Abstract
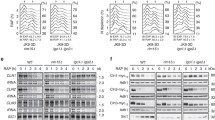
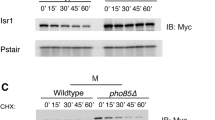
The cAMP–PKA is the major glucose-sensing pathway that controls sexual differentiation in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Sequencing from the pka1 locus of recessive sam mutants, in which cells are highly inclined to sexual differentiation, led to the identification of mutations in the pka1 locus in sam5 (pka1-G441E) and sam7 (pka1-G441R). Rst2 and Ste11 proteins were induced and localized to the nucleus of sam5 and sam7 mutants even under rich glucose conditions, indicating that the function of Pka1 was completely abolished by mutations. Pka1-G441E and Pka1-G441R mutant proteins reside in the cytoplasm, even under glucose-rich conditions, while wild-type Pka1 resides in the nucleus, indicating that the functionality of Pka1 is important for its nuclear localization. This is supported by the observation that the Pka1-T356A mutant, which partially lacks Pka1 function, was localized to both the cytoplasm and the nucleus, but an active phosphomimetic Pka1-T356D mutant prtotein was localized to the nucleus under glucose-rich conditions. In addition to the basal phosphorylation of Pka1 at T356, hyperphosphorylation of Pka1 was observed under glucose-starved conditions, and such hyperphosphorylation was not observed in pka1-G441E, pka1-G441R, pka1-T356A or pka1-T356D mutants. As these mutant proteins failed to interact with a regulatory subunit Cgs1, hyperphosphorylation of Pka1 mutant proteins was considered to be dependent on Cgs1 interaction. Consistent with a role for Cgs1 in Pka1 phosphorylation, we detected the formation of a Cgs1–Pka1 complex prior to Pka1 hyperphosphorylation. Together, these results indicate that nuclear localization of Pka1 depends on its activity and hyperphosphorylation of Pka1 depends on Cgs1 interaction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfa C, Fantes P, Hyams J, McLeod M, Warbrick E (1993) Experiments with fission yeast. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
DeVoti J, Seydoux G, Beach D, McLeod M (1991) Interaction between ran1+ protein kinase and cAMP dependent protein kinase as negative regulators of fission yeast meiosis. EMBO J 10:3759–3768
Gibson RM, Taylor SS (1997) Dissecting the cooperative reassociation of the regulatory and catalytic subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Role of Trp-196 in the catalytic subunit. J Biol Chem 272:31998–32005
Goldar MM, Jeong HT, Tanaka K, Matsuda H, Kawamukai M (2005) Moc3, a novel Zn finger type protein involved in sexual development, ascus formation, and stress response of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Curr Genet 48:345–355
Gupta DR, Paul SK, Oowatari Y, Matsuo Y, Kawamukai M (2011) Complex formation, phosphorylation, and localization of protein kinase A of Schizosaccharomyces pombe upon glucose starvation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:1456–1465
Hanks SK, Hunter T (1995) Protein kinases 6. The eukaryotic protein kinase superfamily: kinase (catalytic) domain structure and classification. Faseb J 9:576–596
Higuchi T, Watanabe Y, Yamamoto M (2002) Protein kinase A regulates sexual development and gluconeogenesis through phosphorylation of the Zn finger transcriptional activator Rst2p in fission yeast. Mol Cell Biol 22:1–11
Hoffman CS (2005) Glucose sensing via the protein kinase A pathway in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biochem Soc Trans 33:257–260
Jeong HT, Oowatari Y, Abe M, Tanaka K, Matsuda H, Kawamukai M (2004a) Interaction between a negative regulator (Msa2/Nrd1) and a positive regulator (Cpc2) of sexual differentiation in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:1621–1626
Jeong HT, Ozoe F, Tanaka K, Nakagawa T, Matsuda H, Kawamukai M (2004b) A novel gene, msa1, inhibits sexual differentiation in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genetics 167:77–91
Kao RS, Morreale E, Wang L, Ivey FD, Hoffman CS (2006) Schizosaccharomyces pombe Git1 is a C2-domain protein required for glucose activation of adenylate cyclase. Genetics 173:49–61
Katayama S, Ozoe F, Kurokawa R, Tanaka K, Nakagawa T, Matsuda H, Kawamukai M (1996) Genetic analysis of the sam mutations, which induce sexual development with no requirement for nutritional starvation in fission yeast. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 60:994–999
Kawamukai M (1999) Isolation of a novel gene, moc2, encoding a putative RNA helicase as a suppressor of sterile strains in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biochim Biophys Acta 1446:93–101
Kawamukai M, Ferguson K, Wigler M, Young D (1991) Genetic and biochemical analysis of the adenylyl cyclase of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cell Regul 2:155–164
Kawamukai M, Gerst J, Field J, Riggs M, Rodgers L, Wigler M, Young D (1992) Genetic and biochemical analysis of the adenylyl cyclase-associated protein, cap, in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Biol Cell 3:167–180
Kim C, Cheng CY, Saldanha SA, Taylor SS (2007) PKA-I holoenzyme structure reveals a mechanism for cAMP-dependent activation. Cell 130:1032–1043
Krawchuk MD, Wahls WP (1999) High-efficiency gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe using a modular, PCR-based approach with long tracts of flanking homology. Yeast 15:1419–1427
Kunitomo H, Higuchi T, Iino Y, Yamamoto M (2000) A zinc-finger protein, Rst2p, regulates transcription of the fission yeast ste11(+) gene, which encodes a pivotal transcription factor for sexual development. Mol Biol Cell 11:3205–3217
Levin LR, Zoller MJ (1990) Association of catalytic and regulatory subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase requires a negatively charged side group at a conserved threonine. Mol Cell Biol 10:1066–1075
Maeda T, Watanabe Y, Kunitomo H, Yamamoto M (1994) Cloning of the pka1 gene encoding the catalytic subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem 269:9632–9637
