Abstract
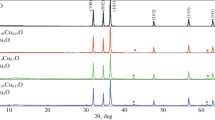
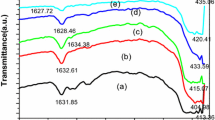
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (N–ZnO) obtained by the Pechini method and calcined using a closed clay container are the focus of the present work. The synthetic route includes a modification in the calcination process (modified Pechini method), that is, without the change in the calcination process. The modified calcination process carried out in a clay container allows for the tunability of the ZnO bandgap. To characterize the materials, X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and UV–visible (UV–Vis) spectroscopy have been performed. The analysis of UV–Vis absorption measurements allows us to conclude that the bandgap of N–ZnO can be tuned from 2.8 to 3.04 eV for ZnO–CC:400 and ZnO–CC:600 (samples of carbon-doped N–ZnO or C–N–ZnO), respectively, which are smaller than the ZnO bulk value of 3.37 eV. This gives rise to new possibilities of adaptation for the N–ZnO to new applications by shifting the bandgap from the UV to the visible region. The XRD and TEM measurements show that all samples are highly crystalline and have small grain sizes, confirming that the ethylene glycol seems to be a useful polymerizing agent for the preparation of C–N–ZnO.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.K. Mishra, H. Mishra, A. Ekielski, S. Talegaonkar, B. Vaydia, Zinc oxide nanoparticles: a promising nanomaterial for biomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today 22, 1825–1834 (2017)
M. Hadiyan, A. Salehi, A. Koohi-Saadi, Sub-ppm acetone gas sensing properties off ree-standing ZnO nanorods. J. Electroceram. 1, 1–9 (2019)
J. Chang, H. Kuo, I. Leu, M. Hon, The effects of thickness and operation temperature on ZnO: Al thin film CO gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 84, 258–264 (2002)
Ü. Özgür, Ya.I. Alivov, C. Liu, A. Teke, M.A. Reshchikov, S. Dogan, V. Avrutin, S.J. Cho, H. Morkoç, A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 041301 (2005)
S.A. Ansari, W. Khan, M. Chaman, A.H. Naqvi, Synthesis, structural and optical properties of Cr doped ZnO nanoparticles. Asian J. Chem. 23, 5622–5624 (2011)
A.A. Azab, E.E. Ateia, S.A. Esmail, Comparative study on the physical properties of transition metaldoped (Co, Ni, Fe, and Mn) ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 124, 1–10 (2018)
Q. Fu, C. Ke, Y. Hu, Z. Zheng, T. Chen, Y. Xu, Al-doped ZnO varistors prepared by a two-step doping process. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 117, 1–6 (2018)
G. Rodriguez-Gattorno, P. Santiago-Jacinto, L. Rendon-Vázquez, J. Németh, I. Dékány, D. Díaz, Novel synthesis pathway of ZnO nanoparticles from the spontaneous hydrolysis of zinc carboxylate salts. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 12597–12604 (2003)
V.A. Soares, A.F. Santos, D.M.S. Ribeiro, M.S. Silva, Study of DC conductivity in nanostructured ceramics of NiMn2O4 pure and doped with Cu and Zn. Int. J. Electroact. Mater. 6, 14–20 (2018)
J. Guo, J. Zhang, M. Zhu, D.X. Ju, X.Y. Xu, B.Q. Cao, Highperformance gas sensor based on ZnO nanowires functionalized by Au nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B 199, 339–345 (2014)
D. Zhao, X. Wan, H. Song, L.Y. Hao, Y.Y. Su, Y. Lv, Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) combined with ZnO quantum dots as a fluorescente sensing platform for phosphate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 197, 50–57 (2014)
J. Huang, S. Liu, N. Yao, X.J. Xu, Optical properties of Eu3+, Dy3+ co-doped ZnO nanocrystals. J. Optoelectron. Lett. 10, 161–163 (2014)
T. Singh, T. Lehnen, T. Leuning, D. Sahub, S. Mathura, Thickness dependence of optoelectronic properties in ALD grown ZnO thin films. J. Appl. Surf. Sci. 289, 27–32 (2014)
L.L. Xing, Y.F. Hu, P.L. Wang, Y.Y. Zhao, Y.X. Nie, P. Deng, X.Y. Xue, Realizing room-temperature self-powered ethanol sensing of Au/ZnO nanowire arrays by coupling the piezotronics effect of ZnO and the catalysis of noble metal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 1–5 (2014)
C.Q. Song, K. Yu, H.H. Yin, H. Fu, Z.L. Zhang, N. Zhang, Z.Q. Zhu, Highly efficient field emission properties of a novel layered VS2/ZnO nanocomposite and flexible VS2 nanosheet. J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 4196–4202 (2014)
J. Yun, W. Qin, K. van Benthem, A.M. Thron, S. Kim, Y.H. Han, Nanovoids in dense hydroxyapatite ceramics after electric field assisted sintering. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 117, 1–7 (2018)
M.S. Silva, S.T. Souza, D.V. Sampaio, J.C.A. Santos, E.J.S. Fonseca, R.S. Silva, Conductive atomic force microscopy characterization of PTCR-BaTiO3 laser-sintered ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36, 1385–1389 (2016)
