Abstract
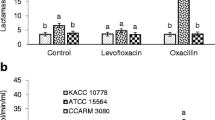
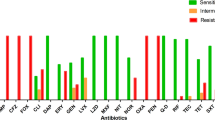
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a notorious superbug which poses serious health threats to humanity. The severity of the infections depends on the prevalence of virulence factors and antibiotic resistance. In this study, attempts have been made to nominate the two most virulent and multidrug-resistant MRSA isolates demonstrating the preliminary features of intestinal adhesion for the futuristic applications of probiotics and postbiotics as antagonists to combat MRSA infections. In this context, six clinical isolates of MRSA were polyphasically characterized for their identity, multidrug resistance, and few selected virulence determinates such as hemolytic activity and production of coagulase, nuclease, and capsule. The gut colonizing ability of MRSA isolates was assessed by mucoadhesion, auto-aggregation, and cell surface hydrophobicity. An antibiogram of MRSA isolates suggested the resistance towards several antibiotics with multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR) index >0.5 (12/241, 12/206, and 5/255) as well as their genome portraying mecA mediated methicillin resistance. Besides exhibiting strong biofilm formation ability, all the isolates exhibited positive responses towards tested virulence assays coupled with their genome displaying Coa, NucA, and CapE genes. On the other hand, isolates exhibited different levels of auto-aggregation (37.90 ± 1.8 to 51.53 ± 3.1%) and mucin adhesion ability (68.93 ± 0.61% to 86.62 ± 1.96%) with a significant (P ≤ 0.05) variation in adhesion to different hydrocarbons. Finally, multivariate Principal Component Analysis and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA) heatmap using Euclidean distance measurement indicated MRSA 12/206 and 5/255 as most resistant and virulent isolates with the potential to adhere to the hydrophobic gut niche.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
MacIntyre CR, Bui CM (2017) Pandemics, public health emergencies and antimicrobial resistance-putting the threat in an epidemiologic and risk analysis context. Arch Public Health 75:1–6
Ragupathi NKD, Sethuvel DPM, Gajendran R, Anandan S, Walia K, Veeraraghavan B (2019) Horizontal transfer of antimicrobial resistance determinants among enteric pathogens through bacterial conjugation. Current Microbial 76:666–672
Huddleston JR (2014) Horizontal gene transfer in the human gastrointestinal tract: potential spread of antibiotic resistance genes. Infect Drug Resist 7:167
Attia H, Szubin R, Yassin AS, Monk JM, Aziz RK (2019) Draft genome sequences of four metallo-beta-lactamase-producing multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates, including two colistin-resistant strains, from Cairo Egypt. Microbiol Resour Announc 8:1–3
Asokan GV, Ramadhan T, Ahmed E, Sanad H (2019) WHO global priority pathogens list: a bibliometric analysis of Medline-PubMed for knowledge mobilization to infection prevention and control practices in Bahrain. Oman Med J 34:184
Foster TJ (2017) Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: current status and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol Rev 41:430–449
Mascaro V, Squillace L, Nobile CG, Papadopoli R, Bosch T, Schouls LM, Casalinuovo F, Musarella R, Pavia M (2019) Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) carriage and pattern of antibiotic resistance among sheep farmers from southern Italy. Infect Drug Resist 12:2561
Udo EE, Boswihi SS, Mathew B, Noronha B, Verghese T, Al-Jemaz A, Al-Saqer F (2020) Emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus belonging to clonal complex 15 (CC15-MRSA) in Kuwait hospitals. Infect Drug Resist 13:617
Crago B, Ferrato C, Drews SJ, Svenson LW, Tyrrell G, Louie M (2012) Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) in food samples associated with foodborne illness in Alberta, Canada from 2007 to 2010. Food Microbial 32:202–205
Lane AB, Copeland NK, Onmus-Leone F, Lawler JV (2018) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus as a probable cause of antibiotic-associated enterocolitis. Case Rep Infect Dis 2018:1–3
Krezalek MA, Hyoju S, Zaborin A, Okafor E, Chandrasekar L, Bindokas V, Guyton K, Montgomery CP, Daum RS, Zaborina O, Boyle-Vavra S (2018) Can methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus silently travel from the gut to the wound and cause postoperative infection? Modeling the “Trojan horse hypothesis.” Ann Surg 267:749–758
