Abstract
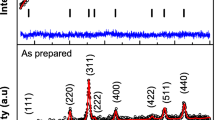
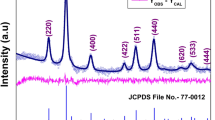
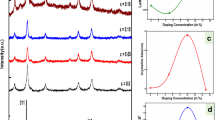
We have performed a systematic study on the effect of Zn substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of crystalline zinc-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles, \(\mathrm {Zn}_{{x}}\hbox {Co}_{{1-x}}\hbox {Fe}_{2}\hbox {O}_{4}\) with x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1, prepared by hydrothermal method. The structural and magnetic properties of these nanoparticles were investigated by XRD, TEM, FTIR, and VSM. All the ferrite nanoparticles were prepared with sizes smaller than 20 nm, thus lying within the range of single-domain regime. The results of Rietveld refinement revealed that all prepared nanoparticles were cubic and single phase, and the increase in Zn concentration resulted in an increase in the lattice constant, x-ray density, and the average bond length on tetrahedral sites. The TEM measurements showed that the nanoparticles were monodisperse and spherical in shape. All FTIR spectra of the prepared ferrites showed two dominant absorption bands, thus confirming the formation of single-phase spinel structure with two sub-lattices: tetrahedral (A-site) and octahedral (B-site). The room temperature M versus H magnetization measurements revealed that the ferrite nanoparticles were ferromagnetic for x = 0 and superparamagnetic for \(x\ge 0.25\). At 10 K, all ferrite nanoparticles showed ferrimagnetic behavior that is weakened by Zn substitution. The saturation magnetization and the first anisotropy constant were observed to decrease with increasing Zn concentration. The zero field cooled and field cooled magnetization data revealed that both superparamagnetic and spin-glass like states may coexist together depending on amount of Zn concentration and temperature.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Ashoori, Electrons in artificial atoms. Nature 379(6564), 413 (1996)
A. López-Ortega, E. Lottini, C.J. Fernandez, C. Sangregorio, Exploring the magnetic properties of cobalt-ferrite nanoparticles for the development of a rare-earth-free permanent magnet. Chem. Mater. 27(11), 4048–4056 (2015)
L. Zhao, H. Zhang, Y. Xing, S. Song, S. Yu, W. Shi, X. Guo, J. Yang, Y. Lei, F. Cao, Studies on the magnetism of cobalt ferrite nanocrystals synthesized by hydrothermal method. J. Solid State Chem. 181(2), 245–252 (2008)
Y. Zheng, L. Jia, F. Xu, G. Wang, X. Shi, H. Zhang, Microstructures and magnetic properties of low temparature sintering nicuzn ferrite ceramics for microwave applications. Ceram. Int. 45(17), 22163–22168 (2019)
M. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari, A. Akbari, Magnetic nanocarriers: evolution of spinel ferrites for medical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 265, 29–44 (2019)
T. Dippong, E.A. Levei, O. Cadar, I.G. Deac, L. Diamandescu, L. Barbu-Tudoran, Effect of nickel content on structural, morphological and magnetic properties of nixco1-xfe2o4/sio2 nanocomposites. J. Alloy. Compd. 786, 330–340 (2019)
A. Goldman, Modern Ferrite Technology (Springer, Berlin, 2006)
R. Raland, D. Saikia, C. Borgohain, J. Borah, Heating efficiency and correlation between the structural and magnetic properties of oleic acid coated MnFe2O4 nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia application. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 50(32), 325004 (2017)
R. Valenzuela, Magnetic Ceramics, vol. 4 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2005)
X. Meng, H. Li, J. Chen, L. Mei, K. Wang, X. Li, Mössbauer study of cobalt ferrite nanocrystals substituted with rare-earth Y3+ ions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321(9), 1155–1158 (2009)
T. Dippong, F. Goga, E.-A. Levei, O. Cadar, Influence of zinc substitution with cobalt on thermal behaviour, structure and morphology of zinc ferrite embedded in silica matrix. J. Solid State Chem. 275, 159–166 (2019)
