Abstract.
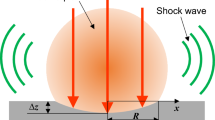
A model to describe the laser ablation of metallic targets is presented. It accounts for the main physical processes involved in the laser–solid–plasma interaction by considering the photon absorption and the ionization mechanisms that are active in the plasma, as well as the laser-produced plasma kinetics. The model is used to simulate the laser ablation of aluminum targets irradiated with a 6-ns UV laser pulse at 0.35 μm, and the results are compared with experimental findings. Calculations show that all the investigated plasma parameters strongly depend on the laser intensity until a roll-off is reached at irradiance ≥1.5 GW cm-2. The satisfactorily good agreement between model predictions and experimental findings confirms that laser–plasma interaction processes and plasma kinetics play a relevant role during nanosecond laser ablation of metals in the laser intensity range of concern in this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 12 February 1999 / Accepted: 12 April 1999 / Published online: 7 July 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amoruso, S. Modeling of UV pulsed-laser ablation of metallic targets . Appl Phys A 69, 323–332 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390051008
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390051008