Abstract
Objectives
To demonstrate the feasibility of using chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging to detect Parkinson’s disease (PD) in patients at 3 Tesla.
Methods
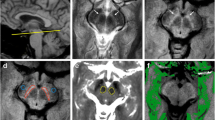
Twenty-seven PD patients (17 men and 10 women; age range, 54–77 years) and 22 age-matched normal controls (13 men and 9 women; age range, 55–73 years) were examined on a 3-Tesla MRI system. Magnetization transfer spectra with 31 different frequency offsets (−6 to 6 ppm) were acquired at two transverse slices of the head, including the basal ganglia and midbrain. One-way analysis of variance tests was used to compare the differences in CEST imaging signals between PD patients and normal controls.
Results
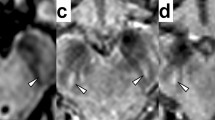
Total CEST signal between the offsets of 0 and 4 ppm in the substantia nigra was significantly lower in PD patients than in normal controls (P = 0.006), which could be associated with the loss of dopaminergic neurons. Protein-based CEST imaging signals at the offset of 3.5 ppm in the globus pallidus, putamen and caudate were significantly increased in PD patients, compared to normal controls (P < 0.001, P = 0.003, P < 0.001, respectively).
Conclusions
CEST imaging signals could potentially serve as imaging biomarkers to aid in the non-invasive molecular diagnosis of PD.
Key Points
• Total CEST signal in substantia nigra decreased in PD patients
• Protein-based CEST signals in basal ganglia increased in PD patients
• CEST could assist with the non-invasive molecular diagnosis for PD patients





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APT:
-
amide proton transfer
- CEST:
-
chemical exchange saturation transfer
- FLAIR:
-
fluid-attenuated inversion recovery
- H&Y:
-
Hoehn and Yahr
- MTRasym :
-
magnetization transfer ratio asymmetry
- NAWM:
-
normal-appearing white matter
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
References
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39:889–909
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:181–184
Tolosa E, Wenning G, Poewe W (2006) The diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 5:75–86
Michell AW, Lewis SJG, Foltynie T, Barker RA (2004) Biomarkers and Parkinson’s disease. Brain 127:1693–1705
Seppi K, Poewe W (2010) Brain magnetic resonance imaging techniques in the diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 20:29–55
Vernon AC, Ballard C, Modo M (2010) Neuroimaging for Lewy body disease: is the in vivo molecular imaging of alpha-synuclein neuropathology required and feasible? Brain Res Rev 65:28–55
Schocke MFH, Seppi K, Esterhammer R et al (2002) Diffusion-weighted MRI differentiates the Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy from PD. Neurology 58:575–580
Vaillancourt DE, Spraker MB, Prodoehl J et al (2009) High-resolution diffusion tensor imaging in the substantia nigra of de novo Parkinson disease. Neurology 72:1378–1384
Wang JJ, Lin WY, Lu CS et al (2011) Parkinson disease: diagnostic utility of diffusion kurtosis imaging. Radiology 261:210–217
Rossi M, Ruottinen H, Elovaara I et al (2010) Brain iron deposition and sequence characteristics in Parkinsonism comparison of SWI, T-2* Maps, T-2-weighted-, and FLAIR-SPACE. Investig Radiol 45:795–802
Haller S, Badoud S, Nguyen D et al (2013) Differentiation between Parkinson disease and other forms of parkinsonism using support vector machine analysis of susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI): initial results. Eur Radiol 23:12–19
Tambasco N, Pelliccioli GP, Chiarini P et al (2003) Magnetization transfer changes of grey and white matter in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroradiology 45:224–230
Anik Y, Iseri P, Demirci A, Komsuoglu S, Inan N (2007) Magnetization transfer ratio in early period of Parkinson disease. Acad Radiol 14:189–192
Morgen K, Sammer G, Weber L et al (2011) Structural brain abnormalities in patients with Parkinson disease: a comparative voxel-based analysis using T1-weighted MR imaging and magnetization transfer imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 32:2080–2086
Zhou J, van Zijl PC (2006) Chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging and spectroscopy. Progr NMR Spectr 48:109–136
Vinogradov E, Sherry AD, Lenkinski RE (2013) CEST: from basic principles to applications, challenges and opportunities. J Magn Reson 229:155–172
Zhou J, Payen J, Wilson DA, Traystman RJ, van Zijl PCM (2003) Using the amide proton signals of intracellular proteins and peptides to detect pH effects in MRI. Nat Med 9:1085–1090
Zhou J, Tryggestad E, Wen Z et al (2011) Differentiation between glioma and radiation necrosis using molecular magnetic resonance imaging of endogenous proteins and peptides. Nat Med 17:130–134
van Buchem MA, Tofts PS (2000) Magnetization transfer imaging. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 10:771–788
