Abstract
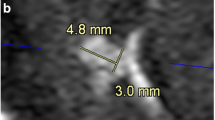
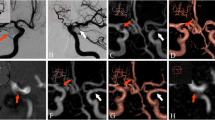
The sensitivities and specificities of three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography (3D-TOF MRA) and 3D digital subtraction angiography (3D-DSA) were compared for evaluation of cerebral aneurysms after endosaccular packing with Guglielmi detachable coils (GDCs). Thirty-three patients with 33 aneurysms were included in this prospective study. 3D-TOF MRA and 3D-DSA were performed in the same week on all patients. Maximal intensity projection (MIP) and 3D reconstructed MRA images were compared with 3D-DSA images. The diameters of residual/recurrent aneurysms detected on 3D-DSA were calculated on a workstation. In 3 (9%) of 33 aneurysms, 3D-TOF MRA did not provide reliable information due to significant susceptibility artifacts on MRA. The sensitivity and specificity rates of MRA were 72.7 and 90.9%, respectively, for the diagnosis of residual/recurrent aneurysm. The diameters of residual/recurrent aneurysms that could not be detected by MRA were significantly smaller than those of detected aneurysms (mean 1.1 vs mean 2.3 mm). In one aneurysm of the anterior communicating artery (ACoA), the relationship between the residual aneurysm and the ACoA was more evident on MRA than DSA images. MRA can detect the recurrent/residual lumen of aneurysms treated with GDCs of up to at least 1.8 mm in diameter. 3D-TOF MRA is useful for follow-up of intracranial aneurysms treated with GDCs, and could partly replace DSA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guglielmi G, Vinuela F, Sepetka I, Macellari F (1991) Electrothrombosis of saccular aneurysms via endovascular approach. I. Electrochemical basis, technique and experimental results. J Neurosurg 75:1–7
Guglielmi G, Vinuela F, Dion J, Duckwiler G (1991) Electrothrombosis of saccular aneurysms via endovascular approach. II. Preliminary clinical experience. J Neurosurg 75:8–14
Guglielmi G, Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Dion J, Lylyk P, Berenstein A, Strother C, Graves V, Halbach V, Nichols D et al (1992) Endovascular treatment of posterior circulation aneurysms by electrothrombosis using detachable coils. J Neurosurg 77:515–524
Richling B, Bavinski G, Gross C, Gruber A, Killer M (1995) Early clinical outcome of patients with ruptured cerebral aneurysms treated by endovascular (GDC) or microsurgical techniques: a single center experience. Intervent Neuroradiol 1:19–27
Graves VB, Strother CM, Duff TA, Perl J (1995) Early treatment of ruptured aneurysms with Guglielmi detachable coils: effect and subsequent rebleeding. Neurosurgery 37:640–648
Fernandez ZA, Guglielmi G, Vinuela F, Duckwiller GR (1994) Endovascular occlusion of intracranial aneurysms with electrically detachable coils: correlation of aneurysm neck size and treatment results. Am J Neuroradiol 15:815–820
Gobin Y, Vinuela F, Gurian J, Guglielmi G, Duckwiler GR, Massoud TF, Martin NA (1996) Treatment of large and giant fusiform intracranial aneurysms with Guglielmi detachable coils. J Neurosurg 84:55–62
Vinuela F, Duckwiller G, Mawad M (1997) Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of acute intracranial aneurysm: perioperative anatomical and clinical outcome in 403 patients. J Neurosurg 86:475–482
Cognard C, Weill A, Castaings L, Rey A, Moret J (1998) Intracranial berry aneurysms: angiographic and clinical results after endovascular treatment. Radiology 206:499–510
Cognard C, Weill A, Spelle L, Piotin M, Castaings L, Rey A, Moret J (1999) Long-term angiographic follow-up of 169 intracranial berry aneurysms occluded with detachable coils. Radiology 212:348–356
Hankey GJ, Warlow CP, Sellar RJ (1990) Cerebral angiographic risk in mild cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 21:209–222
Grzyska U, Freitag J, Zeumer H (1990) Selective arterial intracerebral DSA: complication rate and control of risk factors. Neuroradiology 32:296–299
