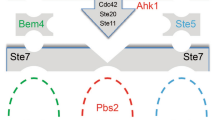
Abstract
Here, we examine the genetic interactions between ESCRT-III mutations in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. From the obtained interaction network, we make predictions about alternative ESCRT-III complexes. By the successful generation of an octuple deletion strain using the CRISPR/Cas9 technique, we demonstrate for the first time that ESCRT-III activity as a whole is not essential for the life of a yeast cell. Endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT)-III proteins are membrane remodeling factors involved in a multitude of cellular processes. There are eight proteins in yeast with an ESCRT-III domain. It is not clear whether the diverse ESCRT-III functions are fulfilled by a single ESCRT-III complex or by different complexes with distinct composition. Genetic interaction studies may provide a hint on the existence of alternative complexes. We performed a genetic mini-array screen by analyzing the growth phenotypes of all pairwise combinations of ESCRT-III deletion mutations under different stress conditions. Our analysis is in line with previous data pointing to a complex containing Did2/CHMP1 and Ist1/IST1. In addition, we provide evidence for the existence of a novel complex consisting of Did2/CHMP1 and Vps2/CHMP2. Some of the interactions on Congo red plates could be explained by effects of ESCRT-III mutations on Rim101 signaling.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison R, Lumb JH, Fassier C, Connell JW, Ten Martin D, Seaman MN, Hazan J, Reid E (2013) An ESCRT-spastin interaction promotes fission of recycling tubules from the endosome. J Cell Biol 202:527–543
Babst M, Wendland B, Estepa EJ, Emr SD (1998) The Vps4p AAA ATPase regulates membrane association of a Vps protein complex required for normal endosome function. EMBO J 17:2982–2993
Babst M, Katzmann DJ, Estepa-Sabal EJ, Meerloo T, Emr SD (2002a) ESCRT-III: an endosome-associated heterooligomeric protein complex required for MVB sorting. Dev Cell 3:271–282
Babst M, Katzmann DJ, Snyder WB, Wendland B, Emr SD (2002b) Endosome-associated complex, ESCRT-II, recruits transport machinery for protein sorting at the multivesicular body. Dev Cell 3:283–289
Bauer I, Brune T, Preiss R, Kölling R (2015) Evidence for a non-endosomal function of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ESCRT-III like protein Chm7. Genetics 201:1439–1452
Bodon G, Chassefeyre R, Pernet-Gallay K, Martinelli N, Effantin G, Hulsik DL, Belly A, Goldberg Y, Chatellard-Causse C, Blot B, Schoehn G, Weissenhorn W, Sadoul R (2011) Charged multivesicular body protein 2B (CHMP2B) of the endosomal sorting complex required for transport-III (ESCRT-III) polymerizes into helical structures deforming the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 286:40276–40286
Dimaano C, Jones CB, Hanono A, Curtiss M, Babst M (2008) Ist1 regulates Vps4 localization and assembly. Mol Biol Cell 19:465–474
Gietz RD, Sugino A (1988) New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene 74:527–534
Hayashi M, Fukuzawa T, Sorimachi H, Maeda T (2005) Constitutive activation of the pH-responsive Rim101 pathway in yeast mutants defective in late steps of the MVB/ESCRT pathway. Mol Cell Biol 25:9478–9490
Hood-DeGrenier JK (2011) Identification of phosphatase 2A-like Sit4-mediated signalling and ubiquitin-dependent protein sorting as modulators of caffeine sensitivity in S. cerevisiae. Yeast 28:189–204
Hurley JH (2015) ESCRTs are everywhere. EMBO J 34:2398–2407
Katzmann DJ, Babst M, Emr SD (2001) Ubiquitin-dependent sorting into the multivesicular body pathway requires the function of a conserved endosomal protein sorting complex, ESCRT-I. Cell 106:145–155
Kinner A, Kölling R (2003) The yeast deubiquitinating enzyme Ubp16 is anchored to the outer mitochondrial membrane. FEBS Lett 549:135–140
Kopecka M, Gabriel M (1992) The influence of congo red on the cell wall and (1,3)-β-D-glucan microfibril biogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol 158:115–126
Kullas AL, Li M, Davis DA (2004) Snf7p, a component of the ESCRT-III protein complex, is an upstream member of the RIM101 pathway in Candida albicans. Eukaryot Cell 3:1609–1618
Lamb TM, Mitchell AP (2003) The transcription factor Rim101p governs ion tolerance and cell differentiation by direct repression of the regulatory genes NRG1 and SMP1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 23:677–686
