Abstract
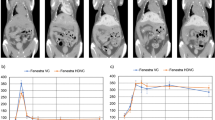
We sought to establish and characterize a mouse liver tumor model as a platform for preclinical assessment of new diagnostics and therapeutics. Radiation-induced fibrosarcoma (RIF-1) was intrahepatically implanted in 27 C3H/Km mice. Serial in vivo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with a clinical 1.5-T-magnet was performed using T1- (T1WI), T2- (T2WI), and diffusion-weighted sequences (DWI), dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI), and contrast-enhanced T1WI, and validated with postmortem microangiography and histopathology. Implantation procedure succeeded in 25 mice with 2 deaths from overdosed anesthesia or hypothermia. RIF-1 grew in 21 mice with volume doubling time of 2.55±0.88 days and final size of 216.2±150.4 mm3 at day 14. Three mice were found without tumor growth and one only with abdominal seeding. The intrahepatic RIF-1 was hypervascularized with negligible necrosis as shown on MRI, microangiography and histology. On DCE-MRI, maximal initial slope of contrast-time curve and volume transfer constant per unit volume of tissue, K, differed between the tumor and liver with only the former significantly lower in the tumor than in the liver (P<0.05). Liver implantation of RIF-1 in mice proves a feasible and reproducible model and appears promising for use to screen new diagnostics and therapeutics under noninvasive monitoring even with a clinical MRI system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hann B, Balmain A (2001) Building ‘validated’ mouse models of human cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:778–784
Kerbel RS (1998) What is the optimal rodent model for anti-tumor drug testing? Cancer Metastasis Rev 17:301–304
Bhujwalla ZM, Tozer GM, Field SB et al (1990) The combined measurement of blood flow and metabolism in RIF-1 tumours in vivo. A study using H2 flow and 31P NMR spectroscopy. NMR Biomed 3:178–183
Chen HH, Le Visage C, Qiu B et al (2005) MR imaging of biodegradable polymeric microparticles: a potential method of monitoring local drug delivery. Magn Reson Med 53:614–620
Kim S-G, Ackerman JJH (1988) Quantitative determination of tumor blood flow and perfusion via deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in mice. Cancer Res 48:3449–3453
Robinson SP, van den Boogaart A, Maxwell RJ (1998) 31P-magnetic resonance spectroscopy and 2H-magnetic resonance imaging studies of a panel of early-generation transplanted murine tumour models. Br J Cancer 77:1752–1760
Tailor DR, Poptani H, Glickson JD et al (2003) High-resolution assessment of blood flow in murine RIF-1 tumors by monitoring uptake of H2 17O with proton T1ρ-weighted imaging. Magn Reson Med 49:1–6
Twentyman PR, Brown JM, Gray JW et al (1980) A new mouse tumor model system (RIF-1) for comparison of end-point studies. J Natl Cancer Inst 64:595–604
Chen F, Sun X, De Keyzer F et al (2006) Liver tumor model with implanted rhabdomyosarcoma in rats: MR imaging, microangiography, and histopathologic analysis. Radiology 239:554–562
Heijstek MW, Kranenburg O, Borel Rinkes IH (2005) Mouse models of colorectal cancer and liver metastases. Dig Surg 22:16–25
Rusciano D, Lorenzoni P, Burger M (1994) Murine models of liver metastasis. Invasion Metastasis 14:349–361
Madhu B, Waterton JC, Griffiths JR (2006) The response of RIF-1 fibrosarcomas to the vascular-disrupting agent ZD6126 assessed by in vivo and ex vivo 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neoplasia 8:560–567
Takehara Y, Sakahara H, Masunaga H (2002) Assessment of a potential tumor-seeking manganese metalloporphyrin contrast agent in a mouse model. Magn Reson Med 47:549–553
Nomura K, Miyagawa S, Harada H (1998) Relationship between doubling time of liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma and residual primary cancer. Dig Surg 15:21–24
Tofts PS, Berkowitz BA (1993) Rapid measurement of capillary permeability using the early part of the dynamic Gd-DTPA MRI enhancement curve. J Magn Reson B 102:129–136
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F, Vandecaveye V (2005) Effect of vascular targeting agent in rat tumor model: dynamic contrast-enhanced versus diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 237:492–499
Tofts PS (1997) Modeling tracer kinetics in dynamic Gd-DTPA MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 7:91–101
Pandharipande PV, Krinsky GA, Rusinek H et al (2005) Perfusion imaging of the liver: Current challenges and future goals. Radiology 234:661–673
Liu Y, Matsui O (2007) Changes of intratumoral microvessels and blood perfusion during establishment of hepatic metastases in mice. Radiology 243:386–395
Veenendaal LM, van Hillegersberg R, Smakman N et al (2006) Synergistic effect of interstitial laser coagulation and doxorubicin in a murine tumor recurrence model of solitary colorectal liver metastasis. Ann Surg Oncol 13:168–175
Van de Putte M, Wang H, Chen F, de Witte P, Ni Y (2008) Hypericin as a marker for determination of tissue viability after intratumoral ethanol injection in a murine liver tumor model. Academic Radiology 15(1):107–113
Van de Putte M, Wang H, Chen F, de Witte P, Ni Y (2008) Hypericin as a marker for determination of tissue viability after radiofrequency ablation in a murine liver tumor model. Oncology Reports 19, in press
Bock NA, Konyer NB, Henkelman RM (2003) Multiple-mouse MRI. Magn Reson Med 49(1):158–167
Xu S, Gade TP, Matei C et al (2003) In vivo multiple-mouse imaging at 1.5 T. Magn Reson Med 49(3):551–557
Herneth AM, Guccione S, Bednarski M (2003) Apparent Diffusion Coefficient: a quantitative parameter for in vivo tumor characterization. Eur J Radiol 45:208–213
Crokart N, Jordan BF, Baudelet C et al (2005) Early reoxygenation in tumors after irradiation: Determining factors and consequences for radiotherapy regimens using daily multiple fractions. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:901–910
Collins DJ, Padhani AR (2004) Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of tumor perfusion. Approaches and biomedical challenges. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag 23:65–83
Tofts PS, Brix G, Buckley DL (1999) Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: standardized quantities and symbols. J Magn Reson Imaging 10:223–232
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the grants awarded by Fonds voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek-Vlaanderen (FWO Vlaanderen) Impulsfinanciering project (ZWAP/05/018), Geconcerteerde Onderzoeksactie (GOA) of the Flemish Government, OT project (OT/06/70) MoSAIC, the K.U. Leuven Molecular Small Animal Imaging Center (KUL EF/05/08), and a EU project Asia-Link CfP 2006- EuropeAid/123738/C/ACT/Multi–proposal no. 128–498/111.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Van de Putte, M., Chen, F. et al. Murine liver implantation of radiation-induced fibrosarcoma: characterization with MR imaging, microangiography and histopathology. Eur Radiol 18, 1422–1430 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0904-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0904-2