Abstract
Key message
Transcription factors from mammals and plants, which play a role in innate immunity, interact with the same microbe-associated molecular pattern (MAMP)-responsive sequences from Arabidopsis thaliana.
Abstract
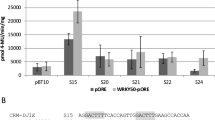
The interaction of mouse NF-κB p65 with MAMP-responsive sequences containing the core motif GACTTT of the WT-box was investigated. This revealed one sequence, derived from the promoter of the A. thaliana gene At1g76960, a gene with unknown function, to activate NF-κB p65 dependent reporter gene expression in plant cells very strongly. A bioinformatic analysis predicts three putative NF-κB p65 binding sites in this sequence and all three sites are required for reporter gene activation and binding. The sequence is one of the weakest MAMP-responsive sequences previously isolated, but the introduction of a GCC-box increases its MAMP responsivity in combination with upstream WT-box sequences. Although a bioinformatic analysis of the unmutated cis-sequence only predicts NF-κB p65 binding, A. thaliana WRKY40 was selected in a yeast one-hybrid screen. WRKY40, which is a transcriptional repressor, requires the sequence TTTTCTA for direct binding. This sequence is similar to the WK-box TTTTCCAC, previously shown to interact with tobacco NtWRKY12. In summary, this work supports the similarity in binding site recognition between NF-κB and WRKY factors.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel FM (2005) Are innate immune signaling pathways in plants and animals conserved? Nat Immunol 6:973–979
Berkowitz B, Huang DB, Chen-Park FE, Sigler PB, Ghosh G (2002) The X-ray crystal structure of the NF-kappa B p50.p65 heterodimer bound to the interferon beta-kappa B site. J Biol Chem 277:24694–24700
Bülow L, Steffens NO, Galuschka C, Schindler M, Hehl R (2006) AthaMap: from in silico data to real transcription factor binding sites. Silico Biol 6:243–252
Cai M, Qiu D, Yuan T, Ding X, Li H, Duan L, Xu C, Li X, Wang S (2008) Identification of novel pathogen-responsive cis-elements and their binding proteins in the promoter of OsWRKY13, a gene regulating rice disease resistance. Plant Cell Environ 31:86–96
Chen YQ, Ghosh S, Ghosh G (1998) A novel DNA recognition mode by the NF-kappa B p65 homodimer. Nat Struct Biol 5:67–73
Choi C, Hwang S-H, Fang IR, Kwon SI, Park SR, Ahn I, Kim JB, Hwang D-J (2015) Molecular characterization of Oryza sativa WRKY6, which binds to W-box-like element 1 of the Oryza sativa pathogenesis-related (PR) 10a promoter and confers reduced susceptibility to pathogens. New Phytol 208:846–859
Contreras-Moreira B (2010) 3D-footprint: a database for the structural analysis of protein–DNA complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D91–D97
Coutu C, Brandle J, Brown D, Brown K, Miki B, Simmonds J, Hegedus DD (2007) pORE: a modular binary vector series suited for both monocot and dicot plant transformation. Transgenic Res 16:771–781
Dubos C, Kelemen Z, Sebastian A, Bülow L, Huep G, Xu W, Grain D, Salsac F, Brousse C, Lepiniec L, Weisshaar B, Contreras-Moreira B, Hehl R (2014) Integrating bioinformatic resources to predict transcription factors interacting with cis-sequences conserved in co-regulated genes. BMC Genom 15:317
Duxbury Z, Ma Y, Furzer OJ, Huh SU, Cevik V, Jones JD, Sarris PF (2016) Pathogen perception by NLRs in plants and animals: parallel worlds. BioEssays 38:769–781
Eulgem T, Rushton PJ, Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2000) The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 5:199–206
Fraiture M, Brunner F (2014) Killing two birds with one stone: trans-kingdom suppression of PAMP/MAMP-induced immunity by T3E from enteropathogenic bacteria. Front Microbiol 5:320
Franco-Zorrilla JM, Lopez-Vidriero I, Carrasco JL, Godoy M, Vera P, Solano R (2014) DNA-binding specificities of plant transcription factors and their potential to define target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:2367–2372
Gnanaprakasam JN, Wang R (2017) MYC in regulating immunity: metabolism and beyond. Genes 8:E88
Haney CH, Urbach J, Ausubel FM (2014) Innate immunity in plants and animals. Biochemist 36:40–44
