Abstract
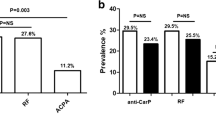
Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies are well-established serological markers that show high sensitivity and specificity in early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and are associated with bone erosions of RA. However, some patients subsequently progress to RA even if there is no presence of anti-CCP antibodies in an early stage. The aim of this study is to evaluate the diagnostic utility of matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) and IgM rheumatoid factor for predicting RA in anti-CCP-negative patients with recent-onset undifferentiated arthritis (UA). Baseline levels of those markers were measured at the entry of the study. A total of 99 patients with UA were included, among them 44 patients (44.4 %) had been classified as having RA by a skilled rheumatologist at some point during 1-year follow-up. Of these 99 patients, 34 patients (34.3 %) had anti-CCP antibodies and 65 patients (65.7 %) had no anti-CCP antibodies. Eleven patients who were anti-CCP-negative developed RA. We compared sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of serum markers of these anti-CCP-negative RA patients. The combined usage of MMP-3 with hsCRP is relatively superior to other markers as predictors of RA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fuchs HA, Kaye JJ, Callahan LF, Nance EP, Pincus T (1989) Evidence of significant radiographic damage in rheumatoid arthritis within the first 2 years of disease. J Rheumatol 16:585–591
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Machold KP, Stamm TA, Eberl GJ, Nell VK, Dunky A, Uffmann M, Smolen JS (2002) Very recent onset arthritis–clinical, laboratory, and radiological findings during the first year of disease. J Rheumatol 29:2278–2287
Harrison BJ, Symmons DP, Barrett EM, Silman AJ (1998) The performance of the 1987 ARA classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis in a population based cohort of patients with early inflammatory polyarthritis. American Rheumatism Association. J Rheumatol 25:2324–2330
Yamamoto S, Kashiwazaki S, Nobunaga T (1994) Study on Japan Rheumatism Association diagnostic criteria for early rheumatoid arthritis-2. Proposed diagnostic criteria for early rheumatoid arthritis. Ryumachi 34:1013–1018
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ et al (2010) 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62:2569–2581
Kennish L, Labitigan M, Budoff S, Filopoulos MT, McCracken WA, Swearingen CJ, Yazici Y (2012) Utility of the new rheumatoid arthritis 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria in routine clinical care. BMJ Open 2:e001117
Schellekens GA, Visser H, de Jong BA, van den Hoogen FH, Hazes JM, Breedveld FC, van Venrooij WJ (2000) The diagnostic properties of rheumatoid arthritis antibodies recognizing a cyclic citrullinated peptide. Arthritis Rheum 43:155–163
van Boekel MA, Vossenaar ER, van den Hoogen FH, van Venrooij WJ (2002) Autoantibody systems in rheumatoid arthritis: specificity, sensitivity and diagnostic value. Arthritis Res 4:87–93
Nielen MMJ, van Schaardenburg D, Reesink HW, van de Stadt RJ, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, de Koning MHM, Habibuw MR, Vandenbroucke JP, Dijkmans BAC (2004) Specific autoantibodies precede the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis: a study of serial measurements in blood donors. Arthritis Rheum 50:380–386
Rantapää-Dahlqvist S, de Jong BA, Berglin E, Hallmans G, Wadell G, Stenlund H, Sundin U, van Venrooij WJ (2003) Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide and IgA rheumatoid factor predict the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:2741–2749
Okada Y, Nagase H, Harris E Jr (1986) A metalloproteinase from human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts that digests connective tissue matrix components. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem 261:14245–14255
Yamanaka H, Matsuda Y, Tanaka M, Sendo W, Nakajima H, Taniguchi A, Kamatani N (2000) Serum matrix metalloproteinase 3 as a predictor of the degree of joint destruction during the six months after measurement, in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:852–858
Nielen MMJ, van Schaardenburg D, Reesink HW, Twisk JW, van de Stadt RJ, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, de Gast T, Habibuw MR, Vandenbroucke JP, Dijkmans BAC (2004) Increased levels of C-reactive protein in serum from blood donors before the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 50:2423–2427
van der Heide A, Jacobs JW, Bijlsma JW, Heurkens AH, van Booma-Frankfort C, van der Veen MJ, Haanen HC, Hofman DM, van Albada-Kuipers GA, ter Borg EJ, Brus HL, Dinant HJ, Kruize AA, Schenk Y (1996) The effectiveness of early treatment with “second-line” antirheumatic drugs. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 124:699–707
