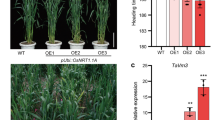
Abstract
Drought and high-salinity are the important constraints that severely affect plant development and crop yield worldwide. It has been established that ethylene response factor (ERF) proteins play important regulatory roles in plant response to abiotic and biotic stresses. Our previous researches have revealed that transgenic tobacco over-expressing TERF1 (encoding a tomato ERF protein) showed enhanced tolerance to abiotic stress. Here, we further investigate the function of TERF1 in transgenic rice. Compared with the wild-type plants, overexpression of TERF1 resulted in an increased tolerance to drought and high-salt in transgenic rice. And the enhanced tolerance may be associated with the accumulation of proline and the decrease of water loss. Furthermore, TERF1 can effectively regulate the expression of stress-related functional genes Lip5, Wcor413-l, OsPrx and OsABA2, as well as regulatory genes OsCDPK7, OsCDPK13 and OsCDPK19 under normal growth conditions. Our analyses of cis-acting elements show that there exist DRE/CRT and/or GCC-box existing in TERF1 targeted gene promoters. Our results revealed that ectopic expression of TERF1 in rice caused a series of molecular and physiological alterations and resulted in the transgenic rice with enhanced tolerance to abiotic stress, indicating that TERF1 might have similar regulatory roles in response to abiotic stress in tobacco and rice.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi F, Onodera H, Toki S, Tanaka H, Komatsu S (2004) OsCDPK13, a calcium-dependent protein kinase gene from rice, is induced by cold and gibberellin in rice leaf sheath. Plant Mol Biol 55:541–552
Abe H, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Urao T, Iwasaki T, Hosokawa D, Shinozaki K (1997) Role of Arabidopsis MYC and MYB homologs in drought- and abscisic acid-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 10:1859–1868
Agarwal P, Agarwal P, Reddy M, Sopory S (2006) Role of DREB transcription factors in abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in plants. Plant Cell Rep 25:1263–1274
Agrawal G, Yamazaki M, Kobayashi M, Hirochika R, Miyao A, Hirochika H (2001) Screening of the rice viviparous mutants generated by endogenous retrotransposon tos17 insertion. Tagging of a zeaxanthin epoxidase gene and a novel ostatc gene. Plant Physiol 125:1248–1257
Bartels D, Sunkar R (2005) Drought and salt tolerance in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 24:23–58
Bates L, Waldren R, Teare I (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Breton G, Danyluk J, Charron J, Sarhan F (2003) Expression profiling and bioinformatic analyses of a novel stress-regulated multispanning transmembrane protein family from cereals and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 32:64–74
Cao Y, Song F, Goodman R, Zheng Z (2006) Molecular characterization of four rice genes encoding ethylene-responsive transcriptional factors and their expressions in response to biotic and abiotic stress. J Plant Physiol 163:1167–1178
de los Reyes B, Morsy M, Gibbons J, Varma T, Antoine W, McGrath J, Halgren R, Redus M (2003) A snapshot of the low temperature stress transcriptome of developing rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) via ESTs from subtracted cDNA library. Theor Appl Genet 107:1071–1082
Desikan R, Cheung M, Bright J, Henson D, Hancock J, Neill S (2004) ABA, hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide signalling in stomatal guard cells. J Exp Bot 55:205–212
De Smet I, Zhang H, Inzé D, Beeckman T (2006) A novel role for abscisic acid emerges from underground. Trends Plant Sci 11:434–439
Dietz KJ (2003) Plant peroxiredoxins. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:93–107
Dubouzet J, Sakuma Y, Ito Y, Kasuga M, Doubouzet E, Miura S, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) OsDREB genes in rice, Oryza sativa L., encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression. Plant J 33:751–763
Eulgem T, Somssich IE (2007) Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:366–371
Fukao T, Xu K, Ronald P, Bailey-Serresa J (2006) A variable cluster of ethylene-responsive-like factors regulates metabolic and developmental acclimation responses to submergence in rice. Plant Cell 18:2021–2034
Gorantla M, Babu P, Reddy Lachagari V, Reddy A, Wusirika R, Bennetzen J, Reddy A (2007) Identification of stress-responsive genes in an indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) using ESTs generated from drought-stressed seedlings. J Exp Bot 58:253–265
