Abstract
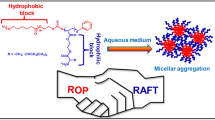
The pH-responsive amphiphilic poly(ε-caprolactone)-block-poly(acrylic acid) (PCL-b-PAA) copolymer was prepared by selective hydrolysis of one novel poly(ε-caprolactone)-block-poly(methoxymethyl acrylate) (PCL-b-PMOMA) block copolymer, which was synthesized by combining ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of ε-caprolactone (ε-CL) and atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) of methoxymethyl acrylate (MOMA). Selective hydrolysis of the hemiketal ester groups on the PMOMA block gave 100% deprotection without the cleavage of the PCL block. The self-assembly behavior of PCL-b-PAA was investigated by fluorescence spectroscopy, DLS and TEM. The spherical micelles were formed with the hydrophobic PCL block as the core and the hydrophilic PAA as the shell by a co-solvent evaporation method. Moreover, the size and size distribution of the micelles varied with pH value and ionic strength in aqueous solution. The cytotoxicity of the PCL-b-PAA was lower, which was confirmed by MTT assay.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee RS, Chen WH, Huang YT (2010) Synthesis and characterization of dual stimuli-responsive block copolymers based on poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-b-poly(pseudoamino acid). Polymer 51:5942–5951
Sun PJ, Zhang Y, Shi LQ, Gan ZH (2010) Thermosensitive nanoparticles self-assembled from PCL-b-PEO-b-PNIPAAm triblock copolymers and their potential for controlled drug release. Macromol Biosci 10:621–631
Wang YC, Li Y, Yang XZ, Yuan YY, Yan LF, Wang J (2009) Tunable thermosensitivity of biodegradable polymer micelles of poly(ε-caprolactone) and polyphosphoester block copolymers. Macromolecules 42:3026–3032
Tang RP, Ji WH, Wang C (2010) Amphiphilic block copolymers bearing ortho ester side-chains: pH-dependent hydrolysis and self-assembly in water. Macromol Biosci 10:192–201
Yang J, Zhang DW, Jiang S, Yang JJ, Nie J (2011) Synthesis of Y-shaped poly(solketal acrylate) containing block copolymers and study on the thermoresponsive behavior for micellar aggregates. J Colloid Interf Sci 352:405–414
Butsele VK, Cajot S, Vlierberghe VS et al (2009) pH-Responsive flower-type micelles formed by a biotinylated poly(2-vinylpyridine)-block-poly (ethylene oxide)-block-poly(ε-caprolactone) triblock copolymer. Adv Funct Mater 19:1416–1425
Zhang WL, He JL, Liu Z, Ni PH, Zhu XL (2010) Biocompatible and pH-responsive triblock copolymer mPEG-b-PCL-b-PDMAEMA: synthesis, self-Assembly, and application. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 48:1079–1091
Crisci A, Hay DNT, Sönke S, Firestone MA (2009) pH-and ionic-strength-induced structural changes in poly(acrylic acid)-lipid-based self-assembled materials. Macromol Symp 281:126–134
Xue YN, Huang ZZ, Zhang JT, Liu M, Zhang M, Huang SW, Zhuo RX (2009) Synthesis and self-assembly of amphiphilic poly(acrylic acid-b-DL-lactide) to form micelles for pH-responsive drug delivery. Polymer 50:3706–3716
Mellman I, Fuchs R, Helenius A (1986) Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem 55:663–700
Gillies ER, Jonsson TB, Fréchet JMJ (2004) Stimuli-responsive supramolecular assemblies of linear-dendritic copolymers. J Am Chem Soc 126:11936–11943
Liu FT, Eisenberg A (2003) Preparation and pH triggered inversion of vesicles from poly(acrylic Acid)-block-polystyrene-block-poly(4-vinyl pyridine). J Am Chem Soc 125:15059–15064
Karanikolas A, Tsolakis P, Bokias G, Tsitsilianis C (2008) Stimuli-responsive poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(2-vinylpyridine)-b-poly(ethylene oxide) triblock copolymers and complexation with poly(acrylic acid) at low pH. Eur Phys J E 27:335–343
Guice KB, Marrou SR, Gondi SR, Sumerlin BS, Loo YL (2008) pH Response of model diblock and triblock copolymer networks containing polystyrene and poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate. Macromolecules 41:4390–4397
Chen JY, Jiang M, Zhang YX, Zhou H (1999) Fluorescence studies on hydrophobic associations of fluorocarbon-modified poly(acrylic acid) solutions. Macromolecules 32:4861–4866
Mori H, Müller AHE (2003) New polymeric architectures with (meth)acrylic acid segments. Prog Polym Sci 28:1403–1439
Zhang LF, Eisenberg A (1995) Multiple morphologies of “crew-cut” aggregates of polystyrene-b-poly(acrylic acid) block copolymers. Science 268:1728
Desbaumes L, Eisenberg A (1999) Single-solvent preparation of crew-cut aggregates of various morphologies from an amphiphilic diblock copolymer. Langmuir 15:36–38
