Abstract
Key message
Numbers of critical genes and pathways were found from the levels of transcriptome and metabolome, which were useful information for understanding of kenaf CMS mechanism.
Abstract
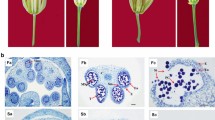
Cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) is a maternally inherited trait in higher plants that leads to the inability to produce or release functional pollen. However, there is lack of comprehensive studies to reveal the molecular basis of CMS occurrence in kenaf. Herein, we performed transcriptome and UPLC-MS-based metabolome analyses in the anthers of a CMS (UG93A) and its maintainer (UG93B) to sort out essential genes and metabolites responding to CMS in kenaf. Transcriptome characterized 7769 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between these two materials, and pathway enrichment analysis indicated that these DEGs were involved mainly in pentose and glucuronate interconversions, starch and sucrose metabolism, taurine and hypotaurine metabolism. In the metabolome assay, a total of 116 significantly different metabolites (SDMs) were identified between the CMS and its maintainer line, and these SDMs were involved in eight KEGG pathways, including flavone and flavonol biosynthesis, glycerophospholipid metabolism, flavonoid biosynthesis, glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchor biosynthesi. Integrated analyses of transcriptome and metabolome showed that 50 genes had strong correlation coefficient values (R2 > 0.9) with ten metabolites enriched in six pathways; notably, most genes and metabolites of flavonoid biosynthesis pathways and flavone and flavonol biosynthesis pathways involved in flavonoids biosynthetic pathways were downregulated in CMS compared to those in maintainer. Taken together, the decreased accumulation of flavonoids resulted from the compromised biosynthesis pathways coupled with energy deficiency in the anthers may contribute largely to CMS in UG93A of kenaf.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts MGM, Hodge R, Kalantidis K, Florack D, Wilson ZA, Mulligan BJ, Stiekema WJ, Scott R, Pereira A (1997) The Arabidopsis MALE STERILITY 2 protein shares similarity with reductases in elongation/condensation complexes. Plant J 12(3):615–623. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.00615.x
Ali M, Hussain RM, Rehman NU, She G, Li P, Wan X, Guo L, Zhao J (2018) De novo transcriptome sequencing and metabolite profiling analyses reveal the complex metabolic genes involved in the terpenoid biosynthesis in Blue Anise Sage (Salvia guaranitica L.). DNA Res 25(6):597–617. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsy028
Bijlsma L, Gil-Solsona R, Hernandez F, Sancho JV (2018) What about the herb? A new metabolomics approach for synthetic cannabinoid drug testing. Anal Bioanal Chem 410(21):5107–5112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1182-8
Bohra A, Jha UC, Adhimoolam P, Bisht D, Singh NP (2016) Cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) in hybrid breeding in field crops. Plant Cell Rep 35(5):967–993. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-1949-3
Bokvaj P, Hafidh S, Honys D (2015) Transcriptome profiling of male gametophyte development in Nicotiana tabacum. Genom Data 3:106–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gdata.2014.12.002
Brooks MH (1962) Comparative analyses of some of the free amino acids in anthers of fertile and genetic cytoplasmic male sterile sorghum. Genetics 47(12):1629–1638
Chaturvedi P, Ischebeck T, Egelhofer V, Lichtscheidl I, Weckwerth W (2013) Cell-specific analysis of the tomato pollen proteome from pollen mother cell to mature pollen provides evidence for developmental priming. J Proteome Res 12(11):4892–4903. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr400197p
Chen LT, Liu YG (2014) Male sterility and fertility restoration in crops. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65(65):579–606. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050213-040119
Chen P, Ran SM, Li R, Huang ZP, Qian JH, Yu ML, Zhou RY (2014) Transcriptome de novo assembly and differentially expressed genes related to cytoplasmic male sterility in kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.). Mol Breed 34(4):1879–1891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0146-8
Chen ZW, Zhao N, Li SS, Grover CE, Nie HS, Wendel JF, Hua JP (2017) Plant mitochondrial genome evolution and cytoplasmic male sterility. Crit Rev Plant Sci 36(1):55–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2017.1327762
