong et al., Phys. Rev. B 82, 024431 (2010)
P. Pandit: Multiferroic properties of Bi0.9- xLa0.1ErxFeO3 ceramics, Solid State Physics Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Mumbai 400085, India, Indore 452013, (2018).
Y. Jin-Hua, C. Xing-Wang, La-substituted BiFeO3: Synthesis and Multiferroic property study, School for Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081. China (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/23/4/047701
M.N. Ashiq, M.J. Iqbal, Effect of Al-Cr doped on the structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of strontium hexaferrite nanomaterials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323(2011), 259–263 (2010)
N. R. Dhineshbabu, R. Vettumperumal, Optical properties of lanthanum-doped coper spinel Ferrites nanoparticles for optoelectronic applications. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. Vol. 9, 377–383 (7), 2017.
M.S. Awan, S. Anjum, F. Sehar, Role of Bi3+ substitution on structural, magnetic and optical properties of spinel ferrite. Appl. Phys. A https://doi.org/10.1007/s00329-06-9708-z (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anjum, S., Mansoor, A., Mustafa, Z. et al. Comparison between centrosymmetric and non-centrosymmetric chromium substituted M-type barium hexaferrites. Appl. Phys. A 126, 731 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03900-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03900-z