White PM, Wardlaw JM, Easton V (2000) Can noninvasive imaging accurately depict intracranial aneurysms? A systematic review. Radiology 217:361–370
Stock KW, Radue EW, Jacob AL, Bao XS, Steinbrich W (1995) Intracranial arteries: prospective blinded comparative study of MR angiography and DSA in 50 patients. Radiology 195:451–456
Hartman J, Nguyen T, Larsen D, Teitelbaum GP (1997) MR artifacts, heat production, and ferromagnetism of Guglielmi detachable coils. Am J Neuroradiol 18:497–501
Derdeyn CP, Graves VB, Turski PA, Masaryk AM, Strother CM (1997) MR angiography of saccular aneurysms after treatment with Guglielmi detachable coils: preliminary experience. Am J Neuroradiol 18:279–286
Kahara VJ, Seppanen SK, Ryymin PS, Mattila P, Kuurne T, Laasonen EM (1998) MR angiography with three-dimensional time-of-flight and targeted maximum-intensity-projection reconstructions in the follow-up of intracranial aneurysms embolized with Guglielmi detachable coils. Am J Neuroradiol 20:1470–1475
Brunereau L, Cottier JP, Sonier CB, Medioni B, Bertrand P, Rouleau P, Sirinelli D, Herbreteau D (1999) Prospective evaluation of time-of-flight MR angiography in the follow-up of intracranial saccular aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. J Comput Assist Tomogr 23:216–223
Weber W, Yousry TA, Felber SR, Henkes H, Nahser HC, Roer N, Kuhne D (2001) Noninvasive follow-up of GDC-treated saccular aneurysms by MR angiography. Eur Radiol 11:1792–1797
Gonner F, Heid O, Remonda L, Nicoli G, Baumgartner RW, Godoy N, Schroth G (1998) MR angiography with ultrashort echo time in cerebral aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. Am J Neuroradiol 19:1324–1328
Boulin A, Pierot L (2001) Follow-up of intracranial aneurysms treated with detachable coils: comparison of gadolinium-enhanced 3D time-of-flight MR angiography and digital subtraction angiography. Radiology 219:108–113
Anzalone N, Righi C, Simionato F, Scomazzoni F, Pagani G, Calori G, Santino P, Scotti G (2000) Three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography in the evaluation of intracranial aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. Am J Neuroradiol 21:746–752
Tanoue S, Kiyosue H, Kenai H, Nakamura T, Yamashita M, Mori H (2000) Three-dimensional reconstructed images after rotational angiography in the evaluation of intracranial aneurysms: surgical correlation. Neurosurgery 47:866–871
Anxionnat R, Bracard S, Ducrocq X, Trousset Y, Launary L, Kerrien E, Braun M, Valliant R, Scomazzoni F, Lebedinsky A, Picard L (2001) Intracranial aneurysms: clinical value of 3D digital subtraction angiography in the therapeutic decision and endovascular treatment. Radiology 218:799–808
Brilstra EH, Rinkel GJE, van der Graaf Y, van Rooij WJ, Algra A (1999) Treatment of intracranial aneurysms by embolization with coils: a systematic review. Stroke 30:470–476
Albuquerque FC, Spetzler RF, Zabramski JM, McDougall CG (2001) Effects of three-dimensional angiography on the coiling of cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery 51:597–606
Kiyosue H, Okahara M, Tanoue S, Nakamura T, Nagatomi H, Mori H (2002) Detection of the residual lumen of intracranial aneurysms immediately after coil embolization by three-dimensional disital subtraction angiographic virtual endoscopic imaging. Neurosurgery 50:476–485
Byrne JV, Sohn MJ, Molyneux AJ, Chir B (1999) Five-year experience in using coil embolization for ruptured intracranial aneurysms: outcomes and incidence of late rebleeding. Am J Neuroradiol 90:656–663
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okahara, M., Kiyosue, H., Hori, Y. et al. Three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography for evaluation of intracranial aneurysms after endosaccular packing with Guglielmi detachable coils: comparison with 3D digital subtraction angiography. Eur Radiol 14, 1162–1168 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2277-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2277-5