Chen P, Li R, Zhou RY (2018) Comparative phosphoproteomic analysis reveals differentially phosphorylated proteins regulate anther and pollen development in kenaf cytoplasmic male sterility line. Amino Acids 50(7):841–862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-018-2564-0
Chen P, Shi QQ, Liang ZC, Lu H, Li R (2019a) Comparative profile analysis reveals differentially expressed microRNAs regulate anther and pollen development in kenaf cytoplasmic male sterility line. Genome 62(7):455–466. https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-2018-0207
Chen P, Wei F, Li R, Li ZQ, Kashif MH, Zhou RY (2019b) Comparative acetylomic analysis reveals differentially acetylated proteins regulating anther and pollen development in kenaf cytoplasmic male sterility line. Physiol Plant 166(4):960–978. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12850
Conesa A, Gotz S, Garcia-Gomez JM, Terol J, Talon M, Robles M (2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 21(18):3674–3676. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610
Deng MH, Wen JF, Huo JL, Zhu HS, Dai XZ, Zhang ZQ, Zhou H, Zou XX (2012) Relationship of metabolism of reactive oxygen species with cytoplasmic male sterility in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Sci Hortic Amsterdam 134:232–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2011.10.027
Ding X, Wang X, Li Q, Yu L, Song Q, Gai J, Yang S (2019) Metabolomics studies on cytoplasmic male sterility during flower bud development in soybean. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122869
Dorion S, Lalonde S, Saini HS (1996) Induction of male sterility in wheat by meiotic-stage water deficit is preceded by a decline in invertase activity and changes in carbohydrate metabolism in anthers. Plant Physiol 111(1):137–145. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.1.137
Ducos E, Touzet P, Boutry M (2001) The male sterile G cytoplasm of wild beet displays modified mitochondrial respiratory complexes. Plant J 26(2):171–180. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01017.x
Goetz M, Godt DE, Guivarc’h A, Kahmann U, Chriqui D, Roitsch T (2001) Induction of male sterility in plants by metabolic engineering of the carbohydrate supply. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(11):6522–6527. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.091097998
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q, Chen Z, Mauceli E, Hacohen N, Gnirke A, Rhind N, di Palma F, Birren BW, Nusbaum C, Lindblad-Toh K, Friedman N, Regev A (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29(7):644–652. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1883
Hafidh S, Fila J, Honys D (2016) Male gametophyte development and function in angiosperms: a general concept. Plant Reprod 29(1–2):31–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-015-0272-4
Hao R, Du X, Yang C, Deng Y, Zheng Z, Wang Q (2019) Integrated application of transcriptomics and metabolomics provides insights into unsynchronized growth in pearl oyster Pinctada fucata martensii. Sci Total Environ 666:46–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.221
Hedhly A, Vogler H, Schmid MW, Pazmino D, Gagliardini V, Santelia D, Grossniklaus U (2016) Starch turnover and metabolism during flower and early embryo development. Plant Physiol 172(4):2388–2402. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.00916
Horn R, Gupta KJ, Colombo N (2014) Mitochondrion role in molecular basis of cytoplasmic male sterility. Mitochondrion 19:198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2014.04.004
Hu J, Yi R, Zhang H, Ding Y (2013) Nucleo-cytoplasmic interactions affect RNA editing of cox2, atp6 and atp9 in alloplasmic male-sterile rice (Oryza sativa L.) lines. Mitochondrion 13(2):87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2013.01.011
Jiang P, Zhang X, Zhu Y, Zhu W, Xie H, Wang X (2007) Metabolism of reactive oxygen species in cotton cytoplasmic male sterility and its restoration. Plant Cell Rep 26(9):1627–1634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0351-6
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28(1):27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27
Karlund A, Moor U, McDougall G, Lehtonen M, Karjalainen RO, Hanhineva K (2016) Metabolic profiling discriminates between strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) cultivars grown in Finland or Estonia. Food Res Int 89:647–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2016.09.013
Lazar G, Goodman HM (2006) MAX1, a regulator of the flavonoid pathway, controls vegetative axillary bud outgrowth in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(2):472–476. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0509463102