Srisuwan S, Voravuthikunchai SP (2017) Rhodomyrtus tomentosa leaf extract inhibits methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus adhesion, invasion, and intracellular survival in human HaCaT keratinocytes. Microb Drug Resist 23:1002–1012
Pospiech A, Neumann B (1995) A versatile quick-prep of genomic DNA from gram-positive bacteria. Trends Genet 11:217–218
Yuan S, Cohen DB, Ravel J, Abdo Z, Forney LJ (2012) Evaluation of methods for the extraction and purification of DNA from the human microbiome. PLoS ONE 7:33865
O’sullivan DJ, Klaenhammer TR (1993) Rapid mini-prep isolation of high-quality plasmid DNA from Lactococcus and Lactobacillus spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:2730–2733
Bauer AW, Kirby WMM, Sherris JC, Turck M (1996) Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disc method. Am J Clin Pathol 45:493–496
CLSI (2013) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing CLSI approved standard M100–S23. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne
Gowrishankar S, Kamaladevi A, Balamurugan K, Pandian SK (2016) In vitro and in vivo biofilm characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from patients associated with pharyngitis infection. BioMed Res Int 2016:1–13
Lee HY, Zou Y, Ahn J (2013) Physiochemical and molecular properties of antimicrobial-exposed Staphylococcus aureus during the planktonic-to-biofilm transition. Ann Microbiol 63:1213–1217
Rahimi F, Katouli M, Karimi S (2016) Biofilm production among methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from catheterized patients with urinary tract infection. Microb Pathog 98:69–76
Hou W, Sun X, Wang Z, Zhang Y (2012) Biofilm-forming capacity of Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa from ocular infections. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:5624–5631
Meidong R, Khotchanalekha K, Doolgindachbaporn S, Nagasawa T, Nakao M, Sakai K, Tongpim S (2018) Evaluation of probiotic Bacillus aerius B81e isolated from healthy hybrid catfish on growth, disease resistance and innate immunity of Pla-mong Pangasius bocourti. Fish Shellfish Immun 73:1–10
Pradhan D (2017) Assessing preclinical safety of indigenous probiotic L. fermentum Lf1 strains. Doctoral dissertation, NDRI, Karnal
Gajdács M (2019) The continuing threat of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 28:52
Li Y, Lee Y, Seo Y, Hwang Y (2019) Relationship of multidrug-resistant gene and extended-spectrum carbapenem-resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Biocell 43:263
Becker K, Van Alen S, Idelevich EA, Schleimer N, Seggewiß J, Mellmann A, Kaspar U, Peters G (2018) Plasmid-encoded transferable mecB-mediated methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Emerg Infect Dis 24:242
Jiang N, Li J, Feßler AT, Wang Y, Schwarz S, Wu C (2019) Novel pseudo-staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec element (φSCC mec T55) in MRSA ST9. J Antimicrob Chemoth 74:819–820
Chavadi M, Narasanna R, Chavan A, Oli AK (2018) Prevalence of methicillin resistant and virulence determinants in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Open Infect Dis J 10:108–115
Bhatia A, Kalra J, Kohli S, Kakati B, Kaushik R (2018) Antibiotic resistance pattern in intensive care unit of a tertiary care teaching hospital. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol 7:906
Udobi CE, Obajuluwa AF, Onaolapo JA (2013) Prevalence and antibiotic resistance pattern of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from an orthopaedic hospital in Nigeria. BioMed Res Int 2013:1–4
Ko YP, Kuipers A, Freitag CM, Jongerius I, Medina E, van Rooijen WJ, Spaan AN, van Kessel KP, Höök M, Rooijakkers SH (2013) Phagocytosis escape by a Staphylococcus aureus protein that connects complement and coagulation proteins at the bacterial surface. PLoS Pathog 9:1003816
Rothman A, Lio J, Lee YI (2018) MRSA colitis: an under-recognized cause of septic shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 197:A5187–A5187
Melgar-Lalanne G, Rivera-Espinoza Y, Téllez-Medina DI, Hernández-Sánchez H (2015) Cell surface properties of halotolerant probiotic lactobacilli. J Adv Biotechnol 4:404–413
Rokana N, Singh BP, Thakur N, Sharma C, Gulhane RD, Panwar H (2018) Screening of cell surface properties of potential probiotic lactobacilli isolated from human milk. J Dairy Res 85:347–354
Kos B, Suskovic J, Vukovic S, Simpraga M, Frece J, Matosic S (2003) Adhesion and aggregation ability of probiotic strain Lactobacillus acidophilus M92. J Appl Microbiol 94:981–987
