Abstract
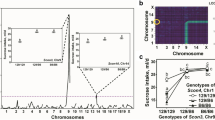
In food preference studies, mammals are often categorized as being either neophilic or neophobic, i.e., preferring or disliking a novel-tasting food. To date, the genetic factors influencing novel food preference have not been elucidated. To understand this phenomenon, we investigated the genetics of food preference in eight inbred strains of mice. We gave them plain-, cinnamon-, or cocoa-flavored powdered food on day 0 for 45 min and then a choice of cinnamon- or cocoa-flavored food 14 days later. We determined their preference for novel versus already-experienced flavored food and found that some inbred strains chose the food that they had been given previously, while others chose a different food. In particular, the DBA/2 strain chose more cinnamon-flavored food after it was pre-exposed to cinnamon, while the B6 strain chose less cinnamon-flavored food after this initial exposure. The BXD recombinant inbred (RI) strain set was then used to map quantitative trait loci (QTLs) that influence this novel food preference. One of these QTLs was found to map to the distal end of Chromosome (Chr) 8.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
EA Bernays K Bright JJ Howard D Raubenheimer D Champagne (1992) ArticleTitleVariety is the spice of life: frequent switching between foods in the polyphagous grasshopper Taeniopoda eques Burneister (Orthoptera: Acridadae). Anim Behav 44 721–731
LL Birch (1990) ArticleTitleDevelopment of food acceptance patterns. Dev Psychol 26 515–519 Occurrence Handle10.1037//0012-1649.26.4.515
VJ Bolivar BJ Caldarone AA Reilly L Flaherty (2000) ArticleTitleHabituation of activity in an open field: a survey of inbred strains and F1 hybrids. Behav Genet 30 285–293 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1026545316455 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7ktFSmuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11206083
VJ Bolivar O Pooler L Flaherty (2001) ArticleTitleInbred strain variation in contextual and cued fear conditioning behavior. Mamm Genome 12 651–656 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003350020039 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXltlyqt7w%3D Occurrence Handle11471061
MN Cook RW Williams L Flaherty (2001) ArticleTitleAnxiety-related behaviors in the elevated zero-maze are affected by genetic factors and retinal degeneration. Behav Neurosci 115 468–476 Occurrence Handle10.1037//0735-7044.115.2.468 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M3ltVWqsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11345971
RT Cook SER Bailey CR McCrohan B Nash RM Woodhouse (2000) ArticleTitleThe influence of nutritional status on the feeding behavior of the field slug, Deroceras reticulatum (Muller). Anim Behav 59 167–176 Occurrence Handle10.1006/anbe.1999.1275 Occurrence Handle10640378
JC Crabbe D Wahlsten BC Dudek (1999) ArticleTitleGenetics of mouse behavior: interactions with laboratory environment. Science 284 1670–1672 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjs1KitLY%3D Occurrence Handle10356397
F Dellu A Contarino H Simon GF Koob LH Gold (2000) ArticleTitleGenetic differences in response to novelty and spatial memory using a two-trial recognition task in mice. Neurobiol Learn Mem 73 31–48 Occurrence Handle10.1006/nlme.1999.3919 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7ltlylsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10686122
GD Ferguson SG Anagnostaras AJ Silva HR Herschman (2000) ArticleTitleDeficits in memory and motor performance in synaptotagmin IV mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97 5598–5603 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.100104597 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjsVWmsLY%3D Occurrence Handle10792055
BG Galef SW Wigmore (1983) ArticleTitleTransfer of information concerning distant foods: a laboratory investigation of the ‘information-centre’ hypothesis. Anim Behav 31 748–758
R Greenberg (1990) ArticleTitleEcological plasticity, neophobia, and resource use in birds. Stud Avian Biol 13 431–437
JP Hegmann B Possidente (1981) ArticleTitleEstimating genetic correlations from inbred strains. Behav Genet 11 103–114 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi6B1c7lvFY%3D Occurrence Handle7271677
B Heinrich (1995) ArticleTitleNeophilia and exploration in juvenile common ravens, Corvus corax. Anim Behav 50 695–704 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0003-3472(95)80130-8
MS Herskin L Munksgaard (2000) ArticleTitleBehavioral reactivity of cattle towards novel food: effects of testing time and food type of neighbors. J Anim Sci 78 2323–2328 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXms1Oqu7Y%3D Occurrence Handle10985406
K Hobden P Pliner (1995) ArticleTitleEffects of a model on food neophobia in humans. Appetite 25 101–113 Occurrence Handle10.1006/appe.1995.0046 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymC3Mbms1I%3D Occurrence Handle8561482
