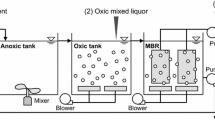
Abstract
Human enteric viruses constitute a public health concern due to their low infectious dose and their resistance to environmental factors and to inactivation processes. We aimed at assessing the performance of a laboratory scale Submerged membrane bioreactor (SMBR) treating abattoir wastewaters for Rotavirus (RV) and total coliphages removal. We also aimed at evaluating removal efficiency of enteric viruses through conventional activated sludge treatment by measuring concentrations of total coliphages, considered as fecal and viral contamination indicators, with double-layer agar technique. The Log10 reduction values of bacteriophages ranged from 1.06 to 1.47. Effluents were analyzed to investigate and quantify RV, hepatitis A virus (HAV), Hepatitis E virus (HEV), Noroviruses genogroup I (NoV GI) and genogroup II (NoVGII), and Enterovirus (EV) by real-time PCR, using standardized detection kits (ceeramTools detection kits®). All effluent samples were positive for RV; concentrations ranged from 5.2 × 105 to 1.3 × 107 genome copies/L. These results highlight the inefficiency of conventional biological process for viral removal. A complete removal of RV during Membrane Bioreactor treatment was obtained. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study providing an evidence of removal of RV simultaneously with total coliphages by SMBR.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arraj A, Bohatier J, Laveran H, Traore O (2005) Comparison of bacteriophage and enteric virus removal in pilot scale activated sludge plants. J Appl Microbiol 98:516–524
Blanch A, Belanche-Muñoz L, Bonjoch X, Ebdon J, Gantzer C, Lucena F, Ottoson J, Kourtis C, Iversen A, Kühn I, Mocé L, Muniesa M, Schwartzbrod J, Skraber S, Papageorgiou GT, Taylor H, Wallis J, Jofre J (2006) Integrated analysis of established and novel microbial and chemical methods for microbial source tyracking. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5915–5926
Boccia D, Tozzi AE, Cotter B, Rizzo C, Russo T, Buttinelli G, Caprioli A, Marziano ML, Ruggeri FM (2002) Waterborne outbreak of norwalk-like virus gastroenteritis at a tourist resort, Italy. Emerg Infect Dis 8:563–568
Cook N, Bridger J, Kendall K, Gomara MI, El-Attar L, Gray J (2004) The zoonotic potential of rotavirus. J Infect 48(4):289–302
Contreras-Coll N, Lucena F, Mooijman K, Havelaar A, Pierz V, Boque M, Gawler A, Höller C, Lambiri M, Mirolo G, Moreno B, Niemi M, Sommer R, Valentin B, Wiedenmann A, Young V, Jofre J (2002) Occurrence and levels of indicator bacteriophages in bathing waters throughout Europe. Water Res 36:4963–4974
Costán-Longares A, Montemayor M, Payán A, Mendez J, Jofre J, Mujeriego R, Lucena F (2008) Microbial indicators and pathogens: removal, relatioships and predictive capabilities in water reclamation facilities. Water Res 42:4439–4448
da Silva AK, Le Saux JC, Parnaudeau S, Pommepuy M, Elimelech M, Le Guyader FS (2007) Evaluation of removal of noroviruses during wastewater treatment, using real-time reverse transcription-PCR: different behaviors of genogroups I and II. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(24):7891–7897
De Luca G, Sacchetti R, Leoni E, Zanetti F (2013) Removal of indicator bacteriophages from municipal wastewater by a full-scale membrane bioreactor and a conventional activated sludge process: implications to water reuse. Bioresour Technol 129:526–531
Francy DS, Stelzer EA, Bushon RN, Brady AM, Williston AG, Riddell KR, Borchardt MA, Spencer SK, Gellner TM (2012) Comparative effectiveness of membrane bioreactors, conventional secondary treatment, and chlorine and UV disinfection to remove microorganisms from municipal wastewaters. Water Res 46(13):4164–4178
Gerba CP, Gramos DM, Nwachuku N (2002) Comparative inactivation of enteroviruses and adenovirus 2 by UV light. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5165–5169
Giammanco GM, Di Bartolo I, Purpari G, Costantino C, Rotolo V, Spoto V, Geraci G, Bosco G, Petralia A, Guercio A, Macaluso G, Calamusa G, De Grazia S, Ruggeri FM, Vitale F, Maida CM, Mammina C (2014) Investigation and control of a Norovirus outbreak of probable waterborne transmission through a municipal groundwater system. J Water Health 12(3):452–464
Gibson KE (2014) Viral pathogens in water: occurrence, public health impact, and available control strategies. Curr Opin Virol 4:50–57
Guzmán C, Jofre J, Blanch AR, Lucena F (2007) Development of a feasible method to extract somatic coliphages from sludge, soil and treated biowaste. J Virol Metods 144:41–48
Guzmán C, Mocé-Llivina L, Lucena F, Jofre J (2008) Evaluation of Escherichia coli Host Strain CB390 for Simultaneous Detection of somatic and F-specific coliphages. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(2):531–534
Harwood VJ, Levine AD, Scott TM, Chivukula V, Lukasik J, Farrah SR, Rose JB (2005) Validity of the indicator organism paradigm for pathogen reduction in reclaimed water and public health protection. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3163–3170
Hassine-Zaafrane M, Sdiri-Loulizi K, Kaplon J, Ben Salem I, Pothier P, Aouni MAmbert-Balay K (2014) Molecular detection of human noroviruses in influent and effluent samples from two biological sewage treatment plants in the region of Monastir, Tunisia. Food Environ Virol 6(2):125–131
