Abstract
Key message
Highly variable regions of chloroplast genome were found to be useful in the detection of plant genetic diversity at micro-evolution level. Our methodology will improve understanding and conservation of plant diversity.
Abstract
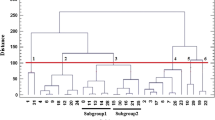
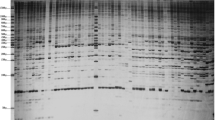
Tree peonies are famous flowers with about 2,000 cultivars in the world, belonging to Paeonia sect. Moutan of the Paeoniaceae. They are traditionally classified based on flower forms and colors. Due to the limited number of DNA and morphological markers, and the existence of synonyms and homonyms, evaluation on genetic diversity of so many cultivars remains a challenge. In most cases, it is difficult and even impossible to discriminate tree peony cultivars when they are not in flower. In this study, single nucleotide polymorphism detected from the hyper-variable regions of chloroplast genome was employed to separate tree peony cultivars into different maternal lineages which can be expressed briefly by a nucleotide molecular formula. Our approach enabled a much higher resolution of cultivar identification and classification that has not been obtained before. The newly developed hyper-variable chloroplast markers, as an independent source of taxonomic characteristics, provided novel evidences and higher resolution ability that are helpful in building an effective classification system for evaluation, conservation, and utilization of the tree peony germplasm resources at cultivar level.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Diekmann K, Hodkinson TR, Barth S (2012) New chloroplast microsatellite markers suitable for assessing genetic diversity of Lolium perenne and other related grass species. Ann Bot 109(4):1–13
Dong WP, Liu J, Yu J, Wang L, Zhou SL (2012) Highly variable chloroplast markers for evaluating plant phylogeny at low taxonomic levels and for DNA barcoding. PLoS ONE 7(4):e35071. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035071
Guo DL, Hou XG, Zhang J (2009) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism analysis of tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa Andrews) cultivars with different flower colours. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 84:131–136
Han XY, Wang LS, Shu QY (2008) Molecular Characterization of tree peony germplasm using sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers. Biochem Genet 46:162–179
Haw SG, Lauener LA (1990) A revision of the infraspecific taxa of Paeonia suffruticosa Andrews. Edinb J Bot 47:273–281
He LX, Li R, Zhang YD (2010) Cytogenetics of the “Dream” hybrid from Paeonia ostii × Paeonia delavayi. J Lanzhou Univ (Natural Sci) 46:70–75
Hong DY (2010) Peonies of the world, taxonomy and phytogeography. Royal Bot Gardens Kew, Missouri Bot Garden, St. Louis, London
Hong DY, Pan KY (1999) A revision of the Paeonia suffruticosa complex (Paeoniaceae). Nordic J Bot 19:289–299
Hosoki T, Kimura D, Hasegawa R, Nagasako T, Nishimoto K, Ohta K, Sugiyama M, Haruki K (1997) Comparative study of Chinese tree peony cultivars by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 70:67–72
Hou XG, Yin WL, Li JJ, Wang HF (2006) AFLP analysis of genetic diversity of 30 tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa Andr.) cultivars. Scientia Agri Sinica 39:1709–1715
Hou XG, Guo DL, Cheng SP, Zhang JY (2011) Development of thirty new polymorphic microsatellite primers for Paeonia suffruticosa. Biol Plantarum 55:708–710
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Li JJ (2005) Chinese tree peony (Xibei, Xinan, Jiangnan Volume). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing, pp 1–205
Li JJ, Zhang XF, Zhao XQ (2011) Chinese tree peonies (In Chinese). Encyclopedia of China Publishing House, Beijing, pp 1–324
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452
Pan J, Zhang DM, Sang T (2007) Molecular phylogenetic evidence for the origin of a diploid hybrid of Paeonia (Paeoniaceae). Am J Bot 94(3):400–408
Suo ZL, Zhou SL, Zhang HJ, Zhang ZM (2004) DNA molecular evidences of the inter-specific hybrids between Paeonia ostii and P. suffruticosa based on ISSR markers. Forest Res 17:700–705 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Suo ZL, Li WY, Yao J, Zhang HJ, Zhang ZM, Zhao DX (2005a) Applicability of leaf morphology and ISSR markers in classification of tree peony cultivars (Paeoniaceae). HortScience 40:329–334
Suo ZL, Zhang HJ, Zhang ZM, Chen FF, Chen FH (2005b) DNA molecular evidences of the hybrids between Paeonia rockii and P. suffruticosa based on ISSR markers. Acta Bot Yunnanica 27:42–48 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Swofford DL (2002) PAUP*: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and related methods). Version 4.0b10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA
Taberlet P, Gielly L, Pautou G, Bouvet J (1991) Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Mol Biol 17:1105–1109
Wang LY (1998) Chinese tree peony. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing, pp 1–213
Wang JX, Xia T, Zhang JM, Zhou SL (2009) Isolation and characterization of fourteen microsatellites from a tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa). Conserv Genet 10:1029–1031
Yuan JH, Cheng FY, Zhou SL (2011) The phylogeographic structure and conservation genetics of the endangered tree peony, Paeonia rockii (Paeoniaceae), inferred from chloroplast gene sequences. Conserv Genet 12:1539–1549
Zhang JM, Wang JX, Xia T, Zhou SL (2009) DNA barcoding: species delimitation in tree peonies. Sci China C Life Sci 52:568–578
Zhang JM, Liu J, Sun HL, Yu J, Wang JX, Zhou SL (2011) Nuclear and chloroplast SSR markers in Paeonia delavayi (Paeoniaceae) and cross-species amplification in P. ludlowii. Am J Bot 98(12):e346–e348
Zhang JJ, Su QY, Liu ZA, Ren HX, Wang LS, Keyser ED (2012) Two EST-derived marker systems for cultivar identification in tree peony. Plant Cell Rep 31:299–310
Zhao X, Zhou ZQ, Lin QB, Pan KY, Hong DY (2008) Phylogenetic analysis of Paeonia sect. Moutan (Paeoniaceae) based on multiple DNA fragments and morphological data. J Syst Evol 46:563–572
Zhou ZQ, Pan KY, Hong DY (2003) Phylogenetic analyses of Paeonia section Moutan (tree peonies, Paeoniaceae) based on morphological data. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica 42:436–446
Zou YP, Cai ML, Wang ZP (1999) Systematic studies on Paeonia sect. Moutan DC. based on RAPD analysis. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica 37:220–227 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 30972412), by the Program of “Guidelines for the Techniques of Molecular Tests of New Plant Varieties” (No. 2007011) of the Science and Technology Development Centre of the State Forestry Administration of China and by the State Forestry Administration of China (Grant 2008-09). The authors thank the following experts for advice and help: Yuping Zou, Shiliang Zhou and Wenpan Dong in molecular experiments, Zhiming Zhang, Xiaoqing Zhao, Wenhai Sun, Jingyu Sun, Jinglian Sun, Baoli Sun, Huijin Zhang, Dezhong Chen, Fuhui Chen, Fufei Chen, Zhipeng Huo and Shulin Zhang in material collection.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. R. Liu.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suo, Z., Zhang, C., Zheng, Y. et al. Revealing genetic diversity of tree peonies at micro-evolution level with hyper-variable chloroplast markers and floral traits. Plant Cell Rep 31, 2199–2213 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1330-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1330-0