Abstract
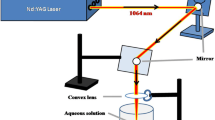
Copper/copper oxide nanowires (NWs) are well known for its antibacterial activity against various pathogens. In the present study, we have shown the enhanced antibacterial activity of the NWs against gram-negative bacterial strains (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhi) and gram-positive bacterial strains (Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus). The increase in the activity is because of the shape and size of the colloidal NWs which were prepared at room temperature in a one-step process by pulsed laser ablation of copper metal target. The purity, shape and size of the colloidal NWs were well characterized by UV–visible absorption spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The NWs were of diameters in the range of 15–30 nm and lengths ranging from 200 to 600 nm. The dose-dependent antibacterial activity of these NWs was found to be more effective against gram-negative bacteria compared to gram-positive bacteria. As gram-negative bacteria have thinner layer of cell wall made up of peptidoglycan possibly which makes them more susceptible to Cu/Cu2O NWs, Cu/Cu2O NWs can be a potent candidate to be used as bactericidal or as growth inhibitor.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.C. Ray, Size and shape dependent second order nonlinear optical properties of nanomaterials and their application in biological and chemical sensing. Chem. Rev. 110, 5332–5365 (2010)
M.K. Singh, A. Agarwal, R. Gopal, R.K. Swarnkar, R.K. Kotnala, Dumbbell shaped nickel nanocrystals synthesized by a laser induced fragmentation method. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 11074–11079 (2011)
T. Zhai, L. Li, X. Wang, X. Fang, Y. Bando, D. Golberg, Recent developments in one-dimensional inorganic nanostructures for photodetectors. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2010). doi:10.1002/adfm.201001259
T. Niidome, Development of functional gold nanorods for bioimaging and photothermal therapy. J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 232, 012011-1-6 (2010)
S.B. Kalidindi, U. Sanyal, B.R. Jagirdar, Nanostructured Cu and Cu@ Cu2O core shell catalysts for hydrogen generation from ammonia—borane. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 10, 5870–5874 (2008)
O. Rubilar, M. Rai, G. Tortella, M.C. Diez, A.B. Seabra, N. Duran, Biogenic nanoparticles: copper, copper oxides, copper sulphides, complex copper nanostructures and their applications. Biotechnol. Lett. 35, 1365–1376 (2013)
M. Raffi, S. Mehrwan, T.M. Bhatti, J.I. Akhter, A. Hameed, W. Yawar, M.M. Ul Hasan, Investigations into the antibacterial behavior of copper nanoparticles against Escherichia coli. Ann. Microbiol. 60, 75–80 (2010)
P. Pandey, S. Merwyn, G.S. Agarwal, B.K. Tripathi, S.C. Pant, Electrochemical synthesis of multi-armed CuO nanoparticles and their remarkable bactericidal potential against waterborne bacteria. J. Nanopart. Res. 14, 709-1-13 (2012)
D. Longano, N. Ditaranto, N. Cioffi, F. Di Niso, T. Sibillano, A. Ancona, A. Conte, M.A.D. Nobile, L. Sabbatini, L. Torsi, Analytical characterization of laser-generated copper nanoparticles for antibacterial composite food packaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 403, 1179–1186 (2012)
P. Kalita, J. Singh, M.K. Singh, P.R. Solanki, G. Sumana, B.D. Malhotra, Ring like self assembled Ni nanoparticles based biosensor for food toxin detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 093702-1-4 (2012)
P. Liu, W. Cai, Z. Haibo, Fabrication and size-dependent optical properties of FeO nanoparticles induced by laser ablation in a liquid medium. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 3261–3266 (2008)
T. Tsuji, Y. Okazaki, Y. Tsuboi, M. Tsuji, Nanosecond time-resolved observations of laser ablation of silver in water. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 1533–1535 (2007)
R.K. Swarnkar, S.C. Singh, R. Gopal, Effect of aging on copper nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation in water: structural and optical characterizations. Bull. Mater. Sci. 34, 1363–1369 (2011)
J.K. Pandey, R.K. Swarnkar, K.K. Soumya, P. Dwivedi, M.K. Singh, S. Sundaram, R. Gopal, Silver nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation: as a potent antibacterial agent for human enteropathogenic gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial strains. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 174, 1021–1031 (2014)
W. Irith, H. Kai, E.W. Robert, Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat. Protoc. 3, 163–175 (2008)
H. Ehrenreich, H.R. Philipp, Optical properties of Ag and Cu. Phys. Rev. 128, 1622–1629 (1962)
K.L. Kelly, E. Coronado, L.L. Zhao, G.C. Schatz, The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 668–677 (2003)
R.K. Swarnkar, R. Gopal, Controlled synthesis of cuprous oxide nanorings by pulsed laser ablation of copper metal in aqueous media of sodium dodecyl sulfate. Sci. Adv. Mater. 4, 511–517 (2012)
Y. Shimotsuma, T. Yuasa, H. Homma, M. Sakakura, A. Nakao, K. Miura, K. Hirao, M. Kawasaki, J. Qiu, P.G. Kazansky, Photoconversion of copper flakes to nanowires with ultrashort pulse laser irradiation. Chem. Mater. 19, 1206–1208 (2007)
J.P. Ruparelia, A. Kumar, S.P. Duttagupta, Strain specificity in antimicrobial activity of silver and copper nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 4, 707–716 (2008)
J.A. Lemire, J.J. Harrison, R.J. Turner, Antimicrobial activity of metals: mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 11, 371–384 (2013)
A.K. Suresh, D.A. Pelletiera, M.J. Doktycz, Relating nanomaterial properties and microbial toxicity. Nanoscale 5, 463–474 (2013)
H.Y. Song, K.K. Ko, I.H. Oh, B.T. Lee, Fabrication of silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial mechanisms. Eur. Cells Mater. 11, 58–59 (2006)
F. Gao, H. Pang, L. Qingyi, Copper-based nanostructures: promising antibacterial agents and photocatalysts. Chem. Commun. 24, 3571–3573 (2009)
J.R. Morones, J.L. Elechiguerra, A. Camacho, K. Holt, J.B. Kouri, J.T. Ram´ırez, M.J. Yacaman, The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 16, 2346–2353 (2005)
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Professor N. P. Lalla, UGC-DAE-CSR Indore, for providing TEM facility and DRDO, New Delhi, for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swarnkar, R.K., Pandey, J.K., Soumya, K.K. et al. Enhanced antibacterial activity of copper/copper oxide nanowires prepared by pulsed laser ablation in water medium. Appl. Phys. A 122, 704 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0232-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0232-3