Abstract
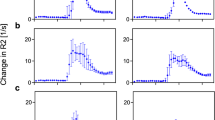
This study analyzed the T2* effect of extracellularly distributed gadolinium contrast agents in arterial blood during tumor studies using T1-weighted sequences at high field strength. A saturation-prepared dual echo sequence with echo times of 1.5 and 3.5 ms was employed at 3 T to simultaneously characterize T1 and T2* of arterial blood during bolus administration of Gd-DTPA in 28 patients with body tumors. T2* effect and T1 effect of Gd-DTPA on image intensity of whole blood were calibrated in human blood samples with different concentrations of contrast agent. T2* was used to estimate concentration near the peak of the bolus. T1 was used to measure lower concentrations when T2* was not significant. T2* was measurable on calibration curves for Gd-DTPA concentrations higher than 4 mM. This concentration was exceeded in 18 patients. The mean signal intensity reduction because of T2* effect was estimated at 22±14% of the T2* compensated signal. Using T2* measurements reduced underestimations of peak arterial Gd-DTPA concentration (59±38%) and overestimation of permeability Ktrans (58%). The T2* effect of gadolinium contrast agents should therefore be accounted for when performing tumors study with T1-weighted sequences at high field strength.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tofts PS, Brix G, Buckley DL, Evelhoch JL, Henderson E, Knopp M, Larsson HBW, Lee TY, Mayr NA, Parker GJM, Port RE, Taylor J, Weisskoff RM (1999) Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced T-1-weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: standardized quantities and symbols. J Magn Reson Imaging 10:223–232
Larsson HBW, Stubgaard M, Sondergaard L, Henriksen O (1994) In-vivo quantification of the unidirectional influx constant for Gd-DTPA diffusion across the myocardial capillaries with MR-imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 4:433–440
Brasch R, Turetschek K (2000) MRI characterization of tumors and grading angiogenesis using macromolecular contrast media: status report. Eur J Radiol 34:148–155
FritzHansen T, Rostrup E, Larsson HBW, Sondergaard L, Ring P, Henriksen O (1996) Measurement of the arterial concentration of Gd-DTPA using MRI: a step toward quantitative perfusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 36:225–231
Fritz-Hansen T, Rostrup E, Ring PB, Larsson HBW (1998) Quantification of gadolinium-DTPA concentrations for different inversion times using an IR-turbo flash pulse sequence: A study on optimizing multislice perfusion imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 16:893–899
Osch MJP van, Vonken E, Viergever MA, van der Grond J, Bakker CJG (2003) Measuring the arterial input function with gradient echo sequences. Magn Reson Med 49:1067–1076
Alsop D, Watkins R, Greenman R, Schenck J, Lenkinski R (2001) In vivo mapping of B1 uniformity produced by a whole body 3 T RF coil. In: Alsop D, Watkins R, Greenman R, Schenck J, Lenkinski R (eds) Proceedings of the 9th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Glasgow, p 1094
azelaire CM de, Duhamel GD, Rofsky NM, Alsop DC (2004) MR imaging relaxation times of abdominal and pelvic tissues measured in vivo at 3.0 T: preliminary results. Radiology 230:652–659
Kuperman VY, Alley MT (1999) Differentiation between the effects of T-1 and T-2* shortening in contrast-enhanced MRI of the breast. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:172–176
Tofts PS, Kermode AG (1991) Measurement of the blood-brain-barrier permeability and leakage space using dynamic MR imaging. I. Fundamental concepts. Magn Reson Med 17:357–367
Schick F (2005) Whole-body MRI at high field: technical limits and clinical potential. Eur Radiol 15:946–959
Ye FQ, Allen PS (1995) Relaxation enhancement of the transverse magnetization of water protons in paramagnetic suspensions of red-blood-cells. Magn Reson Med 34:713–720
Daldrup-Link HE, Brasch RC (2003) Macromolecular contrast agents for MR mammography: current status. Eur Radiol 13:354–365
Osch MJ van, Vonken EJ, Bakker CJ, Viergever MA (2001) Correcting partial volume artifacts of the arterial input function in quantitative cerebral perfusion MRI. Magn Reson Med 45:477–485
Miyati T, Banno T, Mase M, Kasai H, Shundo H, Imazawa M, Ohba S (1997) Dual dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 7:230–235
Uematsu H, Maeda M, Sadato N, Matsuda T, Ishimori Y, Koshimoto Y, Yamada H, Kimura H, Kawamura Y, Hayashi N, Yonekura Y, Ishii Y (2000) Vascular permeability: quantitative measurement with double-echo dynamic MR imaging—theory and clinical application. Radiology 214:912–917
Vonken E, van Osch MJP, Bakker CJG, Viergever MA (2000) Simultaneous quantitative cerebral perfusion and Gd-DTPA extravasation measurement with dual-echo dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI. Magn Reson Med 43:820–827
Just N, D’Arcy JA, Collins DJ, Leach MO (2002) In-vivo measurement of the arterial input function using a T2*-weighted image acquired with a dual gradient echo sequence. In: Just N, D’Arcy JA, Collins DJ Leach MO (eds) Proceedings of the 10th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Honolulu, p 2128
Uematsu H, Maeda M (2005) Double-echo perfusion-weighted MR imaging: basic concepts and application in brain tumors for the assessment of tumor blood volume and vascular permeability. Eur Radiol (14 June, epub ahead of print)
Just N, Koh D, Collins DJ, Leach MO (2003) Gd-DTPA Calibration curves in human blood as a function of haematocrit for the quantification of the arterial input function in femoral arteries. In: Just N, Koh D, Collins DJ, Leach MO (eds) Proceedings of the 11th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Toronto, p 1257
Yablonskiy DA, Haacke EM (1994) Theory of NMR signal behavior in magnetically inhomogeneous tissues—the static dephasing regime. Magn Reson Med 32:749–763
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Bazelaire, C., Rofsky, N.M., Duhamel, G. et al. Combined T2* and T1 measurements for improved perfusion and permeability studies in high field using dynamic contrast enhancement. Eur Radiol 16, 2083–2091 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0198-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0198-1