Matsuo Y, Asakawa K, Toda T, Katayama S (2006) A rapid method for protein extraction from fission yeast. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:1992–1994
Matsuo Y, McInnis B, Marcus S (2008) Regulation of the subcellular localization of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in response to physiological stresses and sexual differentiation in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Eukaryot Cell 7:1450–1459
Matsuo Y, Kishimoto H, Tanae K, Kitamura K, Katayama S, Kawamukai M (2011) Nuclear protein quality is regulated by the ubiquitin–proteasome system through the activity of Ubc4 and San1 in fission yeast. J Biol Chem 286:13775–13790
McInnis B, Mitchell J, Marcus S (2010) Phosphorylation of the protein kinase A catalytic subunit is induced by cyclic AMP deficiency and physiological stresses in the fission yeast, Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 399:665–669
Moore MJ, Kanter JR, Jones KC, Taylor SS (2002) Phosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A. Autophosphorylation versus phosphorylation by phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1. J Biol Chem 277:47878–47884
Oowatari Y, Toma K, Ozoe F, Kawamukai M (2009) Identification of sam4 as a rad24 allele in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:1591–1598
Oowatari Y, Jeong HT, Tanae K, Nakagawa T, Kawamukai M (2011) Regulation and role of an RNA-binding protein Msa2 in controlling the sexual differentiation of fission yeast. Curr Genet 57:191–200
Paul SK, Oowatari Y, Kawamukai M (2009) A large complex mediated by Moc1, Moc2 and Cpc2 regulates sexual differentiation in fission yeast. FEBS J 276:5076–5093
Prentice HL (1992) High efficiency transformation of Schizosaccharomyces pombe by electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res 20:621
Qin J, Kang W, Leung B, McLeod M (2003) Ste11p, a high-mobility-group box DNA-binding protein, undergoes pheromone- and nutrient-regulated nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling. Mol Cell Biol 23:3253–3264
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a lablatory manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Seidler J, Adal M, Kubler D, Bossemeyer D, Lehmann WD (2009) Analysis of autophosphorylation sites in the recombinant catalytic subunit alpha of cAMP-dependent kinase by nano-UPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:1713–1720
Tanabe K, Ito N, Wakuri T, Ozoe F, Umeda M, Katayama S, Tanaka K, Matsuda H, Kawamukai M (2003) Sla1, a Schizosaccharomyces pombe homolog of the human La protein, induces ectopic meiosis when its C terminus is truncated. Eukaryot Cell 2:1274–1287
Tanabe K, Tanaka K, Matsuda H, Kawamukai M (2004) Truncated Sla1 induces haploid meiosis through the Pat1-Mei2 system in fission yeast. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:266–270
Tang Y, McLeod M (2004) In vivo activation of protein kinase A in Schizosaccharomyces pombe requires threonine phosphorylation at its activation loop and is dependent on PDK1. Genetics 168:1843–1853
Taylor SS, Buechler JA, Yonemoto W (1990) cAMP-dependent protein kinase: framework for a diverse family of regulatory enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 59:971–1005
Toda T, Cameron S, Sass P, Zoller M, Wigler M (1987) Three different genes in S. cerevisiae encode the catalytic subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell 50:277–287
Tudisca V, Recouvreux V, Moreno S, Boy-Marcotte E, Jacquet M, Portela P (2010) Differential localization to cytoplasm, nucleus or P-bodies of yeast PKA subunits under different growth conditions. Eur J Cell Biol 89:339–348
Welton RM, Hoffman CS (2000) Glucose monitoring in fission yeast via the Gpa2 galpha, the git5 Gbeta and the git3 putative glucose receptor. Genetics 156:513–521
Wilson-Grady JT, Villen J, Gygi SP (2008) Phosphoproteome analysis of fission yeast. J Proteome Res 7:1088–1097
Yakura M, Ishikura Y, Adachi Y, Kawamukai M (2006a) Involvement of Moc1 in sexual development and survival of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:1740–1749
Yakura M, Ozoe F, Ishida H, Nakagawa T, Tanaka K, Matsuda H, Kawamukai M (2006b) zds1, a novel gene encoding an ortholog of Zds1 and Zds2, controls sexual differentiation, cell wall integrity and cell morphology in fission yeast. Genetics 172:811–825
Yamamoto M (2003) Initiation of meiosis. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Yang P, Du H, Hoffman CS, Marcus S (2003) The phospholipase B homolog Plb1 is a mediator of osmotic stress response and of nutrient-dependent repression of sexual differentiation in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Genet Genomics 269:116–125
Yonemoto W, McGlone ML, Grant B, Taylor SS (1997) Autophosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in Escherichia coli. Protein Eng 10:915–925
Zhou GL, Yamamoto T, Ozoe F, Yano D, Tanaka K, Matsuda H, Kawamukai M (2000) Identification of a 14-3-3 protein from Lentinus edodes that interacts with CAP (adenylyl cyclase-associated protein), and conservation of this interaction in fission yeast. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:149–159
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by the Sasakawa Scientific Research Grant from The Japan Science Society. We thank Dr. T. Kaino, Dr. T Nakagawa, K. Tanae and Y. Matsuo for helpful discussions and experimental support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. Hoffman.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, D.R., Paul, S.K., Oowatari, Y. et al. Multistep regulation of protein kinase A in its localization, phosphorylation and binding with a regulatory subunit in fission yeast. Curr Genet 57, 353–365 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-011-0354-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-011-0354-2