E Johnson (2000) ArticleTitleFood-neophobia in semi-free ranging rhesus macques: effects of food limitation and food source. Am J Primatol 50 25–35 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1098-2345(200001)50:1<25::AID-AJP3>3.3.CO;2-4 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2FltlKmtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10588433
JH Kogan PW Frankland JA Blendy J Coblentz Z Marowitz G Schutz AJ Silva (1996) ArticleTitleSpaced training induces normal long-term memory in CREB mutant mice. Curr Biol 7 1–11
E Lander L Kruglyak (1995) ArticleTitleGenetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet 11 241–247 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXptlSjs74%3D Occurrence Handle7581446
L Levin EG Carr (2001) ArticleTitleFood selectivity and problem behavior in children with developmental disabilities. Behav Modif 25 443–470 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MzntF2mug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11428248
SF Logue EH Owen DL Rasmussen JM Wehner (1997) ArticleTitleAssessment of locomotor activity, acoustic and tactile startle, and prepulse inhibition of startle in inbred mouse strains and F1 hybrids: implications of genetic background for single gene and quantitative trait loci analyses. Neuroscience 80 1075–1086 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0306-4522(97)00164-4 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXls1Ojsrs%3D Occurrence Handle9284061
EH Owen SF Logue DL Rasmussen JM Wehner (1997) ArticleTitleAssessment of learning by the Morris water task and fear conditioning in inbred mouse strains and F1 hybrids: implications of genetic background for single gene mutations and quantitative trait loci analyses. Neuroscience 80 1087–1099 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0306-4522(97)00165-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXls1Ojsrg%3D Occurrence Handle9284062
ML Pelchat (2000) ArticleTitleYou can teach an old dog new tricks: olfaction and responses to novel foods by the elderly. Appetite 35 153–160 Occurrence Handle10.1006/appe.2000.0348 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FisVWruw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10986108
P Pliner K Hobden (1992) ArticleTitleDevelopment of a scale to measure the trait of food neophobia in humans. Appetite 19 105–120 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyC2czivFU%3D Occurrence Handle1489209
P Pliner A Eng K Krishnan (1995) ArticleTitleThe effects of fear and hunger on food neophobia in humans. Appetite 25 77–87 Occurrence Handle10.1006/appe.1995.0042 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymD3snpvFI%3D Occurrence Handle7495328
FD Provenza JJ Lynch CD Cheney (1995) ArticleTitleEffects of a flavor and food restriction on the response of sheep to novel foods. Appl Anim Behav Sci 43 83–93 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0168-1591(95)00552-4
P Roullet JM Lassalle (1990) ArticleTitleGenetic variation, hippocampal mossy fibres distribution, novelty reactions and spatial representation in mice. Behav Brain Res 41 61–70 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0166-4328(90)90054-I Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6C2MfosVw%3D Occurrence Handle2073356
P Rozin (1990) ArticleTitleDevelopment in the food domain. Dev Psychol 26 555–562 Occurrence Handle10.1037//0012-1649.26.4.555
C Thinus-Blanc E Save C Rossi-Arnaud A Tozzi M Ammassari-Teule (1996) ArticleTitleThe differences shown by C57BL/6 and DBA/2 inbred mice in detecting spatial novelty are subserved by a different hippocampal and parietal cortex interplay. Behav Brain Res 80 33–40 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiD287gvVQ%3D Occurrence Handle8905126
R Trullas P Skolnick (1993) ArticleTitleDifferences in fear motivated behaviors among inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology 111 323–331 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqC2srnsF0%3D Occurrence Handle7870970
P Valsecchi BG Galef (1989) ArticleTitleSocial influences on the food preferences of house mice (Mus musculus). Int J Comp Psychol 2 245–256
E Visalberghi E Addessi (2000) ArticleTitleSeeing group members eating a familiar food enhances the acceptance of novel-foods in capuchin monkeys. Anim Behav 60 69–76 Occurrence Handle10.1006/anbe.2000.1425 Occurrence Handle10924205
A Vitale A Queyras (1997) ArticleTitleThe response to novel foods in common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus): the effects of different social contexts. Ethology 103 395–403
SJ Webster L Lefebvre (2000) ArticleTitleNeophobia by the Lesser-Antillean Bullfinch, a foraging generalist, and the Bananaquit, a nectar specialist. Wilson Bull 112 424–427
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bolivar, V.J., Flaherty, L. Genetic control of novel food preference in mice . Mamm Genome 15, 193–198 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-003-2307-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-003-2307-7