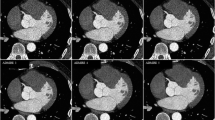
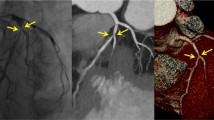
Abstract
Objectives
To compare image noise, image quality and diagnostic accuracy of coronary CT angiography (cCTA) using a novel iterative reconstruction algorithm versus traditional filtered back projection (FBP) and to estimate the potential for radiation dose savings.
Methods
Sixty five consecutive patients (48 men; 59.3 ± 7.7 years) prospectively underwent cCTA and coronary catheter angiography (CCA). Full radiation dose data, using all projections, were reconstructed with FBP. To simulate image acquisition at half the radiation dose, 50% of the projections were discarded from the raw data. The resulting half-dose data were reconstructed with sinogram-affirmed iterative reconstruction (SAFIRE). Full-dose FBP and half-dose iterative reconstructions were compared with regard to image noise and image quality, and their respective accuracy for stenosis detection was compared against CCA.
Results
Compared with full-dose FBP, half-dose iterative reconstructions showed significantly (p = 0.001 – p = 0.025) lower image noise and slightly higher image quality. Iterative reconstruction improved the accuracy of stenosis detection compared with FBP (per-patient: accuracy 96.9% vs. 93.8%, sensitivity 100% vs. 100%, specificity 94.6% vs. 89.2%, NPV 100% vs. 100%, PPV 93.3% vs. 87.5%).
Conclusions
Iterative reconstruction significantly reduces image noise without loss of diagnostic information and holds the potential for substantial radiation dose reduction from cCTA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulla J, Abildstrom SZ, Gotzsche O, Christensen E, Kober L, Torp-Pedersen C (2007) 64-multislice detector computed tomography coronary angiography as potential alternative to conventional coronary angiography: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Heart J 28:3042–3050
Bastarrika G, Lee YS, Huda W, Ruzsics B, Costello P, Schoepf UJ (2009) CT of coronary artery disease. Radiology 253:317–338
Budoff MJ, Dowe D, Jollis JG, Gitter M, Sutherland J, Halamert E, Scherer M, Bellinger R, Martin A, Benton R, Delago A, Min JK (2008) Diagnostic performance of 64-multidetector row coronary computed tomographic angiography for evaluation of coronary artery stenosis in individuals without known coronary artery disease: results from the prospective multicenter ACCURACY (Assessment by Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography of Individuals Undergoing Invasive Coronary Angiography) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 52:1724–1732
Johnson TR, Nikolaou K, Busch S, Leber AW, Becker A, Wintersperger BJ, Rist C, Knez A, Reiser MF, Becker CR (2007) Diagnostic accuracy of dual-source computed tomography in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease. Investig Radiol 42:684–691
Einstein AJ, Henzlova MJ, Rajagopalan S (2007) Estimating risk of cancer associated with radiation exposure from 64-slice computed tomography coronary angiography. JAMA 298:317–323
Hausleiter J, Meyer T, Hermann F, Hadamitzky M, Krebs M, Gerber TC, McCollough C, Martinoff S, Kastrati A, Schomig A, Achenbach S (2009) Estimated radiation dose associated with cardiac CT angiography. JAMA 301:500–507
Ziegler A, Kohler T, Proksa R (2007) Noise and resolution in images reconstructed with FBP and OSC algorithms for CT. Med Phys 34:585–598
Brooks RA, Di Chiro G (1975) Theory of image reconstruction in computed tomography. Radiology 117:561–572
Flicek KT, Hara AK, Silva AC, Wu Q, Peter MB, Johnson CD (2010) Reducing the radiation dose for CT colonography using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction: a pilot study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:126–131
Gosling O, Loader R, Venables P, Roobottom C, Rowles N, Bellenger N, Morgan-Hughes G (2010) A comparison of radiation doses between state-of-the-art multislice CT coronary angiography with iterative reconstruction, multislice CT coronary angiography with standard filtered back-projection and invasive diagnostic coronary angiography. Heart 96:922–926
Hara AK, Paden RG, Silva AC, Kujak JL, Lawder HJ, Pavlicek W (2009) Iterative reconstruction technique for reducing body radiation dose at CT: feasibility study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193:764–771
Leipsic J, Labounty TM, Heilbron B, Min JK, Mancini GB, Lin FY, Taylor C, Dunning A, Earls JP (2010) Estimated radiation dose reduction using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction in coronary CT angiography: the ERASIR study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:655–660
Pontana F, Duhamel A, Pagniez J, Flohr T, Faivre JB, Hachulla AL, Remy J, Remy-Jardin M (2010) Chest computed tomography using iterative reconstruction vs filtered back projection (Part 2): image quality of low-dose CT examinations in 80 patients. Eur Radiol 21:636–643
Pontana F, Pagniez J, Flohr T, Faivre JB, Duhamel A, Remy J, Remy-Jardin M (2010) Chest computed tomography using iterative reconstruction vs filtered back projection (Part 1): evaluation of image noise reduction in 32 patients. Eur Radiol 21:627–635
Prakash P, Kalra MK, Ackman JB, Digumarthy SR, Hsieh J, Do S, Shepard JA, Gilman MD (2010) Diffuse lung disease: CT of the chest with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique. Radiology 256:261–269
Prakash P, Kalra MK, Kambadakone AK, Pien H, Hsieh J, Blake MA, Sahani DV (2010) Reducing abdominal CT radiation dose with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique. Investig Radiol 45:202–210
Flohr TG, McCollough CH, Bruder H, Petersilka M, Gruber K, Suss C, Grasruck M, Stierstorfer K, Krauss B, Raupach R, Primak AN, Kuttner A, Achenbach S, Becker C, Kopp A, Ohnesorge BM (2006) First performance evaluation of a dual-source CT (DSCT) system. Eur Radiol 16:256–268
McCollough CH, Primak AN, Saba O, Bruder H, Stierstorfer K, Raupach R, Suess C, Schmidt B, Ohnesorge BM, Flohr TG (2007) Dose performance of a 64-channel dual-source CT scanner. Radiology 243:775–784
McCollough CH, Schmidt B, Yu L, Primak A, Ulzheimer S, Bruder H, Flohr TG (2008) Measurement of temporal resolution in dual source CT. Med Phys 35:764–768
Leschka S, Stinn B, Schmid F, Schultes B, Thurnheer M, Baumueller S, Stolzmann P, Scheffel H, Flohr TG, Wildermuth S, Alkadhi H (2009) Dual source CT coronary angiography in severely obese patients: trading off temporal resolution and image noise. Investig Radiol 44:720–727
Barrett HH, Swindell W (eds) (1996) Radiological imaging—the theory of image formation, detection and processing, 1st edn. Academic Press, Harcourt Brace & Company, Orlando.
