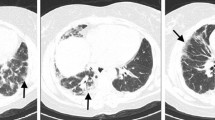
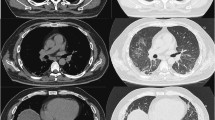
Abstract
Dermatomyositis (DM) is a systemic autoimmune disorder characterized by the inflammation of skeletal muscles and pathognomonic skin rashes, namely heliotrope rash and Gottron’s papules and involvement of other organs. Interstitial lung disease (ILD) seems to be one of the most characteristic manifestations of the lung and associated with increased morbidity and mortality in patients with DM. Despite DM-associated ILD requires aggressive therapy with cytotoxic agents, the efficacy is questionable in some cases, and more effective and less toxic therapies are needed. Recently, although there have been several reports of successful treatment of refractory case of PM and DM with the TNF-α antagonists, including infliximab and etanercept, there was no enough evidence for DM-associated ILD. We described herein a patient with DM-associated ILD who had poor response to conventional therapies and successfully treated with adalimumab.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dalakas MC (1991) Polymyositis, dermatomyositis and inclusion-body myositis. N Engl J Med 325:1487–1498
Marie I, Hachulla E, Cherin P, Dominique S, Hatron PY, Hellot MF, Devulder B, Herson S, Levesque H, Courtois H (2002) Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum 47:614–622
Morganroth PA, Kreider ME, Werth VP (2010) Mycophenolate mofetil for interstitial lung disease in dermatomyositis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 62:1496–1501
Dold S, Justiniano ME, Marquez J, Espinoza LR (2007) Treatment of early and refractory dermatomyositis with infliximab: a report of two cases. Clin Rheumatol 26:1186–1188
Sprott H, Glatzel M, Michel BA (2004) Treatment of myositis with etanercept (Enbrel), a recombinant human soluble fusion protein of TNF-alpha type II receptor and IgG1. Rheumatology 43:524–526
Uthman I, Sayad JE (2004) Refractory polymyositis responding to infliximab. Rheumatology 43:1198–1199
Labioche I, Liozon E, Weschler B, Loustaud-Ratti V, Soria P, Vidal E (2004) Refractory polymyositis responding to infliximab: extensied follow-up. Rheumatology 43:531–532
Anandacoomarasamy A, Howe G, Manolios N (2005) Advanced refractory polymyositis responding to infliximab. Rheumatology 44:562–563
Levine TD (2005) Retuximab in the treatment of dermatomyositis: an open-label pilot study. Arthritis Rheum 52:601–607
Werth VP, Callen JP, Ang G, Sullivan KE (2002) Associations of tumor necrosis factor alpha and HLA polymorphisms with adult dermatomyositis: implications for a unique pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol 119:617–620
Gabay C, Gay-Croisier F, Roux-Lombard P, Meyer O, Maineti C, Guerne PA et al (1994) Elevated serum levels of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in polymyositis/dermatomyositis. A biologic marker of disease activity with a possible role in the lack of acute-phase protein response. Arthritis Rheum 37:1744–1751
Shimizu T, Tomita Y, Son K, Nishinarita S, Sawada S, Horie T (2000) Elevation of serum soluble tumour necrosis factor receptors in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Clin Rheumatol 19:352–359
Kuru S, Inukai A, Liang Y, Doyu M, Takano A, Sobue G (2000) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in muscles of polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Acta Neuropathol (Berlin) 99:585–588
Lundberg IE, Dastmalchi M (2002) Possible pathogenic mechanisms in inflammatory myopathies. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 28:799–822
Kameda H, Takeuchi T (2006) Recent advances in the treatment of interstitial lung disease in patients with polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 6:409–415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JK., Yoo, HG., Ahn, DS. et al. Successful treatment for conventional treatment-resistant dermatomyositis-associated interstitial lung disease with adalimumab. Rheumatol Int 32, 3587–3590 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2220-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2220-4