Abstract
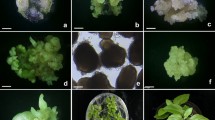
An efficient system for the establishment and multiplication of highly prolific embryogenic cell cultures of grapevine (Vitis sp.) was developed. Using anther-derived pro-embryogenic masses as starting material, cell suspensions of different grapevine cultivars (Tempranillo, Cabernet-Sauvignon) and rootstocks (Kober 125 AA, Kober 5 BB, 110 Richter) were initiated in liquid medium containing NOA (1.0 mg l-1) and BAP (0.25 mg l-1) as growth regulators. Conditioned medium was recovered and utilised for establishing new, highly totipotent cell cultures. The suspensions obtained, showed embryogenic competence resulting in somatic embryo induction and subsequent plant regeneration. In this study, a simplified establishment procedure for grapevine embryogenic cell suspension allowing the fast multiplication of embryogenic material is described. Evidence for the promoting effect of the protein fraction derived from conditioned medium, on cell proliferation was found. In bioassays, addition of ß-d-GlcY affect cell proliferation suggesting that arabinogalactan proteins are required for growth processes in grapevine cell cultures.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AGPs:
-
Arabinogalactan-proteins
- BAP:
-
6-benzylaminopurine
- ß-D-Glc-Y:
-
ß-d-Glucosyl Yariv phenylglycoside
- CEPF:
-
Concentrated extra-cellular protein fraction
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- EP:
-
Extra-cellular protein
- NOA:
-
Naphthoxyacetic acid
- MES:
-
2-(N-Morpholino) ethanesulfonic acid
- FM:
-
Fresh medium
- CM:
-
Conditioned medium
- PEM:
-
Pro-embryogenic masses
- PCV:
-
Packed cell volume
References
Becraft PW (1998) Receptor kinases in plant development. Trends Plant Sci 3:384–388
Burnette WN (1981) “Western blotting”: electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem 112:195–203
Butowt R, Niklas A, Rodriguez-Garcia MI, Majewska-Sawka A (1999) Involvement of JIM13- and JIM8-responsive carbohydrate epitopes in early stages of cell formation. J Plant Res 112:107–116
Chapman A, Blervacq AS, Vasseur J, Hilbert JL (2000) Arabinogalactan-proteins in Cichorium somatic embryogenesis: effect of beta-glucosyl Yariv reagent and epitope localisation during embryo development. Planta 211:305–314
Coutos-Thévenot P, Goebel-Tourand I, Mauro MC, Jouanneau JP, Boulay M, Deloire A, Guern J (1992a Somatic embryogenesis from grapevine cells. I-Improvement of embryo development by changes in culture conditions. Plant Cell Tiss Org 29:125–133
Coutos-Thévenot P, Maes O, Jouenne T, Mauro MC, Jouanneau JP, Boulay M, Deloire A, Guern J (1992b Extracellular protein patterns of grapevine cell suspensions in embryogenic and non-embryogenic situations. Plant Sci 86:137–145
De Jong AJ, Cordewener J, Lo Schiavo F, Terzi M, Vanderkerckhove J, Van Kammen A, De Vries SC (1992) A carrot somatic embryo mutant is rescued by chitinase. Plant Cell 4:425–433
De Jong AJ, Heidstra R, Spaink HP, Vartog MV, Meijer EA, Hendriks T, Schiavo FL, Terzi M, Bisseling T, Van Kammen A, De Vries SC (1993) Rhizobium lipooligosaccharides rescue a carrot somatic embryo mutant. Plant Cell 5:615–620
Dussert S, Mauro MC, Engelmann F (1992) Cryopreservation of grape embryogenic cell suspensions. II-Influence of post-thaw culture conditions and application to differents strains. Cryo Lett 13:15–22
Dyachock JV, Wiweger M, Kenne L, Von Arnold S (2002) Endogenous Nod-factor-like signal molecules promote early somatic embryo development in Norway spruce. Plant Physiol 128:523–533
Guan Y, Nothnagel EA. (2004) Binding of Arabinogalactan proteins by Yariv phenylglycoside triggers wound-like responses in Arabidopsis cell cultures. Plant Physiol 135(3):1346–1366
