Abstract
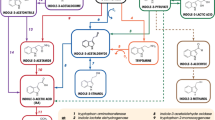
Withanolides are pharmaceutically important C28-phytochemicals produced in most prodigal amounts and diversified forms by Withania somnifera. Metabolic origin of withanolides from triterpenoid pathway intermediates implies that isoprenogenesis could significantly govern withanolide production. In plants, isoprenogenesis occurs via two routes: mevalonate (MVA) pathway in cytosol and non-mevalonate or DOXP/MEP pathway in plastids. We have investigated relative carbon contribution of MVA and DOXP pathways to withanolide biosynthesis in W. somnifera. The quantitative NMR-based biosynthetic study involved tracing of 13C label from 13C1-d-glucose to withaferin A in withanolide producing in vitro microshoot cultures of the plant. Enrichment of 13C abundance at each carbon of withaferin A from 13C1-glucose-fed cultures was monitored by normalization and integration of NMR signal intensities. The pattern of carbon position-specific 13C enrichment of withaferin A was analyzed by a retro-biosynthetic approach using a squalene-intermediated metabolic model of withanolide (withaferin A) biosynthesis. The pattern suggested that both DOXP and MVA pathways of isoprenogenesis were significantly involved in withanolide biosynthesis with their relative contribution on the ratio of 25:75, respectively. The results have been discussed in a new conceptual line of biosynthetic load-driven model of relative recruitment of DOXP and MVA pathways for biosynthesis of isoprenoids.
Key message The study elucidates significant contribution of DOXP pathway to withanolide biosynthesis. A new connotation of biosynthetic load-based role of DOXP/MVA recruitment in isoprenoid biosynthesis has been proposed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam KP, Zapp J (1998) Biosynthesis of the isoprene units of chamomile sesquiterpenes. Phytochemistry 48:953–959
Bouvier F, Rahier A, Camara B (2005) Biogenesis, molecular regulation and function of plant isoprenoids. Prog Lipid Res 44:357–429
Chatterjee S, Srivastava S, Khalid A, Singh N, Sangwan RS, Sidhu OP, Roy R, Khetrapal CL, Tuli R (2010) Comprehensive metabolic fingerprinting of Withania somnifera leaf and root extract. Phytochemistry 71:1085–1094
Chaurasiya ND, Gupta VK, Sangwan RS (2007) Leaf ontogenic phase related dynamics of withaferin A and withanone biogenesis in Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera)—an important medicinal herb. J Plant Biol 50:508–513
Chaurasiya ND, Uniyal GC, Lal P, Misra L, Sangwan NS, Tuli R, Sangwan RS (2008) Analysis of withanolides in root and leaf of Withania somnifera by HPLC with photo diode array and evaporative light scattering detection. Phytochem Anal 19:148–154
Chow KS, Wan KL, Isa MNM, Bahari A, Tan SH, Harikrishna K, Yeang HY (2007) Insights into rubber biosynthesis from transcriptome analysis of Hevea brasiliensis latex. J Exp Bot 58:2429–2440
Cordoba E, Salmi M, León P (2009) Unravelling the regulatory mechanisms that modulate the MEP pathway in higher plants. J Exp Bot 60:2933–2943
De-Eknamkul W, Potduang B (2003) Biosynthesis of β-sitosterol and stigmasterol in Croton sublyratus proceeds via a mixed origin of isoprene units. Phytochemistry 62:389–398
Dudareva N, Andersson S, Orlova L, Gatto N, Rhodes D, Boland W, Gershenzon J (2005) The nonmevalonate pathway supports both monoterpene and sesquiterpene formation in snapdragon flowers. Proceed Natl Acad Sci 102:933–938
Hampel D, Mosandl A, Wüst M (2005) Biosynthesis of mono- and sesquiterpenes in carrot roots and leaves (Daucus carota L.): metabolic cross talk of cytosolic mevalonate and plastidial methylerythritol phosphate pathways. Phytochemistry 66:305–311
Hampel D, Mosandl A, Wüst W (2006) Biosynthesis of mono- and sesquiterpenes in strawberry fruits and foliage: 2H labeling studies. J Agric Food Chem 54:1473–1478
Hazarika BN (2006) Morpho-physiological disorders in in vitro culture of plants. Sci Hort 108:105–120
Hemmerlin A, Harwood JL, Bach TJ (2012) A raison d’être for two distinct pathways in the early steps of plant isoprenoid biosynthesis? Prog Lipid Res 51:95–148
Kuboyama T, Tohda C, Komatsu K (2005) Neuritic regeneration and synaptic reconstruction induced by withanolide A. Brit J Pharmacol 144:961–971
Lichtenthaler HK (1999) 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:47–65
Madina BR, Sharman LK, Chaturvedi P, Sangwan RS, Tuli R (2007) Purification and physico-kinetic characterization of 3β-hydroxy specific sterol glucosyltransferase from Withania somnifera (L) and its stress response. Biochim Biophys Acta 1774:392–402
Mandal C, Dutta A, Mallick A, Chandra S, Misra L, Sangwan RS, Mandal C (2008) Withaferin A induces apoptosis by activating p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascade in leukemic cells of lymphoid and myeloid origin in a transcription-dependent manner through mitochondrial death cascade. Apoptosis 13:1450–1464
Misra L, Lal P, Sangwan RS, Sangwan NS, Uniyal GC, Tuli R (2005) Unusually sulfated and oxygenated steroids from Withania somnifera. Phytochemistry 66:2702–2707
