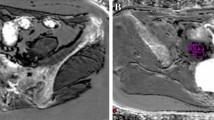
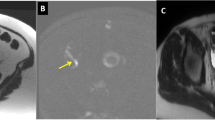
Abstract
Objective
To compare the capabilities of standard pelvic MRI with low-resolution pelvic MRI using fast breath-hold sequences to evaluate deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE).
Methods
Sixty-eight consecutive women with suspected DIE were studied with pelvic MRI. A double-acquisition protocol was carried out in each case. High-resolution (HR)-MRI consisted of axial, sagittal, and coronal TSE T2W images, axial TSE T1W, and axial THRIVE. Low-resolution (LR)-MRI was acquired using fast single shot (SSH) T2 and T1 images. Two radiologists with 10 and 2 years of experience reviewed HR and LR images in two separate sessions. The presence of endometriotic lesions of the uterosacral ligament (USL), rectovaginal septum (RVS), pouch of Douglas (POD), and rectal wall was noted. The accuracies of LR-MRI and HR-MRI were compared with the laparoscopic and histopathological findings.
Results
Average acquisition times were 24 minutes for HR-MRI and 7 minutes for LR-MRI. The more experienced radiologist achieved higher accuracy with both HR-MRI and LR-MRI. The values of sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy did not significantly change between HR and LR images or interobserver agreement for all of the considered anatomic sites.
Conclusions
LR-MRI performs as well as HR-MRI and is a valuable tool for the detection of deep endometriosis extension.
Key Points
• High- and low-resolution MRI perform similarly in deep endometriosis evaluation
• Low-resolution MRI significantly reduces the duration of the examination
• Radiologist experience is fundamental for evaluating deep pelvic endometriosis



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koninckx PR, Meuleman C, Demeyere S, Lesaffre E, Cornillie FJ (1991) Suggestive evidence that pelvic endometriosis is a progressive disease, whereas deeply infiltrating endometriosis is associated with pelvic pain. Fertil Steril 55:759–765
Scioscia M, Bruni F, Ceccaroni M, Steinkasserer M, Stepniewska A, Minelli L (2011) Distribution of endometriotic lesions in endometriosis stage IV supports the menstrual reflux theory and requires specific preoperative assessment and therapy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 90:136–139
Bazot M, Stivalet A, Darai E, Coudray C, Thomassin-Naggara I, Poncelet E (2013) Comparison of 3D and 2D FSE T2-weighted MRI in the diagnosis of deep pelvic endometriosis: preliminary results. Clin Radiol 68:47–54
Bazot M, Darai E, Hourani R et al (2004) Deep pelvic endometriosis: MR imaging for diagnosis and prediction of extension of disease. Radiology 232:379–389
Busard MP, Mijatovic V, Luchinger AB et al (2012) MR imaging of bladder endometriosis and its relationship with the anterior uterine wall: experience in a tertiary referral centre. Eur J Radiol 81:2106–2111
Scardapane A, Lorusso F, Bettocchi S et al (2013) Deep pelvic endometriosis: accuracy of pelvic MRI completed by MR colonography. Radiol Med 118:323–338
Kataoka ML, Togashi K, Yamaoka T et al (2005) Posterior cul-de-sac obliteration associated with endometriosis: MR imaging evaluation. Radiology 234:815–823
Macario S, Chassang M, Novellas S et al (2012) The value of pelvic MRI in the diagnosis of posterior cul-de-sac obliteration in cases of deep pelvic endometriosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199:1410–1415
Chassang M, Novellas S, Bloch-Marcotte C et al (2010) Utility of vaginal and rectal contrast medium in MRI for the detection of deep pelvic endometriosis. Eur Radiol 20:1003–1010
Faccioli N, Foti G, Manfredi R et al (2010) Evaluation of colonic involvement in endometriosis: double-contrast barium enema vs. magnetic resonance imaging. Abdom Imaging 35:414–421
Scardapane A, Bettocchi S, Lorusso F et al (2011) Diagnosis of colorectal endometriosis: contribution of contrast enhanced MR-colonography. Eur Radiol 21:1553–1563
Hawass NE (1997) Comparing the sensitivities and specificities of two diagnostic procedures performed on the same group of patients. Br J Radiol 70:360–366
Chamie LP, Blasbalg R, Pereira RM, Warmbrand G, Serafini PC (2011) Findings of pelvic endometriosis at transvaginal US, MR imaging, and laparoscopy. Radiographics 31:E77–100
Anaf V, Simon P, Fayt I, Noel J (2000) Smooth muscles are frequent components of endometriotic lesions. Hum Reprod 15:767–771
Biscaldi E, Ferrero S, Remorgida V, Rollandi GA (2007) Bowel endometriosis: CT-enteroclysis. Abdom Imaging 32:441–450
Vimercati A, Achilarre MT, Scardapane A et al (2012) Accuracy of transvaginal sonography and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance-colonography for the presurgical staging of deep infiltrating endometriosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 40:592–603
Carbognin G, Guarise A, Minelli L et al (2004) Pelvic endometriosis: US and MRI features. Abdom Imaging 29:609–618
Zanardi R, Del Frate C, Zuiani C, Del Frate G, Bazzocchi M (2003) Staging of pelvic endometriosis using magnetic resonance imaging compared with the laparoscopic classification of the American Fertility Society: a prospective study. Radiol Med 105:326–338
Kinkel K, Frei KA, Balleyguier C, Chapron C (2006) Diagnosis of endometriosis with imaging: a review. Eur Radiol 16:285–298
Bazot M, Darai E (2005) Sonography and MR imaging for the assessment of deep pelvic endometriosis. J Minim Invasive Gynecol 12:178–185, 177, 186
Bazot M, Gasner A, Ballester M, Darai E (2011) Value of thin-section oblique axial T2-weighted magnetic resonance images to assess uterosacral ligament endometriosis. Hum Reprod 26:346–353
Acknowledgments
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Amato Antonio Stabile Ianora. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. Institutional Review Board approved the study. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Methodology: prospective diagnostic or prognostic study, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scardapane, A., Lorusso, F., Scioscia, M. et al. Standard high-resolution pelvic MRI vs. low-resolution pelvic MRI in the evaluation of deep infiltrating endometriosis. Eur Radiol 24, 2590–2596 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3297-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3297-4