Gupta DS, Conger BV (1999) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from suspension cultures of Switchgrass. Crop Sci 39:243–247
Hebert D, Kikkert JR, Smith FD, Reisch BI (1993) Optimization of biolistic transformation of embryogenic grape cell suspensions. Plant Cell Rep 12:585–589
Immerzeel P, Schols HA, Voragen AGJ, De Vries S (2004) Different arabinogalactan proteins are present in carrot (Daucus carota) cell culture medium and in seeds. Physiol Plant 122:181–190
Immerzeel P, Eppink MM, De Vries S, Schols HA, Voragen AGJ (2006) Carrot arabinogalactan proteins are interlinked with pectins. Physiol Plant 128:18–27
Jayasankar S, Gray DJ, Litz RE (1999) High-efficiency somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from suspension cultures of grapevine. Plant Cell Rep 18:533–537
Jayasankar S, Van Aman M, Li Z, Gray DJ (2001) Direct seeding of grapevine somatic embryos and regeneration of plants. In Vitro Cell Dev Plant 37:476–479
Jayasankar S, Bonbada BR, Li Z, Gray DJ (2003) Comparative anatomy and morphology of Vitis vinifera (Vitaceae) somatic embryos from solid- and liquid-culture-derived proembryogenic masses. Am J Bot 90:973–979
Jermyn MA (1978) Comparative specificity of concanavalin A and the ß-lectins. Aust J Plant Physiol 5:687–696
Kaparakis G, Alderson G (2003) Enhancement of in vitro cell proliferation of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) by pluronic F-68, haemoglobin and arabinogalactan proteins. J Hortic Sci Biotech 78:647–649
Kikkert JR, Hubert D, Wallace PG, Streim MJ, Reisch BI (1996) Transgenic plantlets of “Chancellor” grapevine Vitis sp. from biolistic transformation of embryogenic cell suspensions. Plant Cell Rep 15:311–316
Kim YJ, Park T, Kim HS, Such SK, Kim HS, Yun SJ (2004) Effective multiplication of somatic embryos using suspension culture and regeneration in soybean. J Plant Biotech 6:91–96
Kimberly JL, Nothnagel EA (1997) Cell surface arabinogalactan-proteins and their relation to cell proliferation and viability. Protoplasma 196:87–98
Maes O, Coutos-Thevenot P, Jouenne T, Boulay M, Guern J (1997) Influence of extracellular proteins, proteases and protease inhibitors on grapevine somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Org 50:97–105
Majewska-Sawka A, Nothnagel E (2000) The multiple roles of arabinogalactan proteins in plant development. Plant Physiol 122:3–9
Martinelli L, Gribaudo I (2001) Somatic embryogenesis in grapevine. In: Roubelakis-Angelakis KA (ed) Molecular biology and biotechnology of the grapevine. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 327–351
Massonneau A, Coronado MJ, Audran A, Bagniewska A, Mol R, Testillano PS, Goralski G, Dumas C, Rieueno MC, Matthys-Rochon E (2005) Multicellular structures developing during maize microspore culture express endosperm and embryo-specific genes and show different embryogenic potentialities. Eur J Cell Biol 84:663–675
Matthys-Rochon E (2005) Secreted molecules and their role in embryo formation in plants: a mini review. Acta Biol Cracov Bot 47:23–29
Mau SL, Chen CG, Pu ZY, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ, Bacic A, Clarke AE (1995) Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding the protein backbones of arabinogalactan-proteins from the filtrate of suspension-cultured cells of Pyrus communis and Nicotiana alata. Plant J 8:269–281
Mauro MC, Nef C, Fallot J (1986) Stimulation of somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from anther culture of Vitis vinifera cv. Cabernet-Sauvignon. Plant Cell Rep 5:377–380
Nitsch JP, Nitsch C (1969) Haploid plants from pollen grains. Science 163:85–87
Oropeza M, Marcano AK, Garcia ED (2001) Proteins related with embryogenic potential in callus and cell suspensions of sugarcane (Saccharum sp.). In Vitro Cell Dev Plant 37:211–216
