Abstract
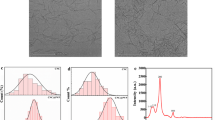
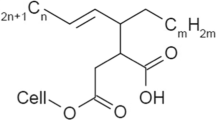
Cellulose acetate (CA) and polyethylenimine (PEI) composite nanofibers were developed via the electrospinning technique. The influence of PEI concentration on the size and morphology of composite fibers was observed by SEM. The secondary fibers produced along with the primary fibers, upon the addition of PEI component. This was named as “bimodal” size distribution. To remove the remaining PEI, the as-spun membranes were immersed in deionized water. The results showed that the existence of PEI in the water-treated process promoted the swelling of fibers. When PEI content was lower, the compatibility of CA and PEI blends was enhanced by the interaction of the polar group between the NH group in PEI and the OH group in CA. The hollow structure of the composite fibers could be observed after water treating, because of the dissolution of PEI inside the fibers. With the increase of PEI content, the side polar groups showed the enhanced repulsion under the effect of the electrical force, which led to PEI diffusing outwardly to the composite fiber surface.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nagiah N, Madhavi L, Anitha R, Srinivasan NT, Sivagnanam UT (2013) Electrospinning of poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid) and gelatin blended thin films: fabrication, characterization, and application in skin regeneration. Polym Bull 70(8):2337–2358
Tanir TE, Hasirci V, Hasirci N (2014) Electrospinning of chitosan/poly(lactic acid-co-glycolic acid)/hydroxyapatite composite nanofibrous mats for tissue engineering applications. Polym Bull 71(11):2999–3016
Kara MOP, Frey MW (2014) Effects of solvents on the morphology and conductivity of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonate) nanofibers. J Appl Polym Sci 131(11):40305
Hendrick E, Frey MW (2014) Increasing surface hydrophilicity in poly(lactic acid) electrospun fibers by addition of PLA-b-PEG co-polymers. J Eng Fiber Fabr 9(2):153–164
Mukundan S, Sant V, Goenka S, Franks J, Rohan LC, Sant S (2015) Nanofibrous composite scaffolds of poly(ester amides) with tunable physicochemical and degradation properties. Eur Polym J 68:21–35
Reddy KR, Hassan M, Gomes VG (2015) Hybrid nanostructures based on titanium dioxide for enhanced photocatalysis. Appl Catal A-Gen 489:1–16
Reddy KR, Gomes VG, Hassan M (2014) Carbon functionalized TiO2 nanofibers for high efficiency photocatalysis. Mater Res Express 1(1):015012
Reddy KR, Nakata K, Ichiai T, Murakami T, Tryk DA, Fujishima A (2011) Facile fabrication and photocatalytic application of Ag nanoparticles-TiO2 nanofiber composites. J Nanosci Nanotechno 11(4):3692–3695
Tsioptsias C, Sakellariou KG, Tsivintzelis I, Papadopoulou L, Panayiotou C (2010) Preparation and characterization of cellulose acetate–Fe2O3 composite nanofibrous materials. Carbohyd Polym 81:925–930
Frey MW (2008) Electrospinning cellulose and cellulose derivatives. Polym Rev 48(2):378–391
Zhang L, Hsieh Y-L (2008) Ultrafine cellulose acetate fibers with nanoscale structural features. J Nanosci Nanotechno 8(9):4461–4469
Ulasov AV, Khramtsov YV, Trusov GA, Rosenkranz AA, Sverdlov ED, Sobolev AS (2010) Properties of PEI-based polyplex nanoparticles that correlate with their transfection efficacy. Mol Ther 19(1):103–112
Celebioglu A, Uyar T (2011) Electrospun porous cellulose acetate fibers from volatile solvent mixture. Mater Lett 65(14):2291–2294
Kim MN, Koh J, Lee Y, Kim H (2009) Preparation of PVA/PAN bicomponent nanofiber via electrospinning and selective dissolution. J Appl Polym Sci 113(1):274–282
Liu SP, Tan LJ, Hu WL, Li XQ, Chen YM (2010) Cellulose acetate nanofibers with photochromic property: fabrication and characterization. Mater Lett 64(22):2427–2430
Zhang L, Hsieh Y-L (2008) Ultra-fine cellulose acetate/poly (ethylene oxide) bicomponent fibers. Carbohyd Polym 71(2):196–207
Chen CZ, Wang LG, Huang Y (2009) Crosslinking of the electrospun polyethylene glycol/cellulose acetate composite fibers as shape-stabilized phase change materials. Mater Lett 63(5):569–571