Li B, Dewey CN (2011) RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform 12:323. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-323
Li J, Pandeya D, Jo YD, Liu WY, Kang BC (2013) Reduced activity of ATP synthase in mitochondria causes cytoplasmic male sterility in chili pepper. Planta 237(4):1097–1109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1824-6
Liao X, Zhao Y, Kong X, Khan A, Zhou B, Liu D, Kashif MH, Chen P, Wang H, Zhou R (2018) Complete sequence of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) mitochondrial genome and comparative analysis with the mitochondrial genomes of other plants. Sci Rep 8(1):12714. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30297-w
Luo D, Xu H, Liu Z, Guo J, Li H, Chen L, Fang C, Zhang Q, Bai M, Yao N, Wu H, Wu H, Ji C, Zheng H, Chen Y, Ye S, Li X, Zhao X, Li R, Liu YG (2013) A detrimental mitochondrial–nuclear interaction causes cytoplasmic male sterility in rice. Nat Genet 45(5):573–577. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2570
Mattioli R, Biancucci M, Lonoce C, Costantino P, Trovato M (2012) Proline is required for male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-12-236
Ning L, Wang H, Li D, Lin Z, Li Y, Zhao W, Chao H, Miao L, Li M (2019) Transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of Shaan2A cytoplasmic male sterility and its maintainer line in Brassica napus. Front Plant Sci 10:252. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00252
Oliver SN, Van Dongen JT, Alfred SC, Mamun EA, Zhao XC, Saini HS, Fernandes SF, Blanchard CL, Sutton BG, Geigenberger P, Dennis ES, Dolferus R (2005) Cold-induced repression of the rice anther-specific cell wall invertase gene OSINV4 is correlated with sucrose accumulation and pollen sterility. Plant Cell Environ 28(12):1534–1551. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01390.x
Oliver SN, Dennis ES, Dolferus R (2007) ABA regulates apoplastic sugar transport and is a potential signal for cold-induced pollen sterility in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 48(9):1319–1330. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcm100
Patti GJ, Yanes O, Siuzdak G (2012) Innovation: Metabolomics: the apogee of the omics trilogy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(4):263–269. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3314
Qu GR, Quan S, Mondol P, Xu J, Zhang DB, Shi JX (2014) Comparative metabolomic analysis of wild type and mads3 mutant rice anthers. J Integr Plant Biol 56(9):849–863. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12245
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2010) edgeR: a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26(1):139–140. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616
Scossa F, Benina M, Alseekh S, Zhang Y, Fernie AR (2018) The integration of metabolomics and next-generation sequencing data to elucidate the pathways of natural product metabolism in medicinal plants. Planta Med 84(12–13):855–873. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0630-1899
Shao Y, Ye G, Ren S, Piao HL, Zhao X, Lu X, Wang F, Ma W, Li J, Yin P, Xia T, Xu C, Yu JJ, Sun Y, Xu G (2018) Metabolomics and transcriptomics profiles reveal the dysregulation of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and related mechanisms in prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 143(2):396–407. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31313
Shi J, Tan HX, Yu XH, Liu YY, Liang WQ, Ranathunge K, Franke RB, Schreiber L, Wang YJ, Kai GY, Shanklin J, Ma H, Zhang DB (2011) Defective pollen wall is required for anther and microspore development in rice and encodes a fatty acyl carrier protein reductase. Plant Cell 23(6):2225–2246. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.087528
Shishova M, Puzanskiy R, Gavrilova O, Kurbanniazov S, Demchenko K, Yemelyanov V, Pendinen G, Shavarda A, Gavrilenko T (2019) Metabolic alterations in male-sterile potato as compared to male-fertile. Metabolites. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9020024
Sun L, Sui X, Lucas WJ, Li Y, Feng S, Ma S, Fan J, Gao L, Zhang Z (2019) Down-regulation of the sucrose transporter CsSUT1 causes male sterility by altering carbohydrate supply. Plant Physiol 180(2):986–997. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.00317
Suzuki H, Rodriguez-Uribe L, Xu JN, Zhang JF (2013) Transcriptome analysis of cytoplasmic male sterility and restoration in CMS-D8 cotton. Plant Cell Rep 32(10):1531–1542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1465-7
