Abstract.
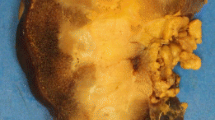
Acquired cystic kidney disease (ACKD), also known as acquired renal cystic disease (ARCD,) occurs in patients who are on dialysis for end-stage renal disease. It is generally accepted that ACKD develops as a consequence of sustained uremia and can first manifest even before dialysis is initiated while the patient is still in chronic renal failure. The role of immune suppression, particularly in transplant recipients, in the development of ACKD, is still under investigation. The prevalence of ACKD is directly related to the duration of dialysis and the risk of cancer is directly related to the presence of cysts. Herein we review the current understanding of the pathophysiology and imaging implications of ACKD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 May 2000; Accepted: 29 June 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choyke, P. Acquired cystic kidney disease. Eur Radiol 10, 1716–1721 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300000601
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300000601