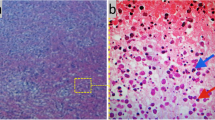
Abstract
Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease is a form of reactive lymphadenopathy, which was firstly described in Japan, but is uncommon in the Western world. We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of nine cases of adult or adolescent Kikuchi’s disease diagnosed in a single Haematology Unit in Athens, Greece between 1990 and 2006. The median age of the patients was 25 years (14–40) and 8/9 were females. All patients presented with cervical lymphadenopathy sparing the supraclavicular fossa; one had associated axillary lymphadenopathy, seven had fever and two were asymptomatic. The median duration of lymphadenopathy before presentation was 30 days (10–45). Just palpable splenomegaly was recorded in three patients. The median value of the maximal lymph node diameter was 2 cm (1–5) and only 1/9 had nodes >2 cm in their largest diameter. Lymphadenopathy was tender in two patients; hard nodes were observed in three patients. The median leukocyte count was 4.7 × 109/l (2.2–4.9) with a normal differential in 7/9 patients. No infectious agent could be demonstrated. One patient had clinical and laboratory evidence of primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APLS). In conclusion, Kikuchi’s disease represents a rare but important diagnostic possibility for patients presenting with lymphadenopathy in Greece and other western countries. In this setting, autoimmune disorders, mainly lupus and APLS, should be considered and excluded by the appropriate laboratory work-up.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fujimoto Y, Kozima Y, Yamaguchi K (1972) Cervical subacute necrotizing lymphadenitis. A new clinicopathological entity. Naika 30:920–927
Kikuchi M (1972) Lymphadenitis showing focal reticulum cell hyperplasia with nuclear debris and phagocytes. Acta Hematol Jpn 35:379–380
Bosch X, Guilabert A, Miquel R, Campo E (2004) Enigmatic Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease. A comprehensive review. Am J Clin Pathol 122:141–152
Charalabopoulos K, Papalimneou V, Charalabopoulos A, Chaidos A, Bai M, Bourantas K, Agnantis N (2002) Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease in Greece. A study of four cases and review of the literature. In Vivo 16:311–316
Norris AH, Krasinskas AM, Salhany KE, Gluckman SJ (1996) Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: a benign cause of fever and lymphadenopathy. Am J Med 171:401–405
Papadimitriou CS, Papaharalampous NX (1985) Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis without granulocytic infiltration. Arch Pathol Lab Med 109:107–108
Dorfman RF, Berry GJ (1988) Kikuchi’s histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis: an analysis of 108 cases with emphasis on differential diagnosis. Semin Diagn Pathol 5:329–345
Pangalis GA, Vassilakopoulos TP, Boussiotis VA, Fessas Ph (1993) Clinical approach to lymphadenopathy. Semin Oncol 20:570–582
Vassilakopoulos TP, Pangalis GA (2000) Application of a prediction rule to select which patients presenting with lymphadenopathy should undergo a lymph node biopsy. Medicine (Baltimore) 79:338–347
Levine JS, Branch W, Rauch J (2002) The antiphospholipid syndrome. N Engl J Med 346:752–763
Kuo TT (1995) Kikuchi’s disease (histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis). A clinicopathologic study of 79 cases with an analysis of histologic subtypes, immunohistology, and DNA ploidy. Am J Surg Pathol 19:798–809
Papadopoulou D, Vergos I, Zacharakis M, Fotiou K (2005) Kikuchi-Fujimoto’s disease in a male with HCV infection. Haema 8:657–659
Charalabopoulos K, Papalimneou V, Charalabopoulos A, Bai M, Agnantis N (2003) Brucella melitensis infection stimulates an immune response leading to Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease. In Vivo 17:51–53
Yu HL, Lee SS, Tsai HC, Huang CK, Chen YS, Lin HH, Wann SR, Liu YC, Tseng HH (2005) Clinical manifestations of Kikuchi’s disease in southern Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 38:35–40
Viguer M, Jimenez-Heffernan JA, Perez P, Lopez-Ferrer P, Gonzalez-Peramato P, Vicandi B (2001) Fine-needle aspiration cytology of Kikuchi’s lymphadenitis: a report of ten cases. Diagn Cytopathol 25:220–224
El-Ramahi KM, Karrar A, Ashraf Ali M (1994) Kikuchi disease and its association with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 3:409–411
Hu S, Kuo TT, Hong HS (2003) Lupus lymphadenitis simulating Kikuchi’s lymphadenitis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a clinicopathological analysis of six cases and review of the literature. Pathol Int 53:221–226
Tumiati B, Bellelli A, Portioli I, Prandi S (1991) Kikuchi’s disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: an independent or dependent event? Clin Rheumatol 10:90–93
Vila LM, Mayor AM, Silvestrini IE (2001) Therapeutic response and long-term follow-up in a systemic lupus erythematosus patient presenting with Kikuchi’s disease. Lupus 10:126–128
Santana A, Lessa B, Galrao L, Lima I, Santiago M (2005) Kikuchi-Fujimoto’s disease associated with systemic lupus erythematosus: case report and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol 24:60–63
Chen HC, Lai JH, Huang GS, Gao HW, Chen CH, Kuo SY, Chang DM (2005) Systemic lupus erythematosus with simultaneous onset of Kikuchi-Fujimoto’s disease complicated with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: a case report and review of the literature. Rheumatol Int 25:303–306
de Larranaga GF, Remondino GI, Forastiero RR, Cunto ER, Narbaitz M, Olenchuk AB, Zala NS, San Juan JA (2005) Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome and Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: the first case reported. Lupus 14:967–969
Papaioannou G, Speletas M, Kaloutsi V, Pavlitou-Tsiontsi A (2002) Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease) associated with antiphospholipid syndrome: case report and literature review. Ann Hematol 81:732–735
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vassilakopoulos, T.P., Pangalis, G.A., Siakantaris, M.P. et al. Kikuchi’s lymphadenopathy: a relatively rare but important cause of lymphadenopathy in Greece, potentially associated with the antiphospholipid syndrome. Rheumatol Int 30, 925–932 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-1077-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-1077-2