Choi NY, Bae YM, Lee SY (2015) Cell surface properties and biofilm formation of pathogenic bacteria. Food Sci Biotechnol 24:2257–2264
Trunk T, Khalil HS, Leo JC (2018) Bacterial autoaggregation. AIMS Microbiol 4:140
Gogra AB, Yao J, Sandy EH, Zheng S, Zaray G, Koroma BM, Hui Z (2010) Cell surface hydrophobicity (CSH) of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Aspergillus niger and the biodegradation of diethyl phthalate (DEP) via microcalorimetry. Am J Sci 6:78–88
Drenkard E, Ausubel FM (2002) Pseudomonas biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance are linked to phenotypic variation. Nature 416:740–743
Ghasemian A, Peerayeh SN, Bakhshi B, Mirzaee M (2016) Comparison of biofilm formation between methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Iran Biomed J 20:175
Ghasemian A, Peerayeh SN, Bakhshi B, Mirzaee M (2015) The microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules (MSCRAMMs) genes among clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from hospitalized children. Iran J Pathol 10:258
Ray SM, Harrison LH, Lynfield R, Dumyati G (2018) Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections among persons who inject drugs—six sites, 2005–2016. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 67:625
Celebioglu HU, Olesen SV, Prehn K, Lahtinen SJ, Brix S, Hachem MA, Svensson B (2017) Mucin- and carbohydrate-stimulated adhesion and subproteome changes of the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. J Proteomics 163:102–110
Shuter J, Hatcher VB, Lowy FD (1996) Staphylococcus aureus binding to human nasal mucin. Infect Immun 64:310–318
Nami Y, Panahi B, Jalaly HM, Bakhshayesh RV, Hejazi MA (2020) Application of unsupervised clustering algorithm and heat-map analysis for selection of lactic acid bacteria isolated from dairy samples based on desired probiotic properties. LWT Food Sci Technol 118:108839
Shome BR, Das Mitra S, Bhuvana M, Krithiga N, Velu D, Shome R, Isloor S, Barbuddhe SB, Rahman H (2011) Multiplex PCR assay for species identification of bovine mastitis pathogens. J Appl Microbiol 111:1349–1356
Pu W, Su Y, Li J, Li C, Yang Z, Deng H, Ni C (2014) High incidence of oxacillin-susceptible mecA-positive Staphylococcus aureus (OS-MRSA) associated with bovine mastitis in China. PLoS ONE 9:88134
El-Behiry A, Elsayed M, Marzouk E, Bathich Y (2015) Detection of virulence genes in Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus agalatctiae isolated from mastitis in the middle east. Br Microbiol Res J 10:1–9
Igbinosa EO, Beshiru A, Akporehe LU, Oviasogie FE, Igbinosa OO (2016) Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and other Staphylococcus species in raw meat samples intended for human consumption in Benin city, Nigeria: implications for public health. Int J Env Res Pub He 13:949
Batte JL, Samanta D, Elasri MO (2016) MsaB activates capsule production at the transcription level in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology 162:575–589
Acknowledgements
Authors are greatly thankful to the Director, ICAR-National Dairy Research Institute, Karnal for providing the necessary research facilities to carry out the present study. BHN is thankful to the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi for providing a Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) during his Master’s degree program. We are highly thankful to the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi for providing clinical isolates of MRSA for R&D purposes.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or nonprofit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BHN: study/research execution, methodology, formal Analysis, and original draft preparation, CR: research execution, formal analysis, and validation, RHM: conceptualization, funding acquisition, methodology, editing, supervision, validation, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The clinical isolates used in the study have been approved by the Institute Ethics Committee of All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi (Ref No: IEC-484/02.08.2019, RP-54/2019).
Consent for Publication
All the authors concur with the publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nataraj, B.H., Ramesh, C. & Mallappa, R.H. Characterization of Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Traits Present in Clinical Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolates. Curr Microbiol 78, 2001–2014 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-021-02477-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-021-02477-x