Abstract.
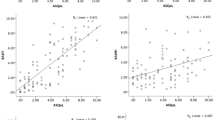
A cohort of 25 patients with spondylarthropathy (SpA) participated in a 3-year follow-up study of functional changes before and after an intensive 3-week inpatient course. They answered questions in the following functional status/disability indices: Bath ankylosing spondylitis functional index (BASFI), Dougados functional index (DFI), health assessment questionnaire for spondylarthropathy (HAQ-S), Bath ankylosing spondylitis disease activity index (BASDAI), Bath ankylosing spondylitis patient global assessment (BAS-G), and horizontal visual analogue scale for stiffness (stiffness VAS) before and after the course and 3 years later by mail. A control group of 18 consecutive SpA patients from the waiting list for an inpatient course filled in the same questionnaires as study patients 3 months before entry and again 3 weeks later at home without rehabilitation. During the waiting time for the inpatient course, control group global assessments (BASDAI, BAS-G, and stiffness-VAS) worsened slightly, and BASFI but not HAQ-S and DFI scores remained unchanged in the 3 weeks without treatment. The results of the 25 study patients showed small and not significant improvements in all functional index scores (BASFI –0.5 points, DFI –1.1, and HAQ-S –0.17), whereas improvements were significant in BASDAI, BAS-G, and stiffness-VAS (–13 mm, –13 mm, and –11 mm, respectively) after the 3-week inpatient course. At 3-year follow-up, these small changes had disappeared and the changes were not significant. The global indices and BASFI worsened slightly (0.4) from baseline results, while DFI was slightly better (–0.4) and HAQ-S remained at the post-treatment level after 3 years. Thus, BASFI was the most sensitive to changes, whereas DFI and HAQ-S were relatively insensitive. All six indices correlated highly significantly with each other (ICC 0.53–0.94). The natural course of spondylarthropathy leads to progression of functional impairments, which seems to be preventable with intensive rehabilitation, at least in the short term. Among the three functional indices, BASFI seems to be the most sensitive tool.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viitanen, J.V., Heikkilä, S. Functional changes in patients with spondylarthropathy. A controlled trial of the effects of short-term rehabilitation and 3-year follow-up. Rheumatol Int 20, 211–214 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002960100101
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002960100101