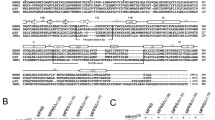
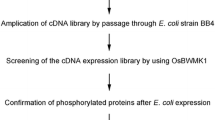
Abstract
Arabidopsis MAP kinase phosphatase 1 (AtMKP1) is a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MPK) phosphatase family, which negatively regulates AtMPKs. We have previously shown that AtMKP1 is regulated by calmodulin (CaM). Here, we examined the phosphorylation of AtMKP1 by its substrate AtMPK6. Intriguingly, AtMKP1 was phosphorylated by AtMPK6, one of AtMKP1 substrates. Four phosphorylation sites were identified by phosphoamino acid analysis, TiO2 chromatography and mass spectrometric analysis. Site-directed mutation of these residues in AtMKP1 abolished the phosphorylation by AtMPK6. In addition, AtMKP1 interacted with AtMPK6 as demonstrated by the yeast two-hybrid system. Finally, the phosphatase activity of AtMKP1 increased approximately twofold following phosphorylation by AtMPK6. By in-gel kinase assays, we showed that AtMKP1 could be rapidly phosphorylated by AtMPK6 in plants. Our results suggest that the catalytic activity of AtMKP1 in plants can be regulated not only by Ca2+/CaM, but also by its physiological substrate, AtMPK6.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreasson E, Ellis B (2009) Convergence and specificity in the Arabidopsis MAPK nexus. Trends Plant Sci 15:106–113
Bartels S, Anderson JC, González Besteiro MA, Carreri A, Hirt H, Buchala A, Métraux J-P, Peck SC, Ulm R (2009) MAP kinase phosphatase1 and protein tyrosine phosphatase1 are repressors of salicylic acid synthesis and SNC1-mediated responses in Arabidopsis. Plant cell 21:2884–2897
Bartels S, González Besteiro MA, Lang D, Ulm R (2010) Emerging functions for plant MAP kinase phosphatases. Trends Plant Sci 15:322–329
Brondello JM, Pouysségur J, McKenzie FR (1999) Reduced MAP kinase phosphatase-1 degradation after p42/p44MAPK-dependent phosphorylation. Science 286:2514–2517
Camps M, Nichols A, Gillieron C, Antonsson B, Muda M, Chabert C, Boschert U, Arkinstall S (1998) Catalytic activation of the phosphatase MKP-3 by ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science 280:1262–1265
Chen L, Montserat J, Lawrence DS, Zhang ZY (1996) VHR and PTP1 protein phosphatases exhibit remarkably different active site specificities toward low molecular weight nonpeptidic substrates. Biochemistry 35:9349–9354
Chen P, Hutter D, Yang X, Gorospe M, Davis RJ, Liu Y (2001) Discordance between the binding affinity of mitogen-activated protein kinase subfamily members for MAP kinase phosphatase-2 and their ability to activate the phosphatase catalytically. J Biol Chem 276:29440–29449
Cohen P (1997) The search for physiological substrates of MAP and SAP kinases in mammalian cells. Trends Cell Biol 7:353–361
Colcombet J, Hirt H (2008) Arabidopsis MAPKs: a complex signaling network involved in multiple biological processes. Biochem J 413:217–226
Davis RJ (2000) Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103:239–252
Droillard M, Boudsocq M, Barbier-Brygoo H, Laurière C (2002) Different protein kinase families are activated by osmotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana cell suspensions. Involvement of the MAP kinases AtMPK3 and AtMPK6. FEBS Lett 527:43–50
Ebisuya M, Kondoh K, Nishida E (2005) The duration, magnitude and compartmentalization of ERK MAP kinase activity: mechanisms for providing signaling specificity. J Cell Sci 118:2997–3002
Fauman EB, Saper MA (1996) Structure and function of the protein tyrosine phosphatases. Trends Biochem Sci 21:413–417
Gómez AR, López-Varea A, Molnar C, de la Calle-Mustienes E, Ruiz-Gómez M, Gómez-Skarmeta JL, de Celis JF (2005) Conserved cross-interactions in Drosophila and Xenopus between Ras/MAPK signaling and the dual-specificity phosphatase MKP3. Dev Dyn 232:695–708
Gottlin EB, Xu X, Epstein DM, Burke SP, Eckstein JW, Ballou DP, Dixon JE (1996) Kinetic analysis of the catalytic domain of human cdc25B. J Biol Chem 271:27445–27449
Ichimura K et al (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci 7:301–308
Katou S, Katrita E, Yamakawa H, Seo S (2005) Catalytic activation of the plant MAPK phosphatase NtMKP1 by its physiological substrate salicylic acid-induced protein kinase but not by calmodulins. J Biol Chem 280:39569–39581
Kerk D, Bulgrien J, Smith DW, Barsam B, Veretnik S, Gribskov M (2002) The complement of protein phosphatase catalytic subunits encoded in the genome of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 129:908–925
Keyse SM (2008) The regulation of stress-activated MAP kinase signaling by protein phosphatases. Topics Curr Genet 20:33–49
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (2001) Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 81:807–869