Leung KF, Dacks JB, Field MC (2008) Evolution of the multivesicular body ESCRT machinery; retention across the eukaryotic lineage. Traffic 9:1698–1716
Levin DE (2005) Cell wall integrity signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 69:262–291
Li W, Mitchell AP (1997) Proteolytic activation of Rim1p, a positive regulator of yeast sporulation and invasive growth. Genetics 145:63–73
Logg K, Warringer J, Hashemi SH, Kall M, Blomberg A (2008) The sodium pump Ena1p provides mechanistic insight into the salt sensitivity of vacuolar protein sorting mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783:974–984
Longtine MS, McKenzie A, Demarini DJ, Shah NG, Wach A, Brachat A, Philippsen P, Pringle JR (1998) Additional modules for versatile and economical PCR-based gene deletion and modification in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 14:953–961
McCullough J, Clippinger AK, Talledge N, Skowyra ML, Saunders MG, Naismith TV, Colf LA, Afonine P, Arthur C, Sundquist WI, Hanson PI, Frost A (2015) Structure and membrane remodeling activity of ESCRT-III helical polymers. Science 350:1548–1551
Nickerson DP, West M, Odorizzi G (2006) Did2 coordinates Vps4-mediated dissociation of ESCRT-III from endosomes. J Cell Biol 175:715–720
Perlin DS (2007) Resistance to echinocandin-class antifungal drugs. Drug Resist Updates 10:121–130
Raymond CK, Howald SI, Vater CA, Stevens TH (1992) Morphological classification of the yeast vacuolar protein sorting mutants: evidence for a prevacuolar compartment in class E vps mutants. Mol Biol Cell 3:1389–1402
Rodrigues J, Lydall D (2018) Cis and trans interactions between genes encoding PAF1 complex and ESCRT machinery components in yeast. Curr Genet 64:1105–1116
Rothfels K, Tanny JC, Molnar E, Friesen H, Commisso C, Segall J (2005) Components of the ESCRT pathway, DFG16, and YGR122w are required for Rim101 to act as a corepressor with Nrg1 at the negative regulatory element of the DIT1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 25:6772–6788
Rue SM, Mattei S, Saksena S, Emr SD (2008) Novel Ist1-Did2 complex functions at a late step in multivesicular body sorting. Mol Biol Cell 19:475–484
Ryan OW, Skerker JM, Maurer MJ, Li X, Tsai JC, Poddar S, Lee ME, DeLoache W, Dueber JE, Arkin AP, Cate JH (2014) Selection of chromosomal DNA libraries using a multiplex CRISPR system. eLife 3:e03703. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.03703
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Scourfield EJ, Martin-Serrano J (2017) Growing functions of the ESCRT machinery in cell biology and viral replication. Biochem Soc Trans 45:613–634
Shim JH, Xiao C, Hayden MS, Lee KY, Trombetta ES, Pypaert M, Nara A, Yoshimori T, Wilm B, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Hogan BL, Mellman I, Ghosh S (2006) CHMP5 is essential for late endosome function and down-regulation of receptor signaling during mouse embryogenesis. J Cell Biol 172:1045–1056
Soreanu I, Hendler A, Dahan D, Dovrat D, Aharoni A (2018) Marker-free genetic manipulations in yeast using CRISPR/CAS9 system. Curr Genet 64:1129–1139
Teis D, Saksena S, Emr SD (2008) Ordered assembly of the ESCRT-III complex on endosomes is required to sequester cargo during MVB formation. Dev Cell 15:578–589
Vietri M, Schink KO, Campsteijn C, Wegner CS, Schultz SW, Christ L, Thoresen SB, Brech A, Raiborg C, Stenmark H (2015) Spastin and ESCRT-III coordinate mitotic spindle disassembly and nuclear envelope sealing. Nature 522:231–235
Weiß P, Huppert S, Kölling R (2008) ESCRT-III protein Snf7 mediates high-level expression of the SUC2 gene via the Rim101 pathway. Eukaryot Cell 7:1888–1894
Xiao J, Chen XW, Davies BA, Saltiel AR, Katzmann DJ, Xu Z (2009) Structural basis of Ist1 function and Ist1-Did2 interaction in the multivesicular body pathway and cytokinesis. Mol Biol Cell 20:3514–3524
Xu W, Smith FJ Jr, Subaran R, Mitchell AP (2004) Multivesicular body-ESCRT components function in pH response regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans. Mol Biol Cell 15:5528–5537
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) Grant KO-963/8-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Kupiec.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brune, T., Kunze-Schumacher, H. & Kölling, R. Interactions in the ESCRT-III network of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet 65, 607–619 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-018-0915-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-018-0915-8