Hehl R (2017) From experiment-driven database analyses to database-driven experiments in Arabidopsis thaliana transcription factor research. Plant Sci 262:141–147
Hehl R, Wingender E (2001) Database-assisted promoter analysis. Trends Plant Sci 6:251–255
Hehl R, Norval L, Romanov A, Bülow L (2016) Boosting AthaMap database content with data from protein binding microarrays. Plant Cell Physiol 57:e4
Hussain RMF, Sheikh AH, Haider I, Quareshy M, Linthorst HJM (2018) Arabidopsis WRKY50 and TGA transcription factors synergistically activate expression of PR1. Front Plant Sci 9:930
Iwata Y, Koizumi N (2005) An Arabidopsis transcription factor, AtbZIP60, regulates the endoplasmic reticulum stress response in a manner unique to plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(14):5280–5285
Jones JD, Vance RE, Dangl JL (2016) Intracellular innate immune surveillance devices in plants and animals. Science 354:6316. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf6395
Kanofsky K, Lehmeyer M, Schulze J, Hehl R (2016) Analysis of microbe-associated molecular pattern-responsive synthetic promoters with the parsley protoplast system. Methods Mol Biol 1482:163–1741
Kanofsky K, Bahlmann AK, Hehl R, Dong DX (2017) Combinatorial requirement of W- and WT-boxes in microbe-associated molecular pattern-responsive synthetic promoters. Plant Cell Rep 36(6):971–986
Kanofsky K, Strauch CJ, Sandmann A, Moller A, Hehl R (2018) Transcription factors involved in basal immunity in mammals and plants interact with the same MAMP-responsive cis-sequence from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 98:565–578
Koschmann J, Machens F, Becker M, Niemeyer J, Schulze J, Bülow L, Stahl DJ, Hehl R (2012) Integration of bioinformatics and synthetic promoters leads to the discovery of novel elicitor-responsive cis-regulatory sequences in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 160:178–191
Lebel E, Heifetz P, Thorne L, Uknes S, Ryals J, Ward E (1998) Functional analysis of regulatory sequences controlling PR-1 gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant J 16:223–233
Lehmeyer M, Kanofsky K, Hanko EK, Ahrendt S, Wehrs M, Machens F, Hehl R (2016) Functional dissection of a strong and specific microbe-associated molecular pattern-responsive synthetic promoter. Plant Biotechnol J 14:61–71
Lian TF, Xu YP, Li LF, Su XD (2017) Crystal structure of tetrameric Arabidopsis MYC2 reveals the mechanism of enhanced interaction with DNA. Cell Rep 19:1334–1342
Machens F, Becker M, Umrath F, Hehl R (2014) Identification of a novel type of WRKY transcription factor binding site in elicitor-responsive cis-sequences from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 84:371–385
Mitsuda N, Ikeda M, Takada S, Takiguchi Y, Kondou Y, Yoshizumi T, Fujita M, Shinozaki K, Matsui M, Ohme-Takagi M (2010) Efficient yeast one-/two-hybrid screening using a library composed only of transcription factors in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 51:2145–2151
Mulero MC, Huang DB, Nguyen HT, Wang VY, Li Y, Biswas T, Ghosh G (2017) DNA-binding affinity and transcriptional activity of the RelA homodimer of nuclear factor kappaB are not correlated. J Biol Chem 292:18821–18830
Nürnberger T, Nennstiel D, Jabs T, Sacks WR, Hahlbrock K, Scheel D (1994) High affinity binding of a fungal oligopeptide elicitor to parsley plasma membranes triggers multiple defense responses. Cell 78:449–460
Nürnberger T, Brunner F, Kemmerling B, Piater L (2004) Innate immunity in plants and animals: striking similarities and obvious differences. Immunol Rev 198:249–266
O’Malley RC, Huang SS, Song L, Lewsey MG, Bartlett A, Nery JR, Galli M, Gallavotti A, Ecker JR (2016) Cistrome and epicistrome features shape the regulatory DNA landscape. Cell 165:1280–1292
Riano-Pachon DM, Ruzicic S, Dreyer I, Müller-Röber B (2007) PlnTFDB: an integrative plant transcription factor database. BMC Bioinform 8:42
Rushton PJ, Torres JT, Parniske M, Wernert P, Hahlbrock K, Somssich IE (1996) Interaction of elicitor-induced DNA-binding proteins with elicitor response elements in the promoters of parsley PR1 genes. EMBO J 15:5690–5700
Rushton PJ, Somssich IE, Ringler P, Shen QJ (2010) WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 15:247–258