Misra L, Mishra P, Pandey A, Sangwan RS, Sangwan NS, Tuli R (2008) Withanolides from Withania somnifera roots. Phytochemistry 69:1000–1004
Mondal S, Mandal C, Sangwan RS, Chandra S, Mandal C (2010) Withanolide D induces apoptosis in leukemia by targeting the activation of neutral sphingomyelinase-ceramide cascade mediated by synergistic activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol Cancer 9:239–255
Munoz-Bertomeu J, Sales E, Ros R, Arrillaga I (2007) Up-regulation of an N-terminal truncated 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase enhances production of essential oils and sterols in transgenic Lavandula latifolia. Plant Biotech J 5:746–758
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays Tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Palazón J, Cusidó RM, Bonfill M, Morales C, Piñol MT (2003) Inhibition of paclitaxel and baccatin III accumulation by mevinolin and fosmidomycin in suspension cultures of Taxus baccata. J Biotechnol 10:157–163
Radochova B, Ticha L (2009) Leaf anatomy during leaf development of photoautotrophically in vitro-grown tobacco plants as affected by growth irradiance. Biol Plant 53:21–27
Rohmer M (2003) Mevalonate-independent methylerythritol phosphate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis elucidation and distribution. Pure Appl Chem 75:375–387
Sabir F, Sangwan RS, Chaurasiya ND, Misra L, Sangwan RS (2008) In vitro withanolide production by Withania somnifera L. cultures. Z Naturforsch 63C:409–412
Sabir F, Sangwan RS, Singh J, Misra LN, Pathak N, Sangwan NS (2011) Biotransformation of withanolides by cell suspension cultures of Withania somnifera (Dunal.). Plant Biotech Rep 5:127–134
Sabir F, Sangwan RS, Kumar R, Sangwan NS (2012) Salt stress-induced responses in growth and metabolism in callus cultures and differentiating in vitro shoots of Indian ginseng (Withania somnifera Dunal). J Plant Growth Regul (in press, doi: 10.1007/s00344-012-9264-x)
Samina A, Husaini AM, Abdin MZ, Rather GM (2009) Overexpression of the HMG‐CoA reductase gene leads to enhanced artemisinin biosynthesis in transgenic Artemisia annua plants. Plant Med 75:1453–1458
Sangwan RS, Chaurasiya ND, Lal P, Misra L, Uniyal GC, Tuli R, Sangwan NS (2007) Withanolide A biogeneration in in vitro shoot cultures of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera Dunal)—a main medicinal plant of Ayurveda. Chem Pharm Bull 55:1371–1375
Sangwan RS, Chaurasiya ND, Lal P, Misra L, Tuli R, Sangwan NS (2008) Withanolide A is inherently de novo biosynthesized in roots of the medicinal plant Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera). Physiol Plant 133:278–287
Sato Y, Ito Y, Okada S, Murakami M, Abe H (2003) Biosynthesis of the triterpenoids, botryococcenes and tetramethylsqualene in the B race of Botryococcus braunii via the non-mevalonate pathway. Tetrahed Lett 44:7035–7037
Schuhr CA, Radykewicz T, Sagner S, Latzel C, Zenk MH, Arigoni D, Bacher A, Rohdich F, Eisenreich W (2003) Quantitative assessment of crosstalk between the two isoprenoid biosynthesis pathways in plants by NMR spectroscopy. Phytochem Rev 2:3–16
Sehgal N, Gupta A, Valli RK, Joshi SD, Mills JT, Hamel E, Khanna P, Jain SC, Thakur SS, Rabindranath V (2012) Withania sonimnifera reverses Alzheimer’s disease pathology by enhancing low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in liver. Proceed Natl Acad Sci 109:3510–3515
Sharma LK, Madina BR, Chaturvedi P, Sangwan RS, Tuli R (2007) Molecular cloning and characterization of one member of 3β-hydroxy sterol glucosyltransferase gene family in Withania somnifera. Arch Biochem Biophys 460:48–55
Skorupinska-Tudek K, Poznanski J, Wojcik J, Bienkowski T, Szostkiewicz I, Zelman-Femiak M, Bajda A, Chojnacki T, Olszowska O, Grunler J, Meyer O, Rohmer M, Danikiewicz W, Swiezewska E (2008) Contribution of the mevalonate and methylerythritol phosphate pathways to the biosynthesis of dolichols in plants. J Biol Chem 283:21024–21035
Towler MJ, Weathers PJ (2007) Evidence of artemisinin production from IPP stemming from both the mevalonate and the nonmevalonate pathways. Plant Cell Rep 26:2129–2136
Tuli R, Sangwan RS (2009) Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera)—a model Indian medicinal plant. Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi
Van Klink J, Becker H, Anderson S, Boland W (2003) Biosynthesis of anthecotuloide, an irregular sesquiterpene lactone from Anthemis cotula L. (Asteraceae) via a non-farnesyl diphosphate route. Org Biomol Chem 1:1503–1508
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to CSIR, New Delhi, for the financial support in the form of a NMITLI Project on Ashwagandha and to Director, CIMAP for providing the requisite facilities. FS also thanks CSIR, India, for the Senior Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Kumar.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaurasiya, N.D., Sangwan, N.S., Sabir, F. et al. Withanolide biosynthesis recruits both mevalonate and DOXP pathways of isoprenogenesis in Ashwagandha Withania somnifera L. (Dunal). Plant Cell Rep 31, 1889–1897 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1302-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1302-4