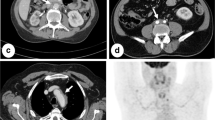
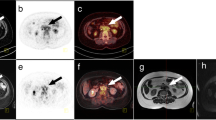
Abstract
The aim of this article was to critically assess the usefulness of hybrid molecular imaging (FDG PET/CT and FDG PET/MR) procedures in the evaluation of inflammatory activity in retroperitoneal fibrosis (RPF). A systematic review of the literature was performed using PubMed without timeline restriction and using the following keywords: retroperitoneal fibrosis, disease activity, diagnostic techniques, PET/CT, PET/MR. We evaluated full text articles written in the English language. Case reports, review articles or editorials and articles not in the field of interest of this review were excluded. Nine articles comprising a total of 186 patients met the inclusion criteria and were included and described in this systematic review. The new hybrid molecular imaging methods give promising results in the evaluation of the activity of the disease, quantification and prediction of therapeutic response and in tailoring medical therapy in RPF. FDG PET/CT can be a valuable tool in detecting disease activity, particularly in asymptomatic patients with RPF with acute phase reactant increase. Hybrid imaging can predict therapy response outcome and the best time for stent removal. Although PET/MR has potential advantage in small lesions and has reduced radiation exposure in comparison to PET/CT, PET quantification parameters have potentially higher diagnostic value over MR parameters in the evaluation of RPF. Acute phase reactants alone may not be reliable for the management and follow-up assessment of the disease. Hybrid imaging in RFP could be more comfortable, more accurate, with less radiation burden than different separate imaging studies acquired at different points in time.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
VaglioA Salvarani C, Buzio C (2006) Retroperitoneal fibrosis. Lancet 367(9506):241–251
Palmisano A, Vaglio A (2009) Chronic periaortitis: a fibro-inflammatory disorder. Best Pract Res 23(3):339–353
Pipitone N, Salvarani C, Peter HH (2010) Chronic periaortitis. Internist 51:45–52
Otomi Y, Otsuka H, Terazawa K, Nose H, Kubo M, Yoneda K, Kitsukawa K, Harada M (2013) (18)F-2-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose uptake in or adjacent to blood vessel walls. J Med Invest 60(1–2):15–20
Yilmaz S, Tanb YZ, Ozhan M, Halac M, Asa S, Sönmezoglu K (2012) FDG PET/CT in monitoring treatment of retroperitoneal fibrosis. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol 31(6):338–339
Lepor H, Walsh PC (1979) Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. J Urol 122(1):1–6
Mehta A, Blodgett MT (2011) Retroperitoneal Fibrosis as a cause of positive FDG PET/CT. J Radiol Case Reports 5(7):35–41
Van Bommel EF, Siemes C, Hak LE, van der Veer SJ, Hendriksz TR (2007) Long-term renal and patient outcome in idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis treated with prednisone. Am J Kidney Dis 49(5):615–625
Monev S (2002) Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis:prompt diagnosis preserves organ function. Cleve Clin J Med 69:160–166
Bertagna F, Treglia G, Leccisotti L (2012) [18F]FDG-PET/CT in patients affected by retroperitoneal fibrosis: a bicentric experience. Jpn J Radiol 30:415–421
Kottra JJ, Dunnick NR (1996) Retroperitoneal fibrosis. Radiol Clin North Am 43:1259–1275
Talati SJ, Abghari R, Kochkodan JJ, Helmer SR (1995) Use of Ga-67 imaging in diagnosis and follow-up after steroid treatment of retroperitoneal fibrosis. Clin Nucl Med 20:995–997
Treglia G, Mattoli MV, Bertagna F, Giubbini R, Giordano A (2013) Emerging role of Fluorine-18-fluorodeoxy glucose positron emission tomography in patients with retroperitoneal fibrosis: a systematic review. Rheumatol Int 33:549–555
Nakajo M, Jinnouchi S, Tanabe H, Tateno R, Nakajo M (2007) 18F-fluoro deoxyglucose positron emission tomography features of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 31(4):539–543
Piccoli GB, ConsiglioV Arena V, Pelosi E, Anastasios D, Ragni F, Fiori C, Cortese G, Deagostini MC, Porpiglia F, Scarpa RM (2010) Positron emission tomography as a tool for the‘tailored’management of retroperitoneal fibrosis: a nephro-urological experience. Nephrol Dial Transpl 25(8):2603–2610
Guignard R, Simukoniene M, Garibotto V, Ratib O (2012) 18F-FDG PET/CT and contrast-enhanced CT in a one-stop diagnostic procedure: a better strategy for management of patients suffering from retroperitoneal fibrosis? Clin Nucl Med 37(5):453–459
Moroni G, Castellani M, Balzani A, Dore R, Bonelli N, Longhi S, Martinelli I, Messa P, Gerundini P (2012) The value of 18FFDG PET/CT in the assessment of active idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39:1635–1642
Fofi C, Prosperi D, Pettorini L, Festuccia F, Pirisino R, Lanni V, Scopinaro F, Punzo G, Menè P (2016) Diagnosis and follow-up of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: role of (18)F-FDG-PET/CT and biochemical parameters in patients with renal involvement. Intern Emerg Med 11(6):809–816
Ruhlmann V, Poeppel TD, Brandt AS, Grüneisen J, Ruhlmann M, Theysohn JM, Forsting M, Bockisch A, Umutlu L (2016) (18)F-FDG PET/MRI evaluation of retroperitoneal fibrosis: a simultaneous multiparametric approach for diagnosing active disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 43(9):1646–1652
Fernando A, Pattison J, Horsfield C, D’Cruz D, Cook G, O’Brien T (2016) [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in the diagnosis, treatment stratification, and monitoring of patients with retroperitoneal fibrosis: a prospective clinical study. Eur Urol. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2016.10.046
Thuermel K, Einspieler I, Wolfram S, Moog P, Meier R, Schwaiger M, Heemann U (2017) Disease activity and vascular involvement in retroperitoneal fibrosis: first experience with fully integrated 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging compared to clinical and laboratory parameters. Clin Exp Rheumatol 35 Suppl 103(1):146–154
Brix G, Lechel U, Glatting G, Ziegler SI, Münzing W, Müller SP, Beyer T (2005) Radiation exposure of patients undergoing whole-body dual-modality 18F-FDG PET/CT examinations. J Nucl Med 46(4):608–613
Tonkopi E, Ross AA, MacDonald A (2013) Journal club: CT dose optimization for whole-body PET/CT examinations. AJR Am J Roentgenol 201(2):257–263
Veenstra DL, Best JH, Hornberger J, Sullivan SD, Hricik DE (1999) Incidence and long-term cost of steroid-related side effects after renal transplantation. Am J Kidney Dis 33(5):829–839
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for the study.
Conflict of interest
Isidora T. Grozdic Milojevic, Bogomir Milojevic, Dragana P.Sobic-Saranovic and Vera M.Artiko declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this type of retrospective study formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grozdic Milojevic, I.T., Milojevic, B., Sobic-Saranovic, D.P. et al. Impact of hybrid molecular imaging in retroperitoneal fibrosis: a systematic review. Rheumatol Int 38, 179–187 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3798-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3798-y