Larsen MR, Thingholm TE, Jensen ON, Roepstorff P, Jørgensen TJ (2005) Highly selective enrichment of phosphorylated peptides from peptide mixtures using titanium dioxide microcolumns. Mol Cell Proteomics 4:873–886
Lee K, Song EH, Kim HS, Yoo JH, Han HJ, Jung MS, Lee SM, Kim KE, Kim MC, Cho MJ, Chung WS (2008) Regulation of MAP kinase phosphatase 1 (AtMKP1) by calmodulin in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 283:23581–23588
Li C, Scott DA, Hatch E, Tian X, Mansour SL (2007) Dusp6 (Mkp3) is a negative feedback regulator of FGF-stimulated ERK signaling during mouse development. Development 134:167–176
Liu Y, Zhang S (2004) Phosphorylation of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase by MPK6, a stress-responsive mitogen-activated protein kinase, induces ethylene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:3386–3399
Marshall CJ (1995) Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell 80:179–185
Martin-Blanco E, Gampel A, Ring J, Virdee K, Kirov N, Tolkovsky AM, Martinez-Arias A (1998) puckered encodes a phosphatase that mediates a feedback loop regulating JNK activity during dorsal closure in Drosophila. Genes Dev 12:557–570
McClean MN, Mody A, Broach JR, Ramanathan S (2007) Cross-talk and decision making in MAP kinase pathways. Nat Genet 39:409–414
Meskiene I, Baudouin E, Schweighofer A, Liwosz A, Jonak C, Rodriguez PL, Jelinek H, Hirt H (2003) Stress-induced protein phosphatase 2C is a negative regulator of a mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 278:18945–18952
Slack DN, Seternes OM, Gabrielsen M, Keyse SM (2001) Distinct binding determinants for ERK2/p38alpha and JNK map kinases mediate catalytic activation and substrate selectivity of map kinase phosphatase-1. J Biol Chem 276:16491–16500
Stewart AE, Dowd S, Keyse SM, McDonald NQ (1999) Crystal structure of the MAPK phosphatase Pyst1 catalytic domain and implications for regulated activation. Nat Struct Biol 6:174–181
Teige M, Scheikl E, Eulgem T, Dóczi R, Ichimura K, Shinozaki K, Dangl JL, Hirt H (2004) The MKK2 pathway mediates cold and salt stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 15:141–152
Thingholm TE, Jørgensen TJ, Jensen ON, Larsen MR (2006) Highly selective enrichment of phosphorylated peptides using titanium dioxide. Nat Protoc 1:1929–1935
Trewavas AJ, Malhó R (1997) Signal perception and transduction: the origin of the phenotype. Plant Cell 9:1181–1195
Ulm R, Revenkova E, di Sansebastiano GP, Bechtold N, Paszkowski J (2001) Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase is required for genotoxic stress relief in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 15:699–709
Ulm R, Ichimura K, Mizoguchi T, Peck SC, Zhu T, Wang X, Shinozaki K, Paszkowski J (2002) Distinct regulation of salinity and genotoxic stress responses by Arabidopsis MAP kinase phosphatase 1. EMBO J 21:6483–6493
Widmann C, Gibson S, Jarpe MB, Johson GL (1999) Mitogen-activated protein kinase: conservation of a three-kinase module from yeast to human. Physiol Rev 79:143–180
Xu SM, Wang XC, Chen J (2007) Zinc finger protein 1 (ThZF1) from salt cress (Thellungiella halophila) is a Cys-2/His-2-type transcription factor involved in drought and salt stress. Plant Cell Rep 26:497–506
Yuvaniyama J, Denu JM, Dixon JE, Saper MA (1996) Crystal structure of the dual specificity protein phosphatase VHR. Science 272:1328–1331
Zhan XL, Deschenes RJ, Guan KL (1997) Differential regulation of FUS3 MAP kinase by tyrosine-specific phosphatases PTP2/PTP3 and dual-specificity phosphatase MSG5 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev 11:1690–1702
Zhang S, Jin CD, Roux SJ (1993) Casein kinase II-type protein kinase from pea cytoplasm and its inactivation by alkaline phosphatase in vitro. Plant Physiol 103:955–962
Zhou B, Zhang ZY (1999) Mechanism of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-3 activation by ERK2. J Biol Chem 274:35526–35534
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Hans J. Bohnert for critical reading and insightful comments. This work was supported by grants from World Class University program (R32-10148) and Basic Science Research Program (2010-0010607) of National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by MOEST, Korea. KEK was supported by scholarships from the BK21 program of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. R. Liu.
H. C. Park, E. H. Song, and X. C. Nguyen contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, H.C., Song, E.H., Nguyen, X.C. et al. Arabidopsis MAP kinase phosphatase 1 is phosphorylated and activated by its substrate AtMPK6. Plant Cell Rep 30, 1523–1531 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1064-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1064-4