Abstract
Objectives
To describe the characteristics of multifocal endosteal thickening in patients on bisphosphonate therapy.
Method
A retrospective study of 68 patients with atypical femoral fractures (as defined by ASBMR) whilst on bisphosphonate therapy was performed. Femoral radiographs were assessed for: focal endosteal thickening, number of lesions, lesion location, femoral bowing, periosteal beak and black line. Medical records were reviewed to obtain relevant clinical data.
Results
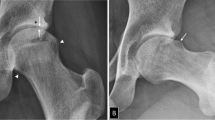
Forty-eight lesions with multifocal endosteal thickening were detected in seven patients (2 unilateral, 5 bilateral), affecting 11.8 % of femora. Location was mainly diaphyseal (95.8 %), upper (10.4 %), middle (58.3 %) and lower femur (31.3 %), involving the lateral (85.4 %), anterior (6.3 %), anterolateral (2.1 %) and posterior cortices (6.3 %). Femoral bowing was present in 85.7 %. Associated findings of a periosteal beak and/or a black line, seen in 14.6 %, were associated with increased fracture risk (100.0 % sensitivity, 93.2 % specificity).
Conclusions
Multifocal endosteal thickening is a new finding seen in patients with low bone mineral density on bisphosphonate therapy. They are rare, frequently bilateral, predominantly diaphyseal in location involving the lateral cortex and often associated with bowing. Caution is advised when seen in association with periosteal beak and/or black line because of a high rate of progression to complete fracture.
Key Points
• Multifocal endosteal thickening in the femur is a newly described radiographic finding.
• It is seen in patients with atypical femoral fractures whilst on bisphosphonate therapy.
• It typically involves the lateral cortex in the lower femur.
• A periosteal beak and/or black line may indicate an impending fracture.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shane E, Burr D, Ebeling PR et al (2010) Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: report of task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res 25:2267–2294
Park-Wyllie LY, Mamdani MM, Juurlink DN et al (2011) Bisphosphonate use and the risk of subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures in older women. JAMA 305:783–789
Rogers LF, Taljanovic M (2010) FDA statement on relationship between bisphosphonate use and atypical subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures: a considered opinion. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:563–566
Porrino JA, Kohl CA, Taljanovic M, Rogers LF (2010) Diagnosis of proximal femoral insufficiency fractures in patients receiving bisphosphonate therapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:1061–1064
Chan SS, Rosenberg ZS, Chan K, Capeci C (2010) Subtrochanteric femoral fractures in patients receiving long-term alendronate therapy: imaging features. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:1581–1586
Kwek EB, Goh SK, Koh JS, Png MA, Howe TS (2008) An emerging pattern of subtrochanteric stress fractures: a long-term complication of alendronate therapy? Injury 39:224–231
Goh SK, Yang KY, Koh JS et al (2007) Subtrochanteric insufficiency fractures in patients on alendronate therapy: a caution. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:349–353
Kwek EB, Koh JS, Howe TS (2008) More on atypical fractures of the femoral diaphysis. N Engl J Med 359:316–318
Koh JS, Goh SK, Png MA, Kwek EB, Howe TS (2010) Femoral cortical stress lesions in long-term bisphosphonate therapy: a herald of impending fracture? J Orthop Trauma 24:75–81
Koh JSB, Goh SK, Png MA et al (2011) Distribution of atypical fractures and cortical stress lesions in the femur: implications on pathophysiology. Singapore Med J 52:77–80
Png MA, Koh JS, Goh SK, Fook-Chong S, Howe TS (2012) Bisphosphonate-related femoral periosteal stress reactions: scoring system based on radiographic and MRI findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 198:869–877
Abrahamsen B, Eiken P, Eastell R (2009) Subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femur fractures in patients treated with alendronate: a register-based national cohort study. J Bone Miner Res 24:1095–1102
Abrahamsen B, Eiken P, Eastell R (2010) Cumulative alendronate dose and the long-term absolute risk of subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femur fractures: a register-based national cohort analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:5258–5265
Odvina CV, Zerwekh JE, Rao DS, Maalouf N, Gottschalk FA, Pak CY (2005) Severely suppressed bone turnover: a potential complication of alendronate therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:1294–1301
Seeger LL, Hewel KC, Yao L, Gold RH, Mirra JM, Chandnani VP, Eckardt JJ (1996) Ribbing disease (multiple diaphyseal sclerosis): imaging and differential diagnosis. Am J Roentgenol 167:689–694
Lo JC, Huang SY, Lee GA, Khandewal S, Provus J, Ettinger B, Gonzalez JR, Hui RL, Grimsrud CD (2012) Clinical correlates of atypical femoral fracture. Bone. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2012.02.632
Shimano MM, Volpon JB (2009) Biomechanics and structural adaptations of the rat femur after hindlimb suspension and treadmill running. Braz J Med Biol Res 42:330–338
Shellhart WC, Hardt AB, Moore RN, Erickson LC (1992) Effects of bisphosphonate treatment and mechanical loading on bone modeling in the rat tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res 278:253–259
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohan, P.C., Howe, T.S., Koh, J.S.B. et al. Radiographic features of multifocal endosteal thickening of the femur in patients on long-term bisphosphonate therapy. Eur Radiol 23, 222–227 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2587-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2587-y