Abstract
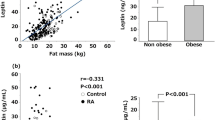
This study was designed to investigate the serum and synovial fluid leptin levels, and inflammatory markers in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Serum and synovial fluid leptin levels were significantly higher (P > 0.05) in RA patients than control group; RA patients with moderate disease activity (DAS < 2.7) having significantly higher leptin levels (P > 0.05) than those with low disease activity (DAS < 2.7). Leukocytes and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) were found to be significantly higher in moderate disease activity RA group compared to low activity group (P > 0.05, P < 0.001, respectively). Serum leptin level is found to be independent of age and inflammatory markers. ESR is positively correlated with DAS activity and CRP values. Our finding of no correlation between leptin and BMI shows that regulation of leptinemia is complex, and leptin levels cannot be used to assess RA activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palmer G, Gabay C (2003) A role for leptin in rheumatic diseases? Ann Rheum Dis 62(10):913–915. doi:10.1136/ard.62.10.913
Otero M, Lago R, Lago F et al (2005) Leptin, from fat to inflammation: old questions and new insights. FEBS Lett 579(2):295–301. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.11.024
Auwerx J, Staels B (1998) Leptin. Lancet 351(9104):737–742. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(97)06348-4
Faggioni R, Feingold KR, Grunfeld C (2001) Leptin regulation of the immune response and the immunodeficiency of malnutrition. FASEB J 15(14):2565–2571. doi:10.1096/fj.01-0431rev
Otero M, Lago R, Gomez R et al (2006) Towards a pro-inflammatory and immunomodulatory emerging role of leptin. Rheumatology (Oxford) 45(8):944–950. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kel157
Loffreda S, Yang SQ, Lin HZ et al (1998) Leptin regulates proinflammatory immune responses. FASEB J 12(1):57–65
Busso N, So A, Chobaz-Péclat V et al (2002) Leptin signaling deficiency impairs humoral and cellular immune responses and attenuates experimental arthritis. J Immunol 168(2):875–882
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31(3):315–324. doi:10.1002/art.1780310302
van der Heijde DM, van’t Hof M, van Riel PL, van de Putte LB (1993) Development of a disease activity score based on judgment in clinical practice by rheumatologists. J Rheumatol 20(3):579–581
Lee SW, Park MC, Park YB, Lee SK (2007) Measurement of the serum leptin level could assist disease activity monitoring in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 27(6):537–540. doi:10.1007/s00296-006-0253-x
Otero M, Lago R, Gomez R et al (2006) Changes in plasma levels of fat-derived hormones adiponectin, leptin, resistin and visfatin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 65(9):1198–1201. doi:10.1136/ard.2005.046540
Bokarewa M, Bokarew D, Hultgren O, Tarkowski A (2003) Leptin consumption in the inflamed joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 62(10):952–956. doi:10.1136/ard.62.10.952
Wisołwska M, Rok M, Jaszczyk B, Stepień K, Cicha M (2007) Serum leptin in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 27(10):947–954. doi:10.1007/s00296-007-0335-4
Gunaydin R, Kaya T, Atay A, Olmez N, Hur A, Koseoglu M (2006) Serum leptin levels in rheumatoid arthritis and relationship with disease activity. South Med J 99(10):1078–1083
Anders HJ, Rihl M, Heufelder A, Loch O, Schattenkirchner M (1999) Leptin serum levels are not correlated with disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Metabolism 48(6):745–748. doi:10.1016/S0026-0495(99)90174-9
Hizmetli S, Kisa M, Gokalp N, Bakici MZ (2007) Are plasma and synovial fluid leptin levels correlated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis? Rheumatol Int 27(4):335–338. doi:10.1007/s00296-006-0264-7
Sarraf P, Frederich RC, Turner EM et al (1997) Multiple cytokines and acute inflammation raise mouse leptin levels: potential role in inflammatory anorexia. J Exp Med 185(1):171–175. doi:10.1084/jem.185.1.171
Nishiya K, Nishiyama M, Chang A, Shinto A, Hashimoto K (2002) Serum leptin levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis are correlated with body mass index. Rinsho Byori 50(5):524–527
Grunfeld C, Pang M, Shigenaga JK et al (1996) Serum leptin levels in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81(12):4342–4346. doi:10.1210/jc.81.12.4342
Popa C, Netea MG, Radstake TR, van Riel PL, Barrera P, van der Meer JW (2005) Markers of inflammation are negatively correlated with serum leptin in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 64(8):1195–1198. doi:10.1136/ard.2004.032243
Tokarczyk-Knapik A, Nowicki M, Wyroślak J (2002) The relation between plasma leptin concentration and body fat mass in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pol Arch Med Wewn 108(2):761–767
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seven, A., Güzel, S., Aslan, M. et al. Serum and synovial fluid leptin levels and markers of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 29, 743–747 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-008-0764-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-008-0764-8