Abstract
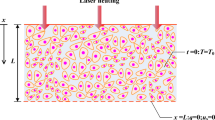
The temporal dynamics of biological tissue swelling under the effect of mid-IR laser radiation is considered theoretically following the experimental investigation published earlier. The probable mechanism of laser swelling is suggested. This mechanism consists of deformation of tissue protein base by vapor pressure, which appears due to evaporation of tissue water. The formation and relaxation of a hump on the surface was determined by both mechanical properties (elastic, plastic) and porosity of material providing water vapor transfer within tissue. It is found that these mechanisms can lead to the formation of both transient and stationary hump structures on the surface. To describe the hump relaxation, we consider a new, evaporation-condensation, mechanism of heat transfer within the region of biotissue with microchannels. This mechanism allows us to explain the value of relaxation time of the hump measured in experiment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Beinhorn, J. Ihlemann, K. Luther, J. Troe: Appl. Phys. A 68, 709 (1999)
M. Himmelbauer, E. Arenholz, D. Bäuerle, K. Schilcher: Appl. Phys. A 63, 337 (1996)
J. Gu, E. Tay, P.K. Lim, P. Lim: Appl. Phys. A 74, 487 (2002)
H. Fukumura, N. Mibuka, S. Eura, H. Masuhara: Appl. Phys. A 53, 255 (1991)
T. Masubuchi, H. Furutani, H. Fukumura, H. Masuhara: J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 2518 (2001)
Q. Ren, R.H. Keates, R.A. Hill, M.W. Berns: Opt. Eng. 34, 642 (1995)
R.A. London, M.E. Glinsky, G.B. Zimmerman, D.S. Bailey, D.C. Eder, S.L. Jacques: Appl. Opt. 36, 9068 (1997)
A.J. Welsh: J. Quantum Electronics 20, 1471 (1984)
B. Majaron, P. Plestenjak, M. Lukac: Appl. Phys. B 69, 71 (1999)
V. Kamensky, F. Feldchtein, V. Gelikonov, L. Snopova, S. Muraviov, A. Malyshev, N. Bityurin, A. Sergeev: Journal of Biomedical optics 4, 137 (1999)
A.Y. Malyshev, V.A. Kamensky, N.M. Bityurin: The dynamics of soft biological tissue preablation swelling under the IR laser irradiation. Preprint No. 558 (IAP RAS, Nizhnii Novgorod 2001)
L.D. Landau, E.M. Lifshitz: Theory of Elasticity, 3rd edn. (Pergamon Press, Oxford 1986)
D. Kolarov, A. Baltov, N. Boncheva: Mekhanika plasticheskikh sred (MIR, Moskva 1979)
L.D. Landau, E.M. Lifshitz: Statistical physics, 2nd edn. (Pergamon Press, Oxford 1980)
M.P. Vukalovich: Tablitsy teplo-fizicheskikh svoistv vody i vodianogo para (Izdatelstvo standartov, Moskva 1969)
E.A. Mason, A.P. Malinauskas: Gas transport in porous media: in dusty-gas model (Elsevier, Amsterdam, New York 1983)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
42.62.-b; 44.30.+v; 81.40.-z
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malyshev, A., Bityurin, N. Laser swelling of soft biological tissue by IR pulses. Appl. Phys. A 79, 1175–1179 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-004-2698-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-004-2698-7