Bukhari MA, Wiles NJ, Lunt M, Harrison BJ, Scott DG, Symmons DP, Silman AJ (2003) Influence of disease-modifying therapy on radiographic outcome in inflammatory polyarthritis at five years: results from a large observational inception study. Arthritis Rheum 48:46–53
van Dongen H, van Aken J, Lard LR, Visser K, Ronday HK, Hulsmans HM, Speyer I, Westedt ML, Peeters AJ, Allaart CF, Toes RE, Breedveld FC, Huizinga TW (2007) Efficacy of methotrexate treatment in patients with probable rheumatoid arthritis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 56:1424–1432
Shovman O, Gilburd B, Zandman-Goddard G, Sherer Y, Orbach H, Gerli R, Shoenfeld Y (2005) The diagnostic utility of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies, matrix metalloproteinase-3, rheumatoid factor, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein in patients with erosive and non-erosive rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Dev Immunol 12:197–202
Dubucquoi S, Solau-Gervais E, Lefranc D, Marguerie L, Sibilia J, Goetz J, Dutoit V, Fauchais AL, Hachulla E, Flipo RM, Prin L (2004) Evaluation of anti-citrullinated filaggrin antibodies as hallmarks for the diagnosis of rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 63:415–419
Matsui T, Shimada K, Ozawa N, Hayakawa H, Hagiwara F, Nakayama H, Sugii S, Ozawa Y, Tohma S (2006) Diagnostic utility of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies for very early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 33:2390–2397
van Venrooij WJ, van Beers JJ, Pruijn GJ (2008) Anti-CCP antibody, a marker for the early detection of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1143:268–285
Rönnelid J, Wick MC, Lampa J, Lindblad S, Nordmark B, Klareskog L, van Vollenhoven RF (2005) Longitudinal analysis of citrullinated protein/peptide antibodies (anti-CP) during 5 year follow up in early rheumatoid arthritis: anti-CP status predicts worse disease activity and greater radiological progression. Ann Rheum Dis 64:1744–1749
Visser H, le Cessie S, Vos K, Breedveld FC, Hazes JM (2002) How to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis early: a prediction model for persistent (erosive) arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:357–365
Vencovsky J, Machacek S, Sedova L, Kafkova J, Gatterova J, Pesakova V, Ruzickova S (2003) Autoantibodies can be prognostic markers of an erosive disease in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 62:427–430
Forslind K, Ahlmen M, Eberhardt K, Hafstrom I, Svensson B, Group BS (2004) Prediction of radiological outcome in early rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice: role of antibodies to citrullinated peptides (anti-CCP). Ann Rheum Dis 63:1090–1095
van Gaalen FA, Linn-Rasker SP, van Venrooij WJ, de Jong BA, Breedveld FC, Verweij CL, Toes RE, Huizinga TW (2004) Autoantibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides predict progression to rheumatoid arthritis in patients with undifferentiated arthritis: a prospective cohort study. Arthritis Rheum 50:709–715
Tamai M, Kawakami A, Uetani M et al (2009) A prediction rule for disease outcome in patients with undifferentiated arthritis using magnetic resonance imaging of the wrists and finger joints and serologic autoantibodies. Arthritis Rheum 61:772–778
Ribbens C, Martin Y, Porras M, Franchimont N, Kaiser MJ, Jaspar JM, Damas P, Houssiau FA, Malaise MG (2002) Increased matrix metalloproteinase-3 serum levels in rheumatic diseases: relationship with synovitis and steroid treatment. Ann Rheum Dis 61:161–166
Thompson D, Pepys MB, Wood SP (1999) The physiological structure of human C-reactive protein and its complex with phosphocholine. Structure 7:169–177
Seven A, Güzel S, Aslan M, Hamuryudan V (2009) Serum and synovial fluid leptin levels and markers of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 29:743–747
Ridker PM (2001) High-sensitivity C-reactive protein: potential adjunct for global risk assessment in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Circulation 103:1813–1818
Singh SK, Suresh MV, Voleti B, Agrawal A (2008) The connection between C-reactive protein and atherosclerosis. Ann Med 40:110–120
Finckh A, Liang MH, van Herckenrode CM, de Pablo P (2006) Long-term impact of early treatment on radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum 55:864–872
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiura, K., Iwaki-Egawa, S., Kawashima, T. et al. The diagnostic utility of matrix metalloproteinase-3 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein for predicting rheumatoid arthritis in anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody-negative patients with recent-onset undifferentiated arthritis. Rheumatol Int 33, 2309–2314 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2716-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2716-1