Y.Q. Fu, J.K. Luo, X.Y. Du, A.J. Flewitt, Y. Li, G.H. Markx, A.J. Walton, W.I. Milne, Recent developments on ZnO films for acoustic wave based bio-sensing and microfluidic applications: a review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 143, 606–619 (2010)
Y.T. Prabhu, K.V. Rao, V.S.S. Kumar, B.S. Kumari, Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by a novel surfactant assisted amine combustion method. Adv. Nanoparticles 02, 45–50 (2013)
J. Lee, J.S. Choi, M. Yoon, Fabrication of ZnO nanoplates for visible light-induced imaging of living cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2, 2311–2317 (2014)
J.Y. Kim, S.Y. Jo, G.J. Sun, A. Katoch, S.W. Choi, S.S. Kim, Tailoring the surface area of ZnO nanorods for improved performance in glucose sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 192, 216–220 (2014)
M. Wang, B. Zhao, S.H. Xu, L. Lin, S.J. Liu, D.N. He, Synthesis of hierarchically structured ZnO nanomaterials via a supercritical assisted solvothermal process. Chem. Commun. 50, 930–932 (2014)
S.K. Lim, S.H. Hong, S.H. Hwang, S.Y. Kim, H.W. Park, Characterization of Ga-doped ZnO nanorods synthesized via microemulsion method. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29, 39–43 (2013)
Q.A.A. Aziz, S. Nor, S.Y. Pung, Z. Lockman, N.A. Hamzah, Y.L. Chan, Ex situ doping of ZnO nanorods by spray pyrolysis technique. Mater. Sci. Forum 756, 16–23 (2013)
P.S. Shewale, G.L. Agawane, S.W. Shin, A.V. Moholka, J.Y. Lee, J.H. Kim, M.D. Uplane, Thickness dependent H2S sensing properties of nanocrystalline ZnO thin films derived by advanced spray pyrolysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 177, 695–702 (2013)
W. Wen, J.M. Wu, Y.D. Wang, Gas-sensing property of a nitrogen-doped zinc oxide fabricated by combustion synthesis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 184, 78–84 (2013)
M.A. Ali, M.R. Idris, M.E. Quayum, Fabrication of ZnO nanoparticles by solution-combustion method for the photocatalytic degradation of organic dye. J. Nanostructure Chem. 3, 1–6 (2013)
M. Pechini, Method of preparing lead and alkaline earth titanates and niobates and coating method using the same from a capacitor. U. S. Patent no. 3330697, 26 Aug. 1963, 11 Jul. 1967
C.T. Chen, F.C. Hsu, S.W. Kuan, Y.F. Chen, The effect of C60 on the ZnO-nanorod surface in organic–inorganic hybrid photovoltaics. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 95, 740–744 (2011)
S. Ghasaban, M. Atai, M. Imani, Simple mass production of zinc oxide nanostructures via low-temperature hydrothermal synthesis. Mater. Res. Express 4, 1–7 (2017)
S.S. Kulkarni, M.D. Shirtat, Optical and structural properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Adv. Res. Phys. Sci. 2, 14–18 (2015)
L. Lilensten, Q. Fu, B.R. Wheaton, A.J. Credle, R.L. Stewart, J.T. Kholi, Kinetic study on lithium-aluminosilicate (LAS) glass-ceramics containing MgO and ZnO. Ceram. Int. 40, 11657–11661 (2014)
G. Madhumitha, G. Elango, S.M. Roopan, Biotechnological aspects of ZnO nanoparticles: overview on synthesis and its applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 100, 571–581 (2016)
Y. Wang, N. Herron, Chemical effects on the optical properties of semiconductor particles. J. Phys. Chem. 91, 5005–5008 (1987)
B. Cullity, Elements of X-ray Diffraction (Addision-Wesley, Reading, 1987), p. 294
S. Vives, E. Gaffet, C. Meunier, X-ray diffraction line profile analysis of iron ball milled powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 366, 229–238 (2004)
A.C.B. Oliveira, D.M.S. Ribeiro, C.G.P. Moraes, R.S. Silva, N.S. Ferreira, M.S. Silva, Synthesis and characterization of nickel manganite ceramics by polymeric precursors method. Mater. Sci. Forum 881, 123–127 (2016)
M.E.L. Sabino, D.M. Oliveira, V.D. Falcão, A.C. Bernardes-Silva, J.R.T. Branco, Structural analysis of ZnO thin films obtained by d.c. sputtering and electron beam evaporation. Powder Diffr. 23, S91–S93 (2008)
E. Carvalho, V. Soares, C.A. Leães, G.E. Paiva, R.S. Silva, M.S. Silva, Radioluminescence study of calcium tungstate crystalline powders and ceramics. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 14, 1–4 (2017)
R. Nasrin, A.H. Bhuiyan, Effect of heat treatment on infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopic studies of the PPnBMA thin films. Appl. Phys. A 124, 1–9 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) and National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, E.S., Silva, M.S., Azevedo, W.M. et al. ZnO nanoparticles with tunable bandgap obtained by modified Pechini method. Appl. Phys. A 125, 504 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2805-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2805-4