Kijewski MF, Judy PF (1987) The noise power spectrum of CT images. Phys Med Biol 32:565–575
Austen WG, Edwards JE, Frye RL, Gensini GG, Gott VL, Griffith LS, McGoon DC, Murphy ML, Roe BB (1975) A reporting system on patients evaluated for coronary artery disease. Report of the Ad Hoc Committee for Grading of Coronary Artery Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Surgery, American Heart Association. Circulation 51:5–40
Bongartz G, Goldung SJ, Jurik AG et al (2004) 2004 CT quality criteria. Luxembourg Luxembourg: European Commission, Brussels Available via http://www.msct.eu/CT_Quality_Criteria.htm. Accessed 28 Dec 2010.
Hamon M, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Malagutti P, Agostoni P, Morello R, Valgimigli M (2006) Diagnostic performance of multislice spiral computed tomography of coronary arteries as compared with conventional invasive coronary angiography: a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 48:1896–1910
Rist C, Johnson TR, Muller-Starck J, Arnoldi E, Saam T, Becker A, Leber AW, Wintersperger BJ, Becker CR, Reiser MF, Nikolaou K (2009) Noninvasive coronary angiography using dual-source computed tomography in patients with atrial fibrillation. Investig Radiol 44:159–167
Henzler T, Hanley M, Arnoldi E, Bastarrika G, Schoepf UJ, Becker HC (2010) Practical strategies for low radiation dose cardiac computed tomography. J Thorac Imaging 25:213–220
Hausleiter J, Meyer T, Hadamitzky M, Huber E, Zankl M, Martinoff S, Kastrati A, Schomig A (2006) Radiation dose estimates from cardiac multislice computed tomography in daily practice: impact of different scanning protocols on effective dose estimates. Circulation 113:1305–1310
Leschka S, Stolzmann P, Schmid FT, Scheffel H, Stinn B, Marincek B, Alkadhi H, Wildermuth S (2008) Low kilovoltage cardiac dual-source CT: attenuation, noise, and radiation dose. Eur Radiol 18:1809–1817
D’Agostino AG, Remy-Jardin M, Khalil C, Delannoy-Deken V, Flohr T, Duhamel A, Remy J (2006) Low-dose ECG-gated 64-slices helical CT angiography of the chest: evaluation of image quality in 105 patients. Eur Radiol 16:2137–2146
Earls JP, Berman EL, Urban BA, Curry CA, Lane JL, Jennings RS, McCulloch CC, Hsieh J, Londt JH (2008) Prospectively gated transverse coronary CT angiography versus retrospectively gated helical technique: improved image quality and reduced radiation dose. Radiology 246:742–753
Achenbach S, Marwan M, Ropers D, Schepis T, Pflederer T, Anders K, Kuettner A, Daniel WG, Uder M, Lell MM (2010) Coronary computed tomography angiography with a consistent dose below 1 mSv using prospectively electrocardiogram-triggered high-pitch spiral acquisition. Eur Heart J 31:340–346
Kalender W (2000) Computed tomography: fundamentals, system technology, image quality, applications, 1st edn. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Raff GL, Gallagher MJ, O’Neill WW, Goldstein JA (2005) Diagnostic accuracy of noninvasive coronary angiography using 64-slice spiral computed tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:552–557
Kubo T, Lin PJ, Stiller W, Takahashi M, Kauczor HU, Ohno Y, Hatabu H (2008) Radiation dose reduction in chest CT: a review. AJR Am J Roentgenol 190:335–343
Mayo JR, Leipsic JA (2009) Radiation dose in cardiac CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192:646–653
Acknowledgement
UJS is a consultant for and receives research support from Bayer-Schering, Bracco, General Electric, Medrad, and Siemens. TA, SV, and BS are employees of Siemens Healthcare. The other authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
This study was supported in part by the Research and Development Program of the Department of Veterans Affairs. The contents do not represent the views of the Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moscariello, A., Takx, R.A.P., Schoepf, U.J. et al. Coronary CT angiography: image quality, diagnostic accuracy, and potential for radiation dose reduction using a novel iterative image reconstruction technique—comparison with traditional filtered back projection. Eur Radiol 21, 2130–2138 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2164-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2164-9