Abstract
Key message
We found that the apple wax related gene played a role in changing plant epidermal permeability and enhancing plant resistance to drought stress by increasing wax accumulation.
Abstract
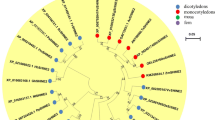
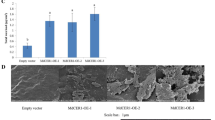
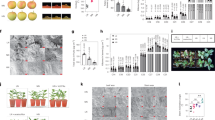
The content and composition of epidermal wax in plants are affected by genetic and environmental factors. The KCS gene encodes the β-ketoalionyl-CoA synthetase, which is a rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs). In this study, we identified the MdKCS2 gene from apple as a homolog of Arabidopsis AtKCS2. The KCS protein is localized on the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. MdKCS2 exhibited the highest expression in apple pericarp, and was induced by abiotic stresses, such as drought and salt. Transgenic analysis indicated that the MdKCS2 improved the resistance to abiotic stress in apple calli. Ectopic expression of MdKCS2 in Arabidopsis increased the content of wax in leaves and stems, changed the permeability of cuticle of leaves, and enhanced plant drought resistance.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
An JP, Li R, Qu FJ, You CX, Wang XF, Hao YJ (2017) Ectopic expression of an apple cytochrome P450 gene MdCYPM1 negatively regulates plant photomorphogenesis and stress response in Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 483(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.026
An JP, Zhang XW, Xu RR, You CX, Wang XF, Hao YJ (2018) Apple MdERF4 negatively regulates salt tolerance by inhibiting MdERF3 transcription. Plant Sci 276:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.08.017
An JP, Wang XF, Espley RV, Lin-Wang K, Bi SQ, You CX, Hao YJ (2020) An Apple B-Box Protein MdBBX37 modulates anthocyanin biosynthesis and hypocotyl elongation synergistically with MdMYBs and MdHY5. Plant Cell Physiol 61(1):130–143. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcz185
Beaudoin F, Wu X, Li F, Haslam RP, Markham JE, Zheng H, Napier JA, Kunst L (2009) Functional characterization of the Arabidopsis beta-ketoacyl-coenzyme A reductase candidates of the fatty acid elongase. Plant Physiol 150(3):1174–1191. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.137497
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16(6):735–743. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00343.x
Denic V, Weissman JS (2007) A molecular caliper mechanism for determining very long-chain fatty acid length. Cell 130(4):663–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.031
Franke R, Hofer R, Briesen I, Emsermann M, Efremova N, Yephremov A, Schreiber L (2009) The DAISY gene from Arabidopsis encodes a fatty acid elongase condensing enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of aliphatic suberin in roots and the chalaza-micropyle region of seeds. Plant J 57(1):80–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03674.x
Haslam TM, Kunst L (2013) Extending the story of very-long-chain fatty acid elongation. Plant Sci 210:93–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.05.008
Hooker TS, Millar AA, Kunst L (2002) Significance of the expression of the CER6 condensing enzyme for cuticular wax production in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 129(4):1568–1580. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.003707
James DW Jr, Lim E, Keller J, Plooy I, Ralston E, Dooner HK (1995) Directed tagging of the Arabidopsis FATTY ACID ELONGATION1 (FAE1) gene with the maize transposon activator. Plant Cell 7(3):309–319. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.7.3.309
Jiang H, Ma QJ, Zhong MS, Gao HN, Li YY, Hao YJ (2021) The apple palmitoyltransferase MdPAT16 influences sugar content and salt tolerance via an MdCBL1–MdCIPK13–MdSUT2.2 pathway. Plant J 106:689–705. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15191
Johnson DA, Richards RA, Turner NC (1983) Yield, water relations, gas exchange, and surface reflectances of near-isogenic wheat lines differing in glaucousness. CropSci 23:318–325
Joubes J, Raffaele S, Bourdenx B, Garcia C, Laroche-Traineau J, Moreau P, Domergue F, Lessire R (2008) The VLCFA elongase gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana: phylogenetic analysis, 3D modelling and expression profiling. Plant Mol Biol 67(5):547–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9339-z
Kim J, Jung JH, Lee SB, Go YS, Kim HJ, Cahoon R, Markham JE, Cahoon EB, Suh MC (2013) Arabidopsis 3-ketoacyl-coenzyme a synthase9 is involved in the synthesis of tetracosanoic acids as precursors of cuticular waxes, suberins, sphingolipids, and phospholipids. Plant Physiol 162(2):567–580. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.210450
