Abstract
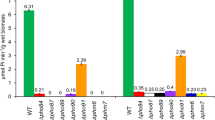
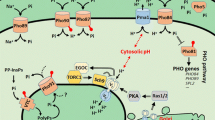
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, nutrient sensing is the major factor controlling cell growth and proliferation. It has been shown that phosphate signalling involves the activation of the protein kinase A (PKA) in response to an elevation of external phosphate when cells have experienced a severe phosphate limitation. Addition of phosphate or its non-metabolized analogue, methylphosphonate (MP), to cells grown under phosphate limitation triggers degradation of the Pho84 phosphate transporter and represses the acidic phosphatase activity. In this study we have shown that of the five inorganic phosphate transporters (Pho84, Pho87, Pho89, Pho90, Pho91) of the plasma membrane, only Pho84 is required for the MP recognition and repression of the acidic phosphatase activity. By use of the PKA inhibitor H89, we demonstrate that down-regulation and degradation of the Pho84 transporter, in response to an elevation of external phosphate, is delayed by the inhibition of PKA. In contrast, down-regulation of the acidic phosphatase is under these conditions not affected by the PKA inhibition. Altogether, these observations suggest that the PKA signalling pathway plays a role in conveying the signal for the down-regulation and degradation of the Pho84 transporter in the vacuolar compartment in response to altered phosphate availability in the external environment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HPi :
-
High phosphate medium
- LPi :
-
Low phosphate medium
- Pi :
-
Inorganic phosphate
- rAPase:
-
Repressible acid phosphatase
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- H89:
-
N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide
- MP:
-
Methylphosphonate
References
Auesukaree C, Homma T, Kaneko Y, Harashima S (2003) Transcriptional regulation of phosphate-responsive genes in low-affinity phosphate-transporter-defective mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 306:843–850
Auesukaree C, Homma T, Tochio H, Shirakawa M, Kaneko Y, Harashima S (2004) Intracellular phosphate serves as a signal for the regulation of the PHO pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 279:17289–17294
Budovskaya YV, Stephan JS, Reggiori F, Klionsky DJ, Herman PK (2004) The Ras/cAMP-dependent protein kinase signaling pathway regulates an early step of the autophagy process in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 279:20663–20671
Bun-ya M, Nishimura M, Harashima S, Oshima Y (1991) The Pho84 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes an inorganic phosphate transporter. Mol Cell Biol 11:3229–3238
Chijiwa T, Mishima A, Hagiwara M, Sano M, Hayashi K, Inoue T, Naito K, Toshioka T, Hidaka H (1990) Inhibition of forskolin-induced neurite outgrowth and protein phosphorylation by a newly synthesized selective inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-89), of PC12D pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem 265:5267–5272
Giots F, Donaton FC, Thevelein JM (2003) Inorganic phosphate is sensed by specific phosphate carriers and acts in concert with glucose as a nutrient signal for activation of the protein kinase A pathway in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol 47:1163–1181
Holsbeeks L, Lagatie O, Van Nuland A, Van de Velde S, Thevelein JM (2004) The eukaryotic plasma membrane as a nutrient-sensing device. Trends Biochem Sci 29:556–564
Horak J (2003) The role of ubiquitin in down-regulation and intracellular sorting of membrane proteins: insights from yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta 1614:139–155
Horak J, Wolf DH (2001) Glucose-induced monoubiquitination of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae galactose transporter is sufficient to signal its internalization. J Bacteriol 183:3083–3088
Hung GC, Brown CR, Wolfe AB, Liu J, Chiang HL (2004) Degradation of the gluconeogenic enzymes fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and malate dehydrogenase is mediated by distinct proteolytic pathways and signaling events. J Biol Chem 279:49138–49150
Kaneko Y, Toh-e A, Oshima Y (1982) Identification of the genetic locus for the structural gene and a new regulatory gene for the synthesis of repressible alkaline phosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 2:127–137
Kruckeberg AL, Neuhaus HE, Feil R, Gottlieb LD, Stitt M (1989) Decreased-activity mutants of phosphoglucose isomerase in the cytosol and chloroplast of Clarkia xantiana. Impact on mass-action ratios and fluxes to sucrose and starch, and estimation of flux control coefficients and elasticity coefficients. Biochem J 261:457–467
Laemmli UK, Beguin F, Gujer-Kellenberg G (1970) A factor preventing the major head protein of bacteriophage T4 from random aggregation. J Mol Biol 47:69–85
Lagerstedt JO, Zvyagilskaya R, Pratt JR, Pattison-Granberg J, Kruckeberg AL, Berden JA, Persson BL (2002) Mutagenic and functional analysis of the C-terminus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pho84 phosphate transporter. FEBS Lett 526:31–37
Lenburg ME, O’Shea EK (1996) Signaling phosphate starvation. Trends Biochem Sci 21:383–387
Martinez P, Persson BL (1998) Identification, cloning and characterization of a derepressible Na+-coupled phosphate transporter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet 258:628–638
Neves MJ, Francois J (1992) On the mechanism by which a heat shock induces trehalose accumulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J 288:859–864
Ogawa N, DeResi J, Brown PO (2000) New components of a system for phosphate accumulation and polyphosphate metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae revealed by genomic expression analysis. Mol Biol Cell 11:4309–4321
Oshima Y (1997) The phosphatase system in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Genet Syst 72:232–334
Persson BL, Lagerstedt JO, Pratt JR, Pattison-Granberg J, Lundh K, Shokrollahzadeh S, Lundh F (2003) Regulation of phosphate acquisition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cur Genet 43:225–244
Petersson J, Pattison J, Kruckeberg AL, Berden JA, Persson BL (1999) Intracellular localization of an active green fluorescent protein-tagged Pho84 phosphate permease in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 462:37–42
Pratt JR, Mouillon JM, Lagerstedt JO, Pattison-Granberg J, Lundh KI,Persson BL (2004) Effects of methylphosphonate, a phosphate analogue, on the expression and degradation of the high-affinity phosphate transporter Pho84, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry 43:14444–14453
Ray BK, Chen J, Ray A (1990) Catalytic subunit of protein kinase A is an interacting partner of the inflammation-responsive transcription factor serum amyloid A-activating factor-1. J Immunol 167:2343–2348
Thevelein JM, Geladé R, Holsbeeks I, Lagatie O, Popova Y, Rolland F, Stolz F, Van de Velde S, Van Dijck P, Vandormael P, Van Nuland A, Van Roey K, Van Zeebroeck G, Yan B (2005) Nutrient sensing systems for rapid activation of the protein kinase A pathway in yeast. Biochem Soc Trans 33:253–256
Toh-e A, Kakimoto S (1975) Genes coding for the structure of the acid phosphatases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet 143:65–70
Wykoff DD, O’Shea EK (2001) Phosphate transport and sensing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 159:1491–1499
Zvyagilskaya R, Parchomenko O, Abramova N, Allard P, Panaretakis T, Pattison-Granberg J, Persson BL (2001) Proton- and sodium-coupled phosphate transport systems and energy status of Yarrowia lipolytica cells grown in acidic and alkaline conditions. J Membr Biol 183:39–50
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. S. Harashima for sending us yeast strains. This work was supported by Human Frontier Science Organization Grant RG00281/2000-M, and Swedish Research Council Grant 621-2003-3558.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mouillon, JM., Persson, B.L. Inhibition of the protein kinase A alters the degradation of the high-affinity phosphate transporter Pho84 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Curr Genet 48, 226–234 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-005-0019-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-005-0019-0