M.S. Darwish, H. Kim, H. Lee, C. Ryu, J.Y. Lee, J. Yoon, Synthesis of magnetic ferrite nanoparticles with high hyperthermia performance via a controlled co-precipitation method. Nanomaterials 9(8), 1176 (2019)
A. Tawfik, I. Hamada, O. Hemeda, Effect of laser irradiation on the structure and electromechanical properties of Co-Zn ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 250, 77–82 (2002)
G. Duong, N. Hanh, D. Linh, R. Groessinger, P. Weinberger, E. Schafler, M. Zehetbauer, Monodispersed nanocrystalline Co1-xZnxFe2O4 particles by forced hydrolysis: synthesis and characterization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 311(1), 46–50 (2007)
U. Naresh, R.J. Kumar, K.C.B. Naidu, Hydrothermal synthesis of barium copper ferrite nanoparticles: nanofiber formation, optical, and magnetic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 236, 121807 (2019)
G. Maity, P. Maji, S. Sain, S. Das, T. Kar, S. Pradhan, Microstructure, optical and electrical characterizations of nanocrystalline znal2o4 spinel synthesized by mechanical alloying: effect of sintering on microstructure and properties. Physica E 108, 411–420 (2019)
D.S. Mathew, R.-S. Juang, An overview of the structure and magnetism of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and their synthesis in microemulsions. Chem. Eng. J. 129(1–3), 51–65 (2007)
C. Chinnasamy, B. Jeyadevan, K. Shinoda, K. Tohji, D. Djayaprawira, M. Takahashi, R.J. Joseyphus, A. Narayanasamy, Unusually high coercivity and critical single-domain size of nearly monodispersed cofe 2 o 4 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83(14), 2862–2864 (2003)
T. Dippong, E.A. Levei, I.G. Deac, E. Neag, O. Cadar, Influence of cu2+, ni2+, and zn2+ ions doping on the structure, morphology, and magnetic properties of co-ferrite embedded in sio2 matrix obtained by an innovative sol-gel route. Nanomaterials 10(3), 580 (2020)
H. Jalili, B. Aslibeiki, A.G. Varzaneh, V.A. Chernenko, The effect of magneto-crystalline anisotropy on the properties of hard and soft magnetic ferrite nanoparticles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 10(1), 1348–1359 (2019)
S. Amiri, H. Shokrollahi, The role of cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoparticles in medical science. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 33(1), 1–8 (2013)
M. Şincai, D. Gâng, D. Bica, L. Vékás, The antitumor effect of locoregional magnetic cobalt ferrite in dog mammary adenocarcinoma. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 225(1–2), 235–240 (2001)
A.L. Tiano, G.C. Papaefthymiou, C.S. Lewis, J. Han, C. Zhang, Q. Li, C. Shi, A.M. Abeykoon, S.J. Billinge, E. Stach et al., Correlating size and composition-dependent effects with magnetic, mossbauer, and pair distribution function measurements in a family of catalytically active ferrite nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 27(10), 3572–3592 (2015)
R.A. Young, The Rietveld Method, vol. 5 (International Union of Crystallography, Chester, 1993)
K.E. Sickafus, R. Hughes, Spinel Compounds: Structure and Property Relations (American Ceramic Society, Westerville, 1999)
L. Kumar, P. Kumar, A. Narayan, M. Kar, Rietveld analysis of xrd patterns of different sizes of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. Int. Nano Lett. 3(1), 8 (2013)
R. Bujakiewicz-Korońska, Ł. Hetmańczyk, B. Garbarz-Glos, A. Budziak, A. Kalvane, K. Bormanis, K. Drużbicki, Low temperature measurements by infrared spectroscopy in cofe2o4 ceramic. Open Phys. 10(5), 1137–1143 (2012)
J. Gomes, M. Sousa, F. Tourinho, J. Mestnik-Filho, R. Itri, J. Depeyrot, Rietveld structure refinement of the cation distribution in ferrite fine particles studied by x-ray powder diffraction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 289, 184–187 (2005)
