Abstract
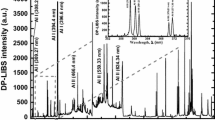
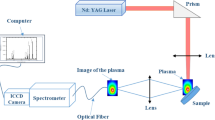
Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) can be considered as a prominent technology for compositional analysis of materials in low-pressure space applications. In space applications, usually LIBS is conducted in a low-pressure environment and proper understanding of the plasma parameters is significant for any improvement in the system. A model is developed to describe the heating and subsequent melting, vaporization and ionization of a target material during LIBS process. A numerical model based on one-dimensional thermal conductivity equation is being used to simulate the target evaporation and a hydrodynamic model is used to simulate plume expansion. Further, an experimental approach of measuring spectral emission from the ablation plume using emission spectroscopy and estimating the plasma state, such as the ionization species, and average plasma temperature, is investigated. An important result of this work is that for different ambient conditions, laser ablation plume dynamics can be estimated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.J. Radziemski, Spectrochim. Acta Part B 57, 1109–1113 (2002)
P.K. Diwakar, D.W. Hahn, Spectrochim. Acta Part B 63, 1038–1046 (2008)
S. Harilal, C.V. Bindhu, M.S. Tillack, F. Najmabadi, A.C. Gaeris, J. Appl. Phys. 93(5), 2380–2388 (2003)
A.K. Sharma, R.K. Thareja, Appl. Surf. Sci. 243, 68–75 (2005)
A. Bogaerts, Z. Chen, R. Gijbels, A. Vertes, Spectrochim. Acta Part B 58, 1867–1893 (2003)
L. Balaz, R. Gijbels, A. Vertes, Anal. Chem 63, 314–320 (1991)
G. Colonna, A. Casavola, M. Capitelli, Spectrochim. Acta Part B 56, 567–586 (2001)
A. Amoruso, Appl. Phys. A 69, 323–332 (1999)
E.I. Tatiana, J. Hermann, P. Delaporte, M. Sentis, Phys. Rev. E 66, 066406 (2002)
NIST Hand book of basic atomic Spectroscopic data, J.E. Sansonetti and W.C. Martin, http://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Handbook/index.html
A. Descoeudres, Ch. Hollenstein, R. Demellayer, G. Walder, J. Phys. D, Appl. Phys. 37, 875–882 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antony, J.K., Jatana, G.S., Vasa, N.J. et al. Modeling of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy for very low-pressure conditions. Appl. Phys. A 101, 161–165 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-010-5782-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-010-5782-1