Abstract
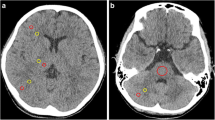
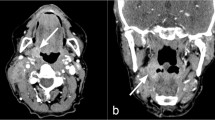
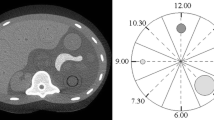
Subjective and objective image quality (IQ) criteria, radiation doses, and acquisition times were compared using incremental monoslice, incremental multislice, and helical multislice acquisition techniques for routine unenhanced brain computed tomography (CT). Twenty-four patients were examined by two techniques in the same imaging session using a 16-row CT system equipped with 0.75-width detectors. Contiguous “native” 3-mm-thick slices were reconstructed for all acquisitions from four detectors for each slice (4×0.75 mm), with one channel available per detector. Two protocols were tailored to compare: (1) one-slice vs four-slice incremental images; (2) incremental vs helical four-slice images. Two trained observers independently scored 12 subjective items of IQ. Preference for the technique was assessed by one-tailed t test and the interobserver variation by two-tailed t test. The two observers gave very close IQ scores for the three techniques without significant interobserver variations. Measured IQ parameters failed to reveal any difference between techniques, and an approximate half radiation dose reduction was obtained by using the full 16-row configuration. Acquisition times were cumulatively shortened by using the multislice and the helical modality.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker HL Jr, Campbell JK, Houser OW, Reese DF (1975) Early experience with the EMI scanner for study of the brain. Radiology 116:327–333
Bradley WG Jr, Waluch V, Yadley RA, Wycoff RR (1984) Comparison of CT and MR in 400 patients with suspected disease of the brain and of the spinal cord. Radiology 152:695–703
Kalender WA, Seissler W, Klotz E, Vock P (1990) Spiral volumetric CT with single-breath-hold technique, continuous transport and continuous scanner rotation. Radiology 176:181–183
Berland LL, Smith JK (1998) Multidetector array: once again, technology creates new opportunities. Radiology 209:327–329
Kuntz R, Skalej M, Stefanou A (1998) Image quality of spiral CT versus conventional CT in routine brain imaging. Eur J Radiol 26:235–240
Bahner ML, Reth W, Zuna I, Engenhart-Cabillic R, Van Kaick G (1998) Spiral CT versus incremental CT: is spiral CT superior in imaging of the brain? Eur Radiol 8:416–420
Ertl-Wagner BB, Hoffman RT, Bruning R, Herrrmann K, Snyder B, Blume JD, Reiser MF (2004) Multidetector row CT angiography of the brain at various kilovoltage settings. Radiology 231:528–535
Staniszewska MA, Obrzut M, Rybka K (2005) Phantom studies for possible dose reduction in CT head procedures. Radiat Prot Dosim 114:326–331
Gundogdu S, Mahmutyazicioglu K, Ozdemir H, Savranlar A, Asil K (2005) Assessment of image quality of a standard and three dose-reducing protocols in adult cranial CT. Eur Radiol 15:1959–68
Mulkens TH, Bellinck PB, Baeyaert M, Ghysen D, Van Dijck X, Mussen E, Venstermans C, Termote JL (2005). Use of an automatic exposure control mechanism for dose optimization in multidetector row CT examinations: clinical evaluation. Radiology 237:213–223
European Commission, Brussels (1998). Quality criteria for computed tomography. EC Working Document Report EUR 16262
AAPM Report 31 (1990) Standardized methods for measuring diagnostic X-rayexposures. Association of Physicists in Medicine
ICRU Report 74 (2006) Patient dosimetry for X-rays used in medical imaging (in press)
Huda W, Lieberman KA, Chang J, Roskopf ML (2004) Patient size and X-ray technique factors in head computed tomography examinations. I. Radiation doses. Med Phys 31:588–594
Jones TR, Kaplan RT, Lane B, Atlas SW, Rubin GD (2001) Single- versus multi-detector row CT of the brain: quality assessment. Radiology 2001;219:750–755
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Stefaan Vynckier and Jean-Marc Denis, Medical Physics group of the Radiation Oncology Department of our institution, who performed and calculated IQ measurements on phantoms, and to Gregory Delrue, technologist of the same department, who prepared them.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernalsteen, D., Cosnard, G., Robert, A. et al. Suitability of helical multislice acquisition technique for routine unenhanced brain CT: an image quality study using a 16-row detector configuration. Eur Radiol 17, 975–982 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0360-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0360-9