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A: Cryst. Phys., Diffr., Theor. General Crystallogr. 32(5), 751–767 (1976)
B. Toksha, S.E. Shirsath, S. Patange, K. Jadhav, Structural investigations and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel auto combustion method. Solid State Commun. 147(11–12), 479–483 (2008)
D.S. Nikam, S.V. Jadhav, V.M. Khot, R. Bohara, C.K. Hong, S.S. Mali, S. Pawar, Cation distribution, structural, morphological and magnetic properties of co 1–x zn x fe 2 o 4 (x= 0–1) nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 5(3), 2338–2345 (2015)
K. Praveena, K. Sadhana, Ferromagnetic properties of zn substituted spinel ferrites for high frequency applications. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 5(4), 1–21 (2015)
S.-T. Xu, Y.-Q. Ma, Y.-F. Xu, X. Sun, B.-Q. Geng, G.-H. Zheng, Z.-X. Dai, Pure dipolar-interacted cofe2o4 nanoparticles and their magnetic properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 62, 142–147 (2015)
M. Chithra, C. Anumol, B. Sahu, S.C. Sahoo, Structural and magnetic properties of znxco1- xfe2o4 nanoparticles: nonsaturation of magnetization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 424, 174–184 (2017)
L. Kumar, M. Kar, Effect of annealing temperature and preparation condition on magnetic anisotropy in nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. IEEE Trans. Magn. 47(10), 3645–3648 (2011)
K. Maaz, A. Mumtaz, S. Hasanain, A. Ceylan, Synthesis and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite (cofe2o4) nanoparticles prepared by wet chemical route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 308(2), 289–295 (2007)
C. Iacovita, A. Florea, L. Scorus, E. Pall, R. Dudric, A.I. Moldovan, R. Stiufiuc, R. Tetean, C.M. Lucaciu, Hyperthermia, cytotoxicity, and cellular uptake properties of manganese and zinc ferrite magnetic nanoparticles synthesized by a polyol-mediated process. Nanomaterials 9(10), 1489 (2019)
R. Topkaya, A. Baykal, A. Demir, Yafet-Kittel-type magnetic order in zn-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with uniaxial anisotropy. J. Nanopart. Res. 15(1), 1359 (2013)
G. Muscas, S. Jovanović, M. Vukomanović, M. Spreitzer, D. Peddis, Zn-doped cobalt ferrite: tuning the interactions by chemical composition. J. Alloy. Compd. 796, 203–209 (2019)
A. Nairan, M. Khan, U. Khan, M. Iqbal, S. Riaz, S. Naseem, Temperature-dependent magnetic response of antiferromagnetic doping in cobalt ferrite nanostructures. Nanomaterials 6(4), 73 (2016)
E. Del Barco, J. Asenjo, X. Zhang, R. Pieczynski, A. Julia, J. Tejada, R. Ziolo, D. Fiorani, A. Testa, Free rotation of magnetic nanoparticles in a solid matrix. Chem. Mater. 13(5), 1487–1490 (2001)
K. Nadeem, H. Krenn, T. Traußnig, R. Würschum, D. Szabó, I. Letofsky-Papst, Effect of dipolar and exchange interactions on magnetic blocking of maghemite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323(15), 1998–2004 (2011)
A.G. Kolhatkar, A.C. Jamison, D. Litvinov, R.C. Willson, T.R. Lee, Tuning the magnetic properties of nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14(8), 15977–16009 (2013)
W. Mohamed, M. Alzaid, M.S.M. Abdelbaky, Z. Amghouz, S. García-Granda, A.M. Abu-Dief, Impact of Co2+ substitution on microstructure and magnetic properties of coxzn1-xfe2o4 nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 9(11), 1602 (2019)
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the deanship of scientific research at the Hashemite University under Project Number: 5/2016. We also acknowledge the Nanotechnology Research Facility of Kuwait University under Project Number: GE01/07.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alzoubi, G.M., Alsmadi, A.M., Alna’washi, G.A. et al. Coexistence of superparamagnetism and spin-glass like behavior in zinc-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 126, 512 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03655-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03655-7