Kunst L, Samuels L (2009) Plant cuticles shine: advances in wax biosynthesis and export. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12(6):721–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.09.009
Kunst L, Taylor DC, Underhill EW (1992) Fatty acid elongation in developing seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Biochem 30(4):425–434
Lee SB, Jung SJ, Go YS, Kim HU, Kim JK, Cho HJ, Park OK, Suh MC (2009) Two Arabidopsis 3-ketoacyl CoA synthase genes, KCS20 and KCS2/DAISY, are functionally redundant in cuticular wax and root suberin biosynthesis, but differentially controlled by osmotic stress. Plant J 60(3):462–475. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03973.x
Leide J, Hildebrandt U, Reussing K, Riederer M, Vogg G (2007) The developmental pattern of tomato fruit wax accumulation and its impact on cuticular transpiration barrier properties: effects of a deficiency in a beta-ketoacyl-coenzyme A synthase (LeCER6). Plant Physiol 144(3):1667–1679. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.099481
Li YY, Mao K, Zhao C, Zhao XY, Zhang HL, Shu HR, Hao YJ (2012) MdCOP1 ubiquitin E3 ligases interact with MdMYB1 to regulate light-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis and red fruit coloration in apple. Plant Physiol 160(2):1011–1022. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.199703
Li C, Haslam TM, Kruger A, Schneider LM, Mishina K, Samuels L, Yang H, Kunst L, Schaffrath U, Nawrath C, Chen G, Komatsuda T, von Wettstein-Knowles P (2018) The beta-ketoacyl-CoA synthase HvKCS1, encoded by Cer-zh, plays a key role in synthesis of barley leaf wax and germination of barley powdery mildew. Plant Cell Physiol 59(4):806–822. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy020
Lian XY, Wang X, Gao HN, Jiang H, Mao K, You CX, Li YY, Hao YJ (2020) Genome wide analysis and functional identification of MdKCS genes in apple. Plant Physiol Biochem 151:299–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.03.034
Lu S, Song T, Kosma DK, Parsons EP, Rowland O, Jenks MA (2009) Arabidopsis CER8 encodes LONG-CHAIN ACYL-COA SYNTHETASE 1 (LACS1) that has overlapping functions with LACS2 in plant wax and cutin synthesis. Plant J 59(4):553–564. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03892.x
Ma QJ, Sun MH, Lu J, Liu YJ, Hu DG, Hao YJ (2017) Transcription factor AREB2 is involved in soluble sugar accumulation by activating sugar transporter and amylase genes. Plant Physiol 174(4):2348–2362. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00502
Pruitt RE, Vielle-Calzada J-P, Ploense SE, Grossniklaus U, Lolle SJ (2000) FIDDLEHEAD, a gene required to suppress epidermal cell interactions in Arabidopsis, encodes a putative lipid biosynthetic enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97(3):1311–1316. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.3.1311
Qi C-H, Zhao X-Y, Jiang H, Zheng P-F, Liu H-T, Li Y-Y, Hao Y-J (2018) Isolation and functional identification of an apple MdCER1 gene. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult (PCTOC) 136(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-1504-8
Qin YM, Hu CY, Pang Y, Kastaniotis AJ, Hiltunen JK, Zhu YX (2007) Saturated very-long-chain fatty acids promote cotton fiber and Arabidopsis cell elongation by activating ethylene biosynthesis. Plant Cell 19(11):3692–3704. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.054437
Shepherd T, Wynne Griffiths D (2006) The effects of stress on plant cuticular waxes. New Phytol 171(3):469–499. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01826.x
Wang RK, Cao ZH, Hao YJ (2014) Overexpression of a R2R3 MYB gene MdSIMYB1 increases tolerance to multiple stresses in transgenic tobacco and apples. Physiol Plant 150(1):76–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12069
Wang Y, Jin S, Xu Y, Li S, Zhang S, Yuan Z, Li J, Ni Y (2020) Overexpression of BnKCS1-1, BnKCS1-2, and BnCER1-2 promotes cuticular wax production and increases drought tolerance in Brassica napus. Crop J 8(1):26–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2019.04.006
Yeats TH, Rose JK (2013) The formation and function of plant cuticles. Plant Physiol 163(1):5–20. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.222737
Yephremov A, Wisman E, Huijser P, Huijser C, Wellesen K, Saedler H (1999) Characterization of the FIDDLEHEAD gene of Arabidopsis reveals a link between adhesion response and cell differentiation in the epidermis. Plant Cell 11(11):2187–2201. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.11.11.2187
Yoshida T, Mogami J, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2014) ABA-dependent and ABA-independent signaling in response to osmotic stress in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 21:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2014.07.009