Touzet P, Meyer EH (2014) Cytoplasmic male sterility and mitochondrial metabolism in plants. Mitochondrion 19:166–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2014.04.009
van der Meer IM, Stam ME, van Tunen AJ, Mol JN, Stuitje AR (1992) Antisense inhibition of flavonoid biosynthesis in petunia anthers results in male sterility. Plant Cell 4(3):253–262. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.4.3.253
Wang J (2013) Transcriptomics and metabolomics studies on cytoplasmic male sterility in cotton. Master's Degree, Nanjing Agricultural University, N5656
Wu Q, Wu J, Li SS, Zhang HJ, Feng CY, Yin DD, Wu RY, Wang LS (2016) Transcriptome sequencing and metabolite analysis for revealing the blue flower formation in waterlily. BMC Genom. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-3226-9
Wu B, Zhu L, Le XC (2017) Metabolomics analysis of TiO2 nanoparticles induced toxicological effects on rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Pollut 230:302–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.06.062
Xia T, Liu JL (1994) Study on the relation between auxin, zeatin and cytoplasmic male sterility in maize (Zea mays L.). Acta Agron Sin 1:26–32
Xie C, Mao X, Huang J, Ding Y, Wu J, Dong S, Kong L, Gao G, Li CY, Wei L (2011) KOBAS 2.0: a web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res 39(Web Server issue):W316–W322. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr483
Xing MM, Sun C, Li HL, Hu SL, Lei L, Kang JG (2018) Integrated analysis of transcriptome and proteome changes related to the Ogura cytoplasmic male sterility in cabbage. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193462
Yang JH, Huai Y, Zhang MF (2009) Mitochondrial atpA gene is altered in a new orf220-type cytoplasmic male-sterile line of stem mustard (Brassica juncea). Mol Biol Rep 36(2):273–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-007-9176-1
Yang K, Zhou X, Wang Y, Feng H, Ren X, Liu H, Liu W (2017) Carbohydrate metabolism and gene regulation during anther development in an androdioecious tree, Tapiscia sinensis. Ann Bot 120(6):967–977. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcx094
Yang L, Wu Y, Zhang M, Zhang J, Stewart JM, Xing C, Wu J, Jin S (2018) Transcriptome, cytological and biochemical analysis of cytoplasmic male sterility and maintainer line in CMS-D8 cotton. Plant Mol Biol 97(6):537–551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-018-0757-2
Ylstra B, Touraev A, Moreno RM, Stoger E, van Tunen AJ, Vicente O, Mol JN, Heberle-Bors E (1992) Flavonols stimulate development, germination, and tube growth of tobacco pollen. Plant Physiol 100(2):902–907. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.100.2.902
Yuan Q, Song C, Gao L, Zhang H, Yang C, Sheng J, Ren J, Chen D, Wang Y (2018) Transcriptome de novo assembly and analysis of differentially expressed genes related to cytoplasmic male sterility in onion. Plant Physiol Biochem 125:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.01.015
Zechmann B, Koffler BE, Russell SD (2011) Glutathione synthesis is essential for pollen germination in vitro. BMC Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-11-54
Zhou R, Zhang X, Zhang J, Gan Z, Wei H (2008) A breakthrough in kenaf cytoplasmic male sterile lines breeding and heterosis utilization. Sci Agric Sin 41(1):314–314. https://doi.org/10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2008.01.043
Zhu J, Chen H, Li H, Gao JF, Jiang H, Wang C, Guan YF, Yang ZN (2008) Defective in tapetal development and function 1 is essential for anther development and tapetal function for microspore maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 55(2):266–277. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03500.x
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Professor Ruiyang Zhou for providing seeds of kenaf cultivar UG93A and UG93B. This research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 31560421 and 31960368) and the earmarked fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (CARS-16-E14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PC conceived and designed the research. MT, ZL, DL and FW analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. MHK and HL revised the manuscript. LH, JY, ZH, WT and RL assist during the experiments. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Neal Stewart.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, M., Li, Z., Luo, D. et al. A comprehensive integrated transcriptome and metabolome analyses to reveal key genes and essential metabolic pathways involved in CMS in kenaf. Plant Cell Rep 40, 223–236 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-020-02628-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-020-02628-7