Pennell RI, Knox JP, Scofield GN, Selvendran RR, Roberts K (1989) A family of abundant plasma membrane-associated glycoproteins related to arabinogalactan proteins is unique to flowering plants. J Cell Biol 108:1967–1977
Perl A, Lotan O, Abu-Abied M, Holland D (1996) Establishment of an Agrobacterium-mediated transformation system for grape (Vitis vinifera L.): the role of antioxidants during grape-Agrobacterium interactions. Nature Biotechnol 14:624–628
Qin Y, Zhao J (2006) Localization of arabinogalactan proteins in eggs cells, zygotes and two-celled proembryos and effects of ß-d-glucosyl Yariv reagent on egg cell fertilization and zygote division in Nicotiana tabacum. J Exp Bot 57:2061–2074
Rajasekaran K, Mullins MG (1979) Embryos and plantlets from cultured anthers of hybrid grapevines. J Exp Bot 30:399–407
Reustle G, Harst M, Alleweldt G (1995) Plant regeneration of grapevine (Vitis sp) protoplasts isolated from embryogenic tissue. Plant Cell Rep 15:238–241
Serpe MD, Nothnagel EA (1994) Effects of Yariv phenylglycosides on Rosa cell suspensions: evidence for the involvement of arabinogalactan-proteins in cell proliferation. Planta 193:542–550
Showalter A (2001) Arabinogalactan-proteins: structure, expression and function. Cell Mol Life Sci 1399–1417
Stamp JA, Meredith CP (1988) Somatic embryogenesis from leaves and anthers of grapevine. Scientia Hort 35:235–250
Taylor NJ, Edwards M, Kiernan RJ, Davey CD, Blakesley D, Henshaw GG (1996) Development of friable embryogenic callus and embryogenic suspension culture systems in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Nature Biotechnol 14:726–730
Tonon G, Berardi G, Rossi C, Bagnaresi U (2001) Synchronized somatic embryo development in embryogenic suspensions of Fraxinus angustifolia. In Vitro Cell Dev Plant 37:462–465
van Engelen FA, De Vries SC (1992) Extracellular proteins in plant embryogenesis. Trends Genet 8:66–70
van Hengel AJ, Gruzzo F, Van Kammen A, De Vries SC (1998) Expression pattern of the carrot EP3 endochitinase genes in suspension cultures and in developing seeds. Plant Physiol 117:43–53
van Hengel AJ, Tadesse Z, Immerzeel P, Schols H, Van Kammen A, De Vries SC (2001) N-acetylglucosamine and glucosamine-containing arabinogalactan proteins control somatic embryogenesis. Plant Physiol 125:1880–1890
van Hengel AJ, Van Kammen A, De Vries SC (2002) A relationship between seed development, arabinogalactan-proteins and the AGP mediated promotion of somatic embryogenesis. Physiol Plant 114:637–641
Vargas TE, De Garcia E, Oroperza M (2005) Somatic embryogenesis in Solanum tuberosum from cell suspension cultures: histological analysis and extracellular protein patterns. J Plant Physiol 162:449–456
Vidal JR, Kikkert JR, Wallace PG, Reisch BI (2003) High-efficiency biolistic transformation and regeneration of “Chardonnay” (Vitis vinifera L.) containing npt-II and antimicrobial peptide genes. Plant Cell Rep 22:252–260
Wang Q, Mawassi M, Sahar N, Li Ping, Colova-Tsolova V., Gafny R, Sela I, Tanne E, Perl A (2004) Cryopreservation of grapevine (Vitis spp.) embryogenic cell suspensions by encapsulation-vitrification. Plant Cell Tiss Org 77:267–275
Willats GT, Steele-King CG, Marcus SE, Knox JP (1999) Side chains of pectic polysaccharides are regulated in relation to cell proliferation and cell differentiation. Plant J 20:619–628
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Reski.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Amar, A., Cobanov, P., Boonrod, K. et al. Efficient procedure for grapevine embryogenic suspension establishment and plant regeneration: role of conditioned medium for cell proliferation. Plant Cell Rep 26, 1439–1447 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0341-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0341-8