Hirayama T, Shinozaki K (2007) Perception and transduction of abscisic acid signals: keys to the function of the versatile plant hormone ABA. Trends Plant Sci 12:343–351
Hong Z, Lakkineni K, Zhang Z, Verma D (2000) Removal of feedback inhibition of delta(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase results in increased proline accumulation and protection of plants from osmotic stress. Plant Physiol 122:1129–1136
Horling F, Lamkemeyer P, Konig J, Finkemeier I, Baier M, Kandlbinder A, Dietz K (2003) Divergent light-, ascorbate- and oxidative stress-dependent regulation of expression of the peroxiredoxin gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 131:317–325
Hu H, Dai M, Yao J, Xiao B, Li X, Zhang Q, Xiong L (2006) Overexpressing a NAM, ATAF, and CUC (NAC) transcription factor enhances drought resistance and salt tolerance in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12987–12992
Huang Z, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Zhang H, Huang D, Huang R (2004) Tomato TERF1 modulates ethylene response and enhances osmotic stress tolerance by activating expression of downstream genes. FEBS Lett 573:110–116
Ito Y, Katsura K, Maruyama K, Taji T, Kobayashi M, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2006) Functional analysis of rice DREB1/CBF-type transcription factors involved in cold-responsive gene expression in transgenic rice. Plant Cell Physiol 47:141–153
Karaba A, Dixit S, Greco R, Aharoni A, Trijatmiko K, Marsch-Martinez N, Krishnan A, Nataraja K, Udayakumar M, Pereira A (2007) Improvement of water use efficiency in rice by expression of HARDY, an Arabidopsis drought and salt tolerance gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15270–15275
Kishor P, Sangam S, Amrutha R, Laxmi P, Naidu K, Rao K, Rao S, Reddy K, Theriappan P, Sreenivasulu N (2005) Regulation of proline biosynthesis, degradation, uptake and transport in higher plants: its implications in plant growth and abiotic stress tolerance. Curr Sci 88:424–438
Klimecka M, Muszyńska G (2007) Structure and functions of plant calcium-dependent protein kinases. Acta Biochim Pol 54:219–233
Lan L, Li M, Lai Y, Xu W, Kong Z, Ying K, Han B, Xue Y (2005) Microarray analysis reveals similarities and variations in genetic programs controlling pollination/fertilization and stress responses in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 59:151–164
Lee B, Henderson D, Zhu J (2005) The Arabidopsis cold-responsive transcriptome and its regulation by ICE1. Plant Cell 17:3155–3175
Liu J, Zhang Z, Qin Q, Peng R, Xiong A, Chen J, Xu F, Zhu H, Yao Q (2007) Isolated and characterization of a cDNA encoding ethylene-responsive element binding protein (EREBP)/AP2-type protein, RCBF2, in Oryza sativa L. Biotechnol Lett 29:165–173
Mahajan S, Tuteja N (2005) Cold, salinity and drought stresses: an overview. Arch Biochem Biophys 444:139–158
Nambara E, Marion-Poll A (2005) Abscisic acid biosynthesis and catabolism. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:165–185
Nanjo T, Kobayashi M, Yoshiba Y, Sanada Y, Wada K, Tsukaya H, Kakubari Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1999) Biological functions of proline in morphogenesis and osmotolerance revealed in antisense transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 18:185–193
Nayyar H, Walia D (2003) Water stress induced proline accumulation in contrasting wheat genotypes as affected by calcium and abscisic acid. Biol plant 46:275–279
Oh S, Song S, Kim Y, Jang H, Kim S, Kim M, Kim Y, Nahm B, Kim J (2005) Arabidopsis CBF3/DREB1A and ABF3 in transgenic rice increased tolerance to abiotic stress without stunting growth. Plant Physiol 138:341–351
Oh S, Kwon C, Choi D, Song S, Kim J (2007) Expression of barley HvCBF4 enhances tolerance to abiotic stress in transgenic rice. Plant Biotechnol J 5:646–656
Rabbani M, Maruyama K, Abe H, Khan M, Katsura K, Ito Y, Yoshiwara K, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Monitoring expression profiles of rice genes under cold, drought, and high-salinity stresses and abscisic acid application using cDNA microarray and RNA gel-blot analyses. Plant Physiol 133:1755–1767
Reddy V, Reddy A (2004) Proteomics of calcium-signaling components in plants. Phytochemistry 65:1745–1776
Rontein D, Basset G, Hanson A (2002) Metabolic engineering of osmoprotectant accumulation in plants. Metab Eng 4:49–56
