Abstract
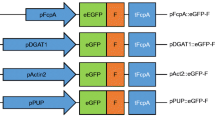
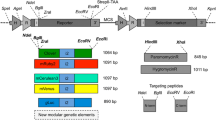
Production of transgenic organisms is a well-established, versatile course of action in molecular biology. Genetic engineering often requires heterologous, dominant antibiotic resistance genes that have been used as selectable markers in many species. However, as heterologous 5′ and 3′ flanking sequences often result in very low expression rates, endogenous flanking sequences, especially promoters, are mostly required and are easily obtained in model organisms, but it is much more complicated and time-consuming to get appropriate sequences from less common organisms. In this paper, we show that aminoglycoside 3′-phosphotransferase gene (aphVIII) based constructs with 3′ and 5′ untranslated flanking sequences (including promoters) from the multicellular green alga Volvox work in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas and flanking sequences from Chlamydomonas work in Volvox, at least if a low expression rate is compensated by an enforced high gene dosage. This strategy might be useful for all investigators that intend to transform species in which genomic sequences are not available, but sequences from related organisms exist.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- aphVIII:
-
Aminoglycoside 3′-phosphotran sferase (VIII) gene
- hsp70A:
-
Heat shock protein 70A ge ne
- rbcS2:
-
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphat-carboxylase small subunit gene 2 from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
- rbcS3:
-
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphat-carboxylase small subunit gene 3 from Volvox carteri
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
References
Adams CR, Stamer KA, Miller JK, McNally JG, Kirk MM, Kirk DL (1990) Patterns of organellar and nuclear inheritance among progeny of two geographically isolated strains of Volvox carteri. Curr Genet 18:141–153
Buchheim MA, Chapman RL (1991) Phylogeny of the colonial green flagellates: a study of 18S and 26S rRNA sequence data. Biosystems 25:85–100
Buchheim MA, McAuley MA, Zimmer EA, Theriot EC, Chapman RL (1994) Multiple origins of colonial green flagellates from unicells: evidence from molecular and organismal characters. Mol Phylogenet Evol 3:322–343
Danilenko VN, Akopiants KE, Sizova IA, Michurina TA (1997) Determination of the nucleotide sequence and characterization of the novel aminoglycoside phosphotransferase aphVIII gene from the Streptomyces rimosus strain. Genetika 33:1478–1486
Davies J, Wright GD (1997) Bacterial resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Trends Microbiol 5:234–240
Debuchy R, Purton S, Rochaix JD (1989) The argininosuccinate lyase gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: an important tool for nuclear transformation and for correlating the genetic and molecular maps of the ARG7 locus. EMBO J 8:2803–2809
Hallmann A, Rappel A (1999) Genetic engineering of the multicellular green alga Volvox: a modified and multiplied bacterial antibiotic resistance gene as a dominant selectable marker. Plant J 17:99–109
Hallmann A, Rappel A, Sumper M (1997) Gene replacement by homologous recombination in the multicellular green alga Volvox carteri. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7469–7474
Harris EH (1989) The Chlamydomonas sourcebook: a comprehensive guide to biology and laboratory use. Academic Press, San Diego
Jakobiak T, Mages W, Scharf B, Babinger P, Stark K, Schmitt R (2004) The bacterial paromomycin resistance gene, aphH, as a dominant selectable marker in Volvox carteri. Protist 155:381–393
Kindle KL (1990) High-frequency nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1228–1232
Kirk DL (1998) Volvox: Molecular-genetic origins of multicellularity and cellular differentiation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lumbreras V, Stevens DL, Purton S (1998) Efficient foreign gene expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mediated by an endogenous intron. Plant J 14:441–447
Provasoli L, Pintner IJ (1959) Artificial media for freshwater algae: problems and suggestions. In: Tyron CA, Hartman RT (eds) The Ecology of alga. Pymatuning laboratory of field biology, Special Publication no. 2, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, pp 84–96
Rausch H, Larsen N, Schmitt R (1989) Phylogenetic relationships of the green alga Volvox carteri deduced from small-subunit ribosomal RNA comparisons. J Mol Evol 29:255–265
Sanford JC, Smith FD, Russell JA (1993) Optimizing the biolistic process for different biological applications. Methods Enzymol 217:483–509
Schiedlmeier B, Schmitt R, Müller W, Kirk MM, Gruber H, Mages W, Kirk DL (1994) Nuclear transformation of Volvox carteri. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5080–5084
Schmitt R, Fabry S, Kirk DL (1992) In search of molecular origins of cellular differentiation in Volvox and its relatives. Int Rev Cytol 139:189–265
Schroda M, Blöcker D, Beck CF (2000) The HSP70A promoter as a tool for the improved expression of transgenes in Chlamydomonas. Plant J 21:121–131
Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 277:221–229
Sodeinde OA, Kindle KL (1993) Homologous recombination in the nuclear genome of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:9199–9203
Starr RC, Jaenicke L (1974) Purification and characterization of the hormone initiating sexual morphogenesis in Volvox carteri f nagariensis Iyengar. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:1050–1054
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Irina Sizova and Peter Hegemann for providing plasmid pSI103, Thomas Jakobiak and Rüdiger Schmitt for providing plasmid pPmr3, and Kordula Puls for expert technical assistance. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 521).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Ebinuma
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hallmann, A., Wodniok, S. Swapped green algal promoters: aphVIII-based gene constructs with Chlamydomonas flanking sequences work as dominant selectable markers in Volvox and vice versa. Plant Cell Rep 25, 582–591 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-006-0121-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-006-0121-x