Abstract
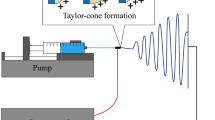
An electrospinning process has been introduced to fabricate micro/nanofiber membranes having high porosity and specific surface area. When constantly/uniformly depositing the micro/nanofiber membrane on a target, the electrospun fibers require flushing out of the high charge and excessive remaining solvent built up, since these factors can interrupt the constant deposition rate of the electrospun fibers on substrates. These limitations can be overcome with a direct-electrospinning process, which can lower the charges of the electrospun fibers through a window of guiding electrodes and remaining solvent of the electrospun fibers during the spinning process by an air-blowing system. Because of the reduced charge accumulation of the electrospun fibers, the micro/nanofibers can be deposited on any kind of target, which may be a conductive or a non-conductive material. The fabricated membrane had a dramatically reduced charge, remaining solvent concentration, sufficient tensile modulus, and small pore-size distribution. To observe the possibility as a biomedical wound-dressing material, a bacteria-shielding test of the fabricated membrane was conducted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.J. Hinrichs, E.J. Lommen, C.R.H. Widevuur, J. Feijen, J. Appl. Biomater. 2, 287 (1992)
L.S. Leipziger, V. Glushko, B. DiBernado, F. Shafaie, J. Noble, J. Nichols, O.M. Alvarez, J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 12, 409 (1985)
M.S. Khil, D.I. Cha, H.Y. Kim, I.S. Kim, N. Bhattarai, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 67, 675 (2003)
D.S. Katti, K.W. Robinson, F.K. Ko, C.T. Laurencin, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 70, 286 (2004)
L. Wang, E. Khor, A. Wee, L.Y. Lim, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 63, 610 (2002)
I.V. Yannas, J.F. Burke, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 14, 65 (1980)
I.V. Yannas, J.F. Burke, P.L. Gordon, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 14, 107 (1980)
N. Dagalakis, J. Flink, P. Stasikelis, J.F. Burke, I.V. Yannas, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 14, 511 (1980)
K. Matsida, S. Suzuki, N. Isshikin, K. Yoshioka, R. Wada, S.H. Hyun, Y. Ikada, Biomaterials 13, 119 (1992)
M.C. Robson, B.D. Stenberg, J.D. Heggers, Clin. Plast. Surg. 3, 485 (1990)
Z.M. Huang, Y.Z. Zhang, M. Kotaki, S. Ramakrishna, Compos. Sci. Technol. 63, 2223 (2003)
E.-R. Kenawy, J.M. Layman, J.R. Watkins, G.L. Bowlin, J.A. Matthews, D.G. Simpson, G.E. Wnek, Biomaterials 24, 907 (2003)
R. Dersch, M. Steinhart, U. Boudriot, A. Greiner, J.H. Wendorff, Polym. Adv. Technol. 16, 276 (2005)
J. Kameoka, H.G. Craighead, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 371 (2003)
G.H. Kim, H.S. Han, J.H. Park, W.D. Kim, Polym. Eng. Sci. 47, 707 (2007)
W.E. Teo, S. Ramakrishuna, Nanotechnology 17, R89 (2006)
D.H. Reneker, I. Chun, Nanotechnology 7, 216 (1996)
G.H. Kim, W.D. Kim, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 013111 (2006)
Q. Qi, P. Hu, J. Xu, A. Wang, Biomacromolecules 7, 2327 (2006)
W.J. Li, C.T. Laurencin, E.J. Caterson, R.S. Tuan, F.K. Ko, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 60, 613 (2002)
J. Huang, S. Virji, B.H. Weiller, R.B. Kaner, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 314 (2003)
D. Adam, Nature 411, 236 (2001)
G.G. Chase, D.H. Reneker, C. Shin, AIChE J. 51, 3109 (2005)
P. Gibson, H. Schreuder-Gibson, D. Rivin, Colloid Surf. A 187–188, 469 (2001)
M.G. McKee, J.M. Layman, M.P. Cashion, T.E. Long, Science 311, 353 (2006)
J. Venugopal, L.L. Ma, S. Ramakrishuna, Tissue Eng. 11, 847 (2005)
L.D. Landau, E.M. Lifshitz, Electrodynamics of Continuous Media (Pergamon, New York, 1984)
G.H. Kim, Y.M. Shkel, J. Mater. Res. 19, 1164 (2004)
I.C. Um, D. Fang, B.S. Hsiao, A. Okamoto, B. Chu, Biomacromolecules 5, 1428 (2004)
V.E. Kalayci, P.K. Patra, Y.K. Kim, S.C. Ugbolue, Polymer 46, 7191 (2005)
S.V. Fridrikh, J.H. Yu, M.P. Brenner, G.C. Rutledge, Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 144502 (2003)
M. Wang, H.J. Jin, D.L. Kaplan, G.C. Rutledge, Macromolecules 37, 6856 (2004)
S.J. Hollister, Nat. Mater. 4, 518 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
47.65.-d; 81.16.-c; 81.07.-b; 61.41.+e; 87.85.J-
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, G., Yoon, H. A direct-electrospinning process by combined electric field and air-blowing system for nanofibrous wound-dressings. Appl. Phys. A 90, 389–394 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-4330-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-4330-0