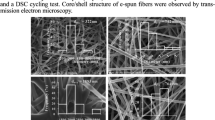
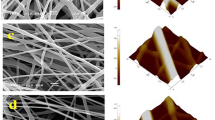
Abstract
Electrospinning is a simple and versatile fiber synthesis technique in which a high-voltage electric field is applied to a stream of polymer melt or polymer solution, resulting in the formation of continuous micro/nanofibers. Halloysite nanotubes (HNT) have been found to achieve improved structural and mechanical properties when embedded into various polymer matrices. This research work focuses on blending poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) (9 and 15 wt%/v) and poly(lactic acid) (PLA) (fixed at 8 wt%/v) solutions with HNT at two different concentrations 1 and 2 wt%/v. Both unmodified HNT and HNT modified with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (ASP) were utilized in this study. Fiber properties have been shown to be strongly related to the solution viscosity and electrical conductivity. The addition of HNT increased the solution viscosity, thus resulting in the production of uniform fibers. For both PCL concentrations, the average fiber diameter increased with the increasing of HNT concentration. The average fiber diameters with HNT-ASP were reduced considerably in comparison to those with unmodified HNT when using 15 wt%/v PCL. Slightly better dispersion was obtained for PLA: PCL composites embedded with HNT-ASP compared to unmodified HNT. Furthermore, the addition of HNT-ASP to the polymeric blends resulted in a moderate decrease in the degree of crystallinity, as well as slight reductions of glass transition temperature of PCL, the crystallization temperature and melting temperature of PLA within composite materials. The infrared spectra of composites confirmed the successful embedding of HNT-ASP into PLA: PCL nanofibers relative to unmodified HNT due to the premodification using ASP to reduce the agglomeration behavior. This study provides a new material system that could be potentially used in drug delivery, and may facilitate good control of the drug release process.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Heydarkhan-Hagvall, K. Schenke-Layland, A. Dhanasopon, F. Rofail, H. Smith, B. Wu, R. Shemin, R. Beygui, W. MacLellan, Biomaterials 29, 2907 (2008)
Q. Pham, U. Sharma, A. Mikos, Tissue Eng. 12, 1197 (2006)
D. Liang, B. Hsiao, B. Chu, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59, 1392 (2007)
H. Jiang, Y. Hu, P. Zhao, Y. Li, K. Zhu, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part B, Appl. Biomater. 79, 50 (2006)
D. Yang, Y. Li, J. Nie, Carbohydr. Polym. 69, 538 (2007)
Y. Ji, K. Ghosh, X. Shu, B. Li, J. Sokolov, G. Prestwich, R. Clark, M. Rafailovich, Biomaterials 27, 3782 (2006)
J. Han, C. Branford-White, L. Zhu, Carbohydr. Polym. 79, 214 (2010)
G. Kim, H. Yoon, Y. Park, Appl. Phys. A, Mater, Sci. Process. 100, 1197 (2010)
K. Kim, M. Yu, X. Zong, J. Chiu, D. Fang, Y. Seo, B. Hsiao, B. Chu, M. Hadjiargyrou, Biomaterials 24, 4977 (2003)
W. Cui, X. Li, X. Zhu, G. Yu, S. Zhou, J. Weng, Biomacromolecules 7, 1623 (2006)
M. Liu, B. Guo, M. Du, F. Chen, D. Jia, Polymer 50, 3022 (2009)
A. Touny, J. Lawrence, A. Jones, S. Bhaduri, J. Mater. Res. 25, 857 (2010)
E. Kenawy, G. Bowlin, K. Mansfield, J. Layman, D. Simpson, E. Sanders, G. Wnek, J. Control. Release 81, 57 (2002)
P. Haque, I. Barker, A. Parsons, K. Thurecht, I. Ahmed, G. Walker, C. Rudd, D. Irvine, J. Polym. Sci., Part A, Polym. Chem. 48, 3082 (2010)
L.E. Alexander, X-Ray Diffraction Methods in Polymer Science (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1969)
M. Zamani, M. Morshed, J. Varshosaz, M. Jannesari, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 75, 179 (2010)
K. Arayanarakul, N. Choktaweesap, D. Aht ong, C. Meechaisue, P. Supaphol, Macromol. Mater. Eng. 291, 581 (2006)
M. Spasova, O. Stoilova, N. Manolova, I. Rashkov, G. Altankov, J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 22, 62 (2007)
M. Liu, B. Guo, M. Du, D. Jia, Appl. Phys. A, Mater. Sci. Process. 88, 391 (2007)
A. Boultif, D. Louer, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 37, 724 (2004)
N. Ning, Q. Yin, F. Luo, Q. Zhang, R. Du, Q. Fu, Polymer 48, 7374 (2007)
Y. Dong, D. Chaudhary, H. Haroosh, T. Bickford, J. Mater. Sci. 46, 6148 (2011)
M. Shibata, Y. Inoue, M. Miyoshi, Polymer 47, 3557 (2006)
P. Picciani, E. Medeiros, Z. Pan, D. Wood, W. Orts, L. Mattoso, B. Soares, Macromol. Mater. Eng. 295, 618 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The Ph.D. scholarship awarded by the Iraqi government to Mr. Hazim J. Haroosh and the financial support of Curtin Internal Research Grants (IRG) 2010 (Project No. 47604) to Dr. Yu Dong are gratefully acknowledged. The authors also wish to thank the Curtin Electron Microscopy lab and Applied Physics lab for technical assistance with SEM and XRD analyses, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haroosh, H.J., Dong, Y., Chaudhary, D.S. et al. Electrospun PLA: PCL composites embedded with unmodified and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (ASP) modified halloysite nanotubes (HNT). Appl. Phys. A 110, 433–442 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-7233-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-7233-7