Abstract.
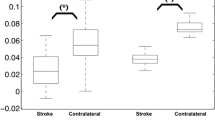
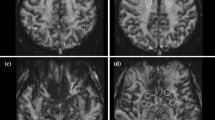
The purpose of the present study was to analyse specific advantages of calculated parameter images and their limitations using an optimized echo-planar imaging (EPI) technique with high spatial and temporal resolution. Dynamic susceptibility contrast magnetic resonance imaging (DSC-MRI) was performed in 12 patients with cerebrovascular disease and in 13 patients with brain tumours. For MR imaging of cerebral perfusion an EPI sequence was developed which provides a temporal resolution of 0.68 s for three slices with a 128 × 128 image matrix. To evaluate DSC-MRI, the following parameter images were calculated pixelwise: (1) Maximum signal reduction (MSR); (2) maximum signal difference (ΔSR); (3) time-to-peak (Tp); and (4) integral of signal-intensity-time curve until Tp (SInt). The MSR maps were superior in the detection of acute infarctions and ΔSR maps in the delineation of vasogenic brain oedema. The time-to-peak (Tp) maps seemed to be highly sensitive in the detection of poststenotic malperfused brain areas (sensitivity 90 %). Hyperperfused areas of brain tumours were detectable down to a diameter of 1 cm with high sensitivity ( > 90 %). Distinct clinical and neuroradiological conditions revealed different suitabilities for the parameter images. The time-to-peak (Tp) maps may be an important advantage in the detection of poststenotic “areas at risk”, due to an improved temporal resolution using an EPI technique. With regard to spatial resolution, a matrix size of 128 × 128 is sufficient for all clinical conditions. According to our results, a further increase in matrix size would not improve the spatial resolution in DSC-MRI, since the degree of the vascularization of lesions and the susceptibility effect itself seem to be the limiting factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 24 December 1997; Revision received: 6 April 1998; Accepted: 19 May 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bitzer, M., Klose, U., Nägele, T. et al. Echo planar perfusion imaging with high spatial and temporal resolution: methodology and clinical aspects. Eur Radiol 9, 221–229 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300050659
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300050659