Zhang CL, Mao K, Zhou LJ, Wang GL, Zhang YL, Li YY, Hao YJ (2018) Genome-wide identification and characterization of apple long-chain Acyl-CoA synthetases and expression analysis under different stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 132:320–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.09.004
Zhang YL, Zhang CL, Wang GL, Wang YX, Qi CH, You CX, Li YY, Hao YJ (2019a) Apple AP2/EREBP transcription factor MdSHINE2 confers drought resistance by regulating wax biosynthesis. Planta 249(5):1627–1643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-019-03115-4
Zhang GY, Shan SL, Wu YB, Huang SQ, Li DF, Deng JL, Qi JM (2019ba) The KCS gene is involved in the formation of chloroplast stromules and other physiological processes in jute (Corchorus capsularis L.). Ind Crops Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111781
Zhang CL, Hu X, Zhang YL, Liu Y, Wang GL, You CX, Li YY, Hao YJ (2020a) An apple long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 2 gene enhances plant resistance to abiotic stress by regulating the accumulation of cuticular wax. Tree Physiol 40(10):1450–1465. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpaa079
Zhang CL, Zhang YL, Hu X, Xiao X, Wang GL, You CX, Li YY, Hao YJ (2020b) An apple long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase, MdLACS4, induces early flowering and enhances abiotic stress resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci 297:110529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110529
Zhang FJ, Xie YH, Jiang H, Wang X, Hao YJ, Zhang ZL, You CX (2021) The ankyrin repeat-containing protein MdANK2B regulates salt tolerance and ABA sensitivity in Malus domestica. Plant Cell Rep 40:405–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-020-02642-9
Zheng Y, Schumaker KS, Guo Y (2012) Sumoylation of transcription factor MYB30 by the small ubiquitin-like modifier E3 ligase SIZ1 mediates abscisic acid response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(31):12822–12827. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1202630109
Zhong MS, Jiang H, Cao Y, Wang YX, You CX, Li YY, Hao YJ (2020) MdCER2 conferred to wax accumulation and increased drought tolerance in plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 149:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.013
Zhou LJ, Mao K, Qiao Y, Jiang H, Li YY, Hao YJ (2017) Functional identification of MdPIF1 as a phytochrome interacting factor in apple. Plant Physiol Biochem 119:178–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.08.027
Zhou LJ, Zhang CL, Zhang RF, Wang GL, Li YY, Hao YJ (2019) The SUMO E3 ligase MdSIZ1 targets MdbHLH104 to regulate plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity and iron homeostasis. Plant Physiol 179(1):88–106. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.00289
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported Grants from National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD1000200) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (32072539, 31772275).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL conceived and designed research. XL, HG and HJ conducted experiments. XL and CL analyzed data. XL and YL wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Chun-Hai Dong.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
299_2021_2776_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1Supplement Fig. S1 Comparison of conserved motifs of KCS2 proteins. Malus domestica, apple; Pyrus ussuriensis × Pyrus communis, yali pear; Pyrus × bretschneideri, white pear; Prunus persica, almond; Hibiscus syriacus, rose of sharon; Citrus sinensis, orange; Glycine max, soybean; Arabidopsis thaliana, arabidopsis; Ananas comosus, pineapple; Setaria italica, millet; Zea mays, corn (TIF 2639 KB)
299_2021_2776_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary file2Supplement Fig. S2 Detection of MdKCS2 transgenic Arabidopsis. (A) PCR detection of MdKCS2 transgenic Arabidopsis. (B) Expression of MdKCS2 in WT and MdKCS2 transgenic Arabidopsis. These values are mean ± SD of three independent replicates. Bars with different letters are significantly different at P < 0.05, according to Tukey test (TIF 92 KB)
299_2021_2776_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary file3Supplement Fig. S3 Protein interaction networks predicted for AtKCS2 (A) and MdKCS2 proteins (B). Use STRING online software to predict the network of AtKCS2 (A) and MdKCS2 (B) proteins (TIF 241 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lian, XY., Gao, HN., Jiang, H. et al. MdKCS2 increased plant drought resistance by regulating wax biosynthesis. Plant Cell Rep 40, 2357–2368 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-021-02776-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-021-02776-4