Saijo Y, Hata S, Kyozuka J, Shimamoto K, Izui K (2000) Over-expression of a single Ca2+-dependent protein kinase confers both cold and salt/drought tolerance on rice plants. Plant J 23:319–327
Saijo Y, Kinoshita N, Ishiyama K, Hata S, Kyozuka J, Hayakawa T, Nakamura T, Shimamoto K, Yamaya T, Izui K (2001) A Ca2+-dependent protein kinase that endows rice plants with cold- and salt-stress tolerance functions in vascular bundles. Plant Cell Physiol 42:1228–1233
Screenivasulu N, Sopory S, KaviKishor P (2007) Deciphering the regulatory mechanisms of abiotic stress tolerance in plants by genomic approaches. Gene 388:1–13
Seki M, Narusaka M, Ishida J, Nanjo T, Fujita M, Oono Y, Kamiya A, Nakajima M, Enju A, Sakurai T, Satou M, Akiyama K, Taji T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Carninci P, Kawai J, Hayashizaki Y, Shinozaki K (2002) Monitoring the expression profiles of 7000 Arabidopsis genes under drought, cold and high-salinity stresses using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant J 31:279–292
Seki M, Umezawa T, Urano K, Shinozaki K (2007) Regulatory metabolic networks in drought stress responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:296–302
Siripornadulsil S, Traina S, Verma D, Sayre R (2002) Molecular mechanisms of proline-mediated tolerance to toxic heavy metals in transgenic microalgae. Plant Cell 14:2837–2847
Skopelitis D, Paranychianakis N, Paschalidis K, Pliakonis E, Delis I, Yakoumakis D, Kouvarakis A, Papadakis A, Stephanou E, Roubelakis-Angelakisa K (2006) Abiotic stress generates ROS that signal expression of anionic glutamate dehydrogenases to form glutamate for proline synthesis in tobacco and grapevine. Plant Cell 18:2767–2781
Su J, Wu R (2004) Stress-inducible synthesis of proline in transgenic rice confers faster growth under stress conditions than that with constitutive synthesis. Plant Sci 166:941–948
Tran LS, Nakashima K, Sakuma Y, Simpson SD, Fujita Y, Maruyama K, Fujita M, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2004) Isolation and functional analysis of Arabidopsis stress-inducible NAC transcription factors that bind to a drought-responsive cis-element in the early responsive to dehydration stress 1 promoter. Plant Cell 9:2481–2498
Tuberosa R, Salvi S (2006) Genomics-based approaches to improve drought tolerance of crops. Trends Plant Sci 11:405–412
Valliyodan B, Nguyen H (2006) Understanding regulatory networks and engineering for enhanced drought tolerance in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:1–7
Verslues P, Zhu J (2005) Before and beyond ABA: upstream sensing and internal signals that determine ABA accumulation and response under abiotic stress. Biochem Soc Trans 33:375–379
Vieira Dos Santos C, Rey P (2006) Plant thioredoxins are key actors in the oxidative stress response. Trends Plant Sci 11:329–334
Wan B, Lin Y, Mou T (2007) Expression of rice Ca2+-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs) genes under different environmental stresses. FEBS Lett 581:1179–1189
Xu K, Xu X, Fukao T, Canlas P, Maghirang-Rodriguez R, Heuer S, Ismail A, Bailey-Serres J, Ronald P, Mackill D (2006) Sub1A is an ethylene-response-factor-like gene that confers submergence tolerance to rice. Nature 442:705–708
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2005) Organization of cis-acting regulatory elements in osmotic- and cold-stress-responsive promoters. Trends Plant Sci 10:88–94
Zhang Q (2007) Strategies for developing Green Super Rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:16402–16409
Zhang X, Zhang Z, Chen J, Chen Q, Wang X, Huang R (2005) Expressing TERF1 in tobacco enhances drought tolerance and abscisic acid sensitivity during seedling development. Planta 222:494–501
Zhou J, Wang X, Jiao Y, Qin Y, Liu X, He K, Chen C, Ma L, Wang J, Xiong L, Zhang Q, Fan L, Deng X (2007) Global genome expression analysis of rice in response to drought and high-salinity stresses in shoot, flag leaf, and panicle. Plant Mol Biol 63:591–608
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos 30730060, 30525034) and the National Basic Research Program of China (2006CB1001002; 2006CB101700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W.-H. Wu.
Shumei Gao, Haiwen Zhang and Yun Tian contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, S., Zhang, H., Tian, Y. et al. Expression of TERF1 in rice regulates expression of stress-responsive genes and enhances tolerance to drought and high-salinity. Plant Cell Rep 27, 1787–1795 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0602-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0602-1