Bernkop-Schnürch A, Moser V, Leitner V (2004) Synthesis and in vitro characterization of a poly(acrylic acid)-homocystein. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 30:9–17
Ponchel G, Touchard F, Duchêne D, Peppas NA (1987) Bioadhesive analysis of controlled-release systems I. Fracture and interpenetration analysis in poly(acrylic acid) containing systems. J Control Rel 5:129–141
Thermes F, Rozier A, Plazonnet B, Grove J (1992) Bioadhesion: the effect of polyacrylic acid on the ocular bioavailability of timolol. Int J Pharm 81:59–65
Patten TE, Matyjaszewki K (1998) Atom transfer radical polymerization and the synthesis of polymeric materials. Adv Mater 10:901–903
Sun YL, Peng ZP, Liu XX, Tong Z (2010) Synthesis and pH-sensitive micellization of doubly hydrophilic poly(acrylic acid)-b-poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(acrylic acid) triblock copolymer in aqueous solutions. Colloid Polym Sci 288:997–1003
Javakhishvili I, Hvilsted S (2009) Gold nanoparticles protected with thiol-derivatized amphiphilic poly(ε-caprolactone)-b-poly(acrylic acid). Biomacromolecules 10:74–81
Zhang Q, Remsen EE, Wooley KL (2000) Shell cross-linked nanoparticles containing hydrolytically degradable, crystalline core domains. J Am Chem Soc 122:3642–3651
Wittemann A, Azzam T, Eisenberg A (2007) Biocompatible polymer vesicles from biamphiphilic triblock copolymers and their Interaction with bovine serum albumin. Langmuir 23:2224–2230
Lee HJ, Lee SC (2010) Fabrication of core-shell hybrid nanoparticles by mineralization on poly(ε-caprolactone)-b-poly(methacrylic acid) copolymer micelles. Polym Bull 65:743–752
Jansen ABA, Russel JT (1965) Some novel penicillin drivatives. J Chem Soc 2127–2131
Vnwetswinkel S, Carlier V, Marchand-Brynaert J et al (1996) Solvolysis of the methoxymethyl protecting group in penicillin derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett 37:2761–2762
Kim S, Park YH, Kee IS (1991) Mild deprotection of methoxymethyl, methylthio -methyl, methoxy ethoxymethyl and [beta]-(trimethylsilyl) ethoxymethyl esters with magnesium bromide in ether. Tetrahedron Lett 32:3099–3100
Peng D, Zhang XH, Huang XY (2006) Synthesis of amphiphilic graft copolymer with hydrophilic poly(acrylic acid) backbone and hydrophobic polystyrene side chains. Polymer 47:6072–6080
Peng D, Zhang XH, Huang XY (2006) Novel starlike amphiphilic graft copolymers with hydrophilic poly(acrylic acid) backbone and hydrophobic poly(methyl methacrylate) side chains. Macromolecules 39:4945–4947
Yang D, Tong L, Li YJ, Hu JH, Zhang S, Huang XY (2010) A novel well-defined amphiphilic diblock copolymer containing perfluorocyclobutyl aryl ether-based hydrophobic segment. Polymer 51:1752–1760
Stridsberg KM, Ryner M, Albertsson AC (2002) Controlled ring-opening polymerization: polymers with designed macromolecular architecture. Adv Polym Sci 157:41–65
Lang MD, Wong RP, Chu CC (2002) Synthesis and structural analysis of functionalized poly(ε-caprolactone)-based three-arm star polymers. J Polym Sci Part A 20:1127–1141
Yun WZ, Huang XB, Tang XZ (2005) Synthesis of star-shaped PCL-b-PMMA/PSt from cyclotriphosphazene initiator by ring-opening polymerization and atom transfer radical polymerization. Polym Bull 55:225–233
Zhang B, Li YP, Wang W, Chen L, Wang SW, Wang JY (2009) Chemoenzymatic synthesis of Y-shaped diblock copolymer. Polym Bull 62:643–655
Kalyanasundaram K, Thomas JK (1977) Environmental effect on vibronic band intensities in pyrene monomer fluorescence and their application in studies of micellar systems. J Am Chem Soc 99:2039–2044
Lee SC, Kim KJ, Jeong YK, Chang JH, Choi J (2005) pH-Induced reversible complexation of poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ε-caprolactone)-b-poly(methacrylic acid) copolymer micelles. Macromolecules 38:9291–9297
Arimura H, Ohya YC, Ouchi T (2005) Formation of core-shell type biodegradable polymeric cells from amphiphilic poly(aspartic acid)-block-polylactide diblock copolymer. Biomacromolecules 6:720–725
Acknowledgments
Financial supports from “Shu Guang” Project of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (WD0913008, WD1014036), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20804015), and Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (200802511021) were gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Gu, C., Zhang, Y. et al. Synthesis and self-assembly of pH-responsive amphiphilic poly(ε-caprolactone)-block-poly(acrylic acid) copolymer. Polym. Bull. 68, 69–83 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-011-0520-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-011-0520-1