Tian Y, Wu M, Liu RG, Li YX, Wang DQ, Tan JJ, Wu RC, Huang Y (2010) Electrospun membrane of cellulose acetate for heavy metal ion adsorption in water treatment. Carbohyd Polym 83(2):743–748
Wang YQ, Su YL, Sun Q, Ma XL, Jiang ZY (2006) Generation of anti-biofouling ultrafiltration membrane surface by blending novel branched amphiphilic polymers with polyethersulfone. J Membr Sci 286:228–236
Herlem G, Gharbi T, Sedrine NB, Woo-Il B (2010) Analyzing ab initio infrared spectra and electronic properties of polyethylenimine water complexes in the solid state. J Mol Struct 945:27–32
Nango M, Klotz LM (1978) Catalysis by polyethylenimine derivatives with two functional groups. J Polym Sci Pol Chem 16:1265–1273
Cao SG, Hu BH, Liu HQ (2009) Synthesis of PH-responsive crosslinked poly[styrene-co-(maleic sodium anhydride)] and cellulose composite hydrogel nanofibers by electrospinning. Polym Int 58:545–551
Mahdavi H, Shahalizade T (2015) Preparation, characterization and performance study of cellulose acetate membranes modified by aliphatic hyperbranched polyester. J Membr Sci 473:256–266
Deitzel JM, Kleinmeyer J, Harris D, Tan NCB (2001) The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun nanofibers and textiles. Polymer 42(1):261–272
Zhou C, Chu R, Wu R, Wu Q (2011) Electrospun polyethylene oxide/cellulose nanocrystal composite nanofibrous mats with homogeneous and heterogeneous microstructures. Biomacromolecules 12(7):2617–2625
Demir MM, Yilgor I, Yilgor E, Erman B (2002) Electrospinning of polyurethane fibers. Polymer 43(11):3303–3309
Zhang YP, Lee SH, Reddy KR, Gopalan AI, Lee KP (2007) Sythesis and characterization of core-shell SO2 nanoparticles/poly(3-aminophenylboronic acid) composites. J Appl Polym Sci 104(4):2743–2750
Reddy KR, Raghu AV, Jeong HM (2008) Synthesis and characterization of novel polyurethanes based on 4,4′-{1,4-phenylenebis[methylylidenenitrilo]}diphenol. Polym Bull 60:609–616
Li PY, Zhang SJ, Chen SX, Zhang QK, Pan JJ, Ge BQ (2008) Preparation and adsorption properties of polythylenimine containing fibrous adsorbent for carbon dioxide capture. J Appl Polym Sci 108(6):3851–3858
Zeng K, Liu Y, Zheng S (2008) Poly(ethylene imine) hybrids containing polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes: preparation, structure and properties. Eur Polym J 44(12):3946–3956
Ramesh S, Shanti R, Morris E (2013) Characterization of conducting cellulose acetate polymer electrolytes doped with “green” ionic mixture. Carbohyd Polym 91(1):14–21
Meier MM, Kanis LA, Lima JC, Pires ATN, Soldi V (2004) Poly(caprolactone triol)as plasticizer agent for cellulose acetate films: influence of the preparation procedure and plasticizer content on the physic-chemical properties. Polym Advan Technol 15:593–600
Cheng CZ, Wang LG, Huang Y (2011) Electrospun phase change fibers based on polyethylene glycol/cellulose acetate blends. Appl Energ 88(9):3133–3139
Kim C, Jeong YI, Ngoc BTN, Yang KS, Kojima M, Kim YA, Endo M, Lee JW (2007) Synthesis and characterization of porous carbon nanofibers with hollow cores through the thermal treatment of electrospun copolymeric nanofiber webs. Small 3(1):91–95
Kriegel C, Kit KA, McClements DJ, Weiss J (2009) Nanofibers as carrier systems for antimicrobial microemulsions. Part I: fabrication and characterization. Langmuir 25(2):1154–1161
Chen HY, Di JC, Wang N, Dong H, Wu J, Zhao Y, Yu J, Jiang L (2011) Fabrication of hierarchically porous inorganic nanofibers by a general microemulsion electrospinning approach. Small 7(13):1779–1983
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Youth Foundation of Jilin Province (No. 201101059), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51103058) and Automotive and Material key Laboratory Foundation of Jilin University (No. 10-450060501458, 10-450060326014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, JZ., Xue, HL., Li, L. et al. Fabrication and morphology study of electrospun cellulose acetate/polyethylenimine nanofiber. Polym. Bull. 73, 2889–2906 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1630-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1630-6