Sambrook J, Russell RW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold spring harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sebastian A, Contreras-Moreira B (2014) footprintDB: a database of transcription factors with annotated cis elements and binding interfaces. Bioinformatics 30:258–265
Shang Y, Yan L, Liu ZQ, Cao Z, Mei C, Xin Q, Wu FQ, Wang XF, Du SY, Jiang T, Zhang XF, Zhao R, Sun HL, Liu R, Yu YT, Zhang DP (2010) The Mg-chelatase H subunit of Arabidopsis antagonizes a group of WRKY transcription repressors to relieve ABA-responsive genes of inhibition. Plant Cell 22:1909–1935
Stroud JC, Oltman A, Han A, Bates DL, Chen L (2009) Structural basis of HIV-1 activation by NF-kappaB—a higher-order complex of p50:RelA bound to the HIV-1 LTR. J Mol Biol 393:98–112
Urbach JM, Ausubel FM (2017) The NBS-LRR architectures of plant R-proteins and metazoan NLRs evolved in independent events. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:1063–1068
van Verk MC, Pappaioannou D, Neeleman L, Bol JF, Linthorst HJM (2008) A novel WRKY transcription factor is required for induction of PR-1a gene expression by salicylic acid and bacterial elicitors. Plant Physiol 146:1983–1995
Wehner N, Hartmann L, Ehlert A, Bottner S, Onate-Sanchez L, Dröge-Laser W (2011) High-throughput protoplast transactivation (PTA) system for the analysis of Arabidopsis transcription factor function. Plant J 68:560–569
Weirauch MT, Hughes TR (2011) A catalogue of eukaryotic transcription factor types, their evolutionary origin, and species distribution. Subcell Biochem 52:25–73
Weirauch MT, Yang A, Albu M, Cote AG, Montenegro-Montero A, Drewe P, Najafabadi HS, Lambert SA, Mann I, Cook K, Zheng H, Goity A, van Bakel H, Lozano JC, Galli M, Lewsey MG, Huang E, Mukherjee T, Chen X, Reece-Hoyes JS, Govindarajan S, Shaulsky G, Walhout AJ, Bouget FY, Ratsch G, Larrondo LF, Ecker JR, Hughes TR (2014) Determination and inference of eukaryotic transcription factor sequence specificity. Cell 158:1431–1443
Yamasaki K, Kigawa T, Inoue M, Tateno M, Yamasaki T, Yabuki T, Aoki M, Seki E, Matsuda T, Tomo Y, Hayami N, Terada T, Shirouzu M, Tanaka A, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yokoyama S (2005) Solution structure of an Arabidopsis WRKY DNA binding domain. Plant Cell 17:944–956
Yamasaki K, Kigawa T, Watanabe S, Inoue M, Yamasaki T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yokoyama S (2012) Structural basis for sequence-specific DNA recognition by an Arabidopsis WRKY transcription factor. J Biol Chem 287:7683–7691
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T, Mori K (2001) XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 107:881–891
Zhou QY, Tian AG, Zou HF, Xie ZM, Lei G, Huang J, Wang CM, Wang HW, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2008) Soybean WRKY-type transcription factor genes, GmWRKY13, GmWRKY21, and GmWRKY54, confer differential tolerance to abiotic stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Biotechnol J 6:486–503
Zhou M, Lu Y, Bethke G, Harrison BT, Hatsugai N, Katagiri F, Glazebrook J (2017) WRKY70 prevents axenic activation of plant immunity by direct repression of SARD1. New Phytol 217:700–712
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Elke Faurie for excellent technical assistance. We are grateful to Christopher Eickhorst and Kazuhiko Namikawa for the gift of mouse mRNA. Great thanks to Miriam Becker for technical assistance when using the french press. This work was supported by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Germany (Hochschulpakt 2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RH and KK conceived and designed research. KK, JR, MS, CJS, and LCA conducted experiments. KK, JR, MS, CJS, LCA, and RH analyzed data. RH wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Communicated by Manju Gupta.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanofsky, K., Riggers, J., Staar, M. et al. A strong NF-κB p65 responsive cis-regulatory sequence from Arabidopsis thaliana interacts with WRKY40. Plant Cell Rep 38, 1139–1150 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02433-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02433-x