Hellara O, Melki W, Mastouri M, Ben Chaabène N, Loghmari H, Ben Mansour W, Bdioui F, Safer L, Saffar H (2014) Serodiagnosis of acute hepatitis in adults patients : results of a prospective study in a central region of Tunisia. Tunis Med 92(3):201–207
Jebri S, Jofre J, Barkallah I, Saidi M, Hmaied F (2012) Presence and fate of coliphages and enteric viruses in three wastewater treatment plants effluents and activated sludge from Tunisia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:2195–2201
Jebri S, Hmaied F, Jofre J, Yahya M, Mendez J, Barkallah I, Hamdi M (2013) Effect of gamma irradiation on bacteriophages used as viral indicators. Water Res 47:3673–3678
Jofre J, Ollé E, Ribas F, Vidal A, Lucena F (1995) Potential usefulness of bacteriophages that infect Bacteroides fragilis as model organisms for monitoring virus removal in drinking water treatment plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3227–3231
Jurzik L, Hamza IA, Puchert W, Uberla K, Wilhelm M (2010) Chemical and microbiological parameters as possible indicators for human enteric viruses in surface water. Int J Hyg Environ Health 213:210–216
Keskes S, Hmaied F, Gannoun H, Bouallagui H, Godon JJ, Hamdi M (2012) Performance of a submerged membrane bioreactor for the aerobic treatment of abattoir wastewater. Bioresour Technol 103(1):28–34
Koroglu M, Yakupogullari Y, Otlu B, Ozturk S, Ozden M, Ozer A, Sener K, Durmaz R (2011) A waterborne outbreak of epidemic diarrhea due to group A rotavirus in Malatya, Turkey. New Microbiol 34:17–24
Kotwal G, Cannon JL (2014) Environmental persistence and transfer of enteric viruses. Curr Opin Virol 4:37–43
Kuo DH, Simmons FJ, Blair S, Hart E, Rose JB, Xagoraraki I (2010) Assessment of human adenovirus removal in a full-scale membrane bioreactor treating municipal wastewater. Water Res 44(5):1520–1530
Li D, Gu AZ, Zeng SY, Yang W, He M, Shi HC (2011) Monitoring and evaluation of infectious rotaviruses in various wastewater effluents and receiving waters revealed correlation and seasonal pattern of occurrences. J Appl Microbiol 110(5):1129–1137
Lucena F, Duran AE, Morón A, Calderón E, Campos C, Gantzer C, Skraber S, Jofre J (2004) Reduction of bacterial indicators and bacteriophages infecting faecal bacteria in primary and secondary wastewater treatments. J Appl Microbiol 97:1069–1076
Mandilara GD, Smeti EM, Mavridou AT, Lambiri MP, Vatopoulos AC, Rigas FP (2006) Correlation between bacterial indicators and bacteriophages in sewage and sludge. FEMS Microbiol Lett 263:119–126
Parashar UD, Gibson CJ, Bresse JS, Glass RI (2006) Rotavirus and severe childhood diarrhea. Emerg Infect Dis 12:304–306
Rezezutka A, Cook N (2004) Survival of human enteric viruses in the environment and food. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28:441–453
Sdiri-Loulizi K, Gharbi-Khélifi H, de Rougemont A, Chouchane S, Sakly N, Ambert-Balay K, Hassine M, Guédiche MN, Aouni M, Pothier P (2008) Acute infantile gastroenteritis associated with human enteric viruses in Tunisia. J Clin Microbiol 46(4):1349–1355
Sdiri-Loulizi K, Hassine M, Aouni Z, Gharbi-Khelifi H, Chouchane S, Sakly N, Neji-Guédiche M, Pothier P, Aouni M, Ambert-Balay K (2010) Detection and molecular characterization of enteric viruses in environmental samples in Monastir, Tunisia between January 2003 and April 2007. J Appl Microbiol 109(3):1093–1104
Sdiri-Loulizi K, Ambert-Balay K, Gharbi-Khelifi H, Hassine M, Chouchane S, Sakly N, Neji-Guédiche M, Pothier P, Aouni M (2011) Molecular epidemiology and clinical characterization of group A rotavirus infections in Tunisian children with acute gastroenteritis. Can J Microbiol 57(10):810–819
Simmons F, Kuo D, Xagoraraki I (2011) Removal of human enteric viruses by a full-scale membrane bioreactor during municipal wastewater processing. Water Res 45:2739–2750
Skraber S, Gassilloud B, Gantzer C (2004) Comparison of coliforms and coliphages as tools for assessment of viral contamination in river water. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3644–3649
Soltani M, Bouanene I, Trabelsi A, Harbi A, Hachicha M, Amri F, Boussnina S, Gueddiche MN, Sfar MT, Teleb N, Ben Ghorbel M, Ben Hamida E (2012) Epidemiology of rotavirus gastroenteritis among children under 5 years of age in Tunisia—results of sentinel hospital surveillance 2009 to 2011. Rev Epidemiol Sante Pub 60(6):473–480
Swain S, Baral P, Hutin Y, Rao T, Murhekar M, Gupte M (2010) A hepatitis E outbreak caused by a temporary interruption in a municipal water treatment system, Baripada, Orissa, India, 2004. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 104:66–69
USEPA (2004) Guidelines for water reuse. EPA Report No. 625-R-04-108. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
WHO (1989) Health guidelines for the use of waste water in agriculture and aquaculture. Technical report series 778. WHO, Geneva
Zhou J, Wang XC, Ji Z, Xu L, Yu Z (2015) Source identification of bacterial and viral pathogens and their survival/fading in the process of wastewater treatment, reclamation, and environmental reuse. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31(1):109–120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hmaied, F., Keskes, S., Jebri, S. et al. Removal of Rotavirus and Bacteriophages by Membrane Bioreactor Technology from Sewage. Curr Microbiol 71, 540–545 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0882-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0882-y