Henkelman RM, Stanisz GJ, Graham SJ (2001) Magnetization transfer in MRI: a review. NMR Biomed 14:57–64
Cai KJ, Haris M, Singh A et al (2012) Magnetic resonance imaging of glutamate. Nat Med 18:302–306
Kogan F, Singh A, Debrosse C et al (2013) Imaging of glutamate in the spinal cord using GluCEST. NeuroImage 77:262–267
Chan KWY, McMahon MT, Kato Y et al (2012) Natural D-glucose as a biodegradable MRI contrast agent for detecting cancer. Magn Reson Med 68:1764–1773
Walker-Samuel S, Ramasawmy R, Torrealdea F et al (2013) In vivo imaging of glucose uptake and metabolism in tumors. Nat Med. doi:10.1038/nm.3252
Ling W, Regatte RR, Navon G, Jerschow A (2008) Assessment of glycosaminoglycan concentration in vivo by chemical exchange-dependent saturation transfer (gagCEST). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:2266–2270
Jin T, Wang P, Zong XP, Kim SG (2012) Magnetic resonance imaging of the Amine-Proton EXchange (APEX) dependent contrast. NeuroImage 59:1218–1227
Jia G, Abaza R, Williams JD et al (2011) Amide proton transfer MR imaging of prostate cancer: a preliminary study. J Magn Reson Imaging 33:647–654
Dula AN, Arlinghaus LR, Dortch RD et al (2013) Amide proton transfer imaging of the breast at 3 T: establishing reproducibility and possible feasibility assessing chemotherapy response. Magn Reson Med 70:216–224
Zhou J, Zhu H, Lim M et al (2013) Three-dimensional amide proton transfer MR imaging of gliomas: initial experience and comparison with gadolinium enhancement. J Magn Reson Imaging 38:1119–1128
Sun PZ, Zhou J, Sun W, Huang J, van Zijl PCM (2007) Detection of the ischemic penumbra using pH-weighted MRI. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1129–1136
Zhao X, Wen Z, Huang F et al (2011) Saturation power dependence of amide proton transfer image contrasts in human brain tumors and strokes at 3 T. Magn Reson Med 66:1033–1041
Kirik D, Rosenblad C, Burer C et al (2002) Parkinson-like neurodegeneration induced by targeted overexpression of alpha-synuclein in the nigrostriatal system. J Neurosci 22:2780–2791
Hodaie M, Neimat JS, Lozano AM (2007) The dopaminergic nigrostriatal system and Parkinson’s disease: molecular events in development, disease, and cell death, and new therapeutic strategies. Neurosurgery 60:17–28
Braak H, Sandmann-Keil D, Gai W, Braak E (1999) Extensive axonal Lewy neurites in Parkinson’s disease: a novel pathological feature revealed by alpha-synuclein immunocytochemistry. Neurosci Lett 265:67–69
Tong JC, Wong H, Guttman M et al (2010) Brain alpha-synuclein accumulation in multiple system atrophy, Parkinson’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy: a comparative investigation. Brain 133:172–188
Wen Z, Hu S, Huang F et al (2010) MR imaging of high-grade brain tumors using endogenous protein and peptide-based contrast. NeuroImage 51:616–622
Zhou J, Blakeley JO, Hua J et al (2008) Practical data acquisition method for human brain tumor amide proton transfer (APT) imaging. Magn Reson Med 60:842–849
Zhou J, Hong X, Zhao X, Gao J-H, Yuan J (2013) APT-weighted and NOE-weighted image contrasts in glioma with different RF saturation powers based on magnetization transfer ratio asymmetry analyses. Magn Reson Med 70:320–327
Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2003) Molecular pathways of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:819–822
Peden AH, Ironside JW (2012) Molecular pathology in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Drug Targets 13:1548–1559
Keupp J, Baltes C, Harvey PR, van den Brink J (2011) Parallel RF transmission based MRI technique for highly sensitive detection of amide proton transfer in the human brain. Proc 19th Annual Meeting ISMRM, Montreal, Quebec, p 710
Acknowledgments
This study has received funding by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (812111480), the fund of the 12th Five-year Plan for National Science & Technology Supporting Program (2012BAI10B04) and the National Institutes of Health (R01EB009731, R01CA166171 and R01NS083425). The authors thank Dr. Michel Modo (University of Pittsburgh) and Dr. Yun Zhou and Dr. Arman Rahmim (Johns Hopkins University) for helpful discussion, and Ms. Mary McAllister for editorial assistance.
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Min Chen (Director of Department of Radiology). The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Institutional review board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Methodology: retrospective, diagnostic or prognostic study, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Peng, S., Wang, R. et al. Chemical exchange saturation transfer MR imaging of Parkinson’s disease at 3 Tesla. Eur Radiol 24, 2631–2639 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3241-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3241-7