Abstract
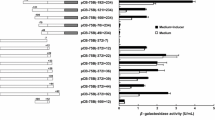
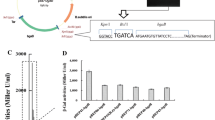
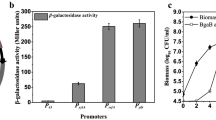
The expression and application of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) chitinase genes have been extensively investigated. However, little information is available regarding the regulation of chitinase gene expression in Bt. In this study, a shuttle promoter-probe vector was constructed incorporating the thermostable β-galactosidase gene bgaB of B. stearothermophilus as the reporter for the study of Bt promoters. Using this plasmid, the activity of the chiA gene promoter in Bt was investigated. Deletion analysis of the putative chiA promoter region revealed that the sequence located ~75 bp DNA from positions −116 to −42, with respect to the translation start site, is the core promoter of chiA gene. Furthermore, a site for chitin induction was identified near position −36. This site for negative regulation was indicated downstream of the RNA polymerase binding sites of the promoter of chiA. The expression of chiA started in cell grown for about 6 h and reached the maximum after 60 h of incubation. Induction of chiA expression by chitin was demonstrated by an increase in β-galactosidase activity of ~2.5-fold.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arantes O, Lereclus D (1991) Construction of cloning vectors for Bacillus thuringiensis. Gene 108(1):115–119
Barboza-Corona JE, Nieto-Mazzocco E, Veldazquez-Robledo R, Salcedo-Hernandez R, Bautista M, Jimenez B, Ibarra JE (2003) Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the chitinase gene chiA74 from Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl Environ Microb 69(2):1023–1029
Barboza-Corona JE, Ortiz-Rodriguez T, de la Fuente-Salcido N, Bideshi DK, Ibarra JE, Salcedo-Hernandez R (2009) Hyperproduction of chitinase influences crystal toxin synthesis and sporulation of Bacillus thuringiensis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 96(1):31–42
Barboza-Corona JE, Reyes-Rios DM, Salcedo-Hernandez R, Bideshi DK (2008) Molecular and biochemical characterization of an endochitinase (ChiA-HD73) from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp kurstaki HD-73. Mol Biotechnol 39(1):29–37
Bertram R, Rigali S, Wood N, Lulko AT, Kuipers OP, Titgemeyer F (2011) Regulon of the N-acetylglucosamine utilization regulator NagR in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 193(14):3525–3536
Chen W, Chen H, Xia Y, Zhao J, Tian F, Zhang H (2008) Production, purification, and characterization of a potential thermostable galactosidase for milk lactose hydrolysis from Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Dairy Sci 91(5):1751–1758
Chen YL, Lu W, Chen YH, Xiao L, Cai J (2007) Cloning, expression and sequence analysis of chiA, chiB in Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. colmeri 15A3. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 47(5):843–848
Colson S, Stephan J, Hertrich T, Saito A, van Wezel GP, Titgemeyer F, Rigali S (2007) Conserved cis-acting elements upstream of genes composing the chitinolytic system of streptomycetes are DasR-responsive elements. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 12(1–2):60–66
Delic I, Robbins P, Westpheling J (1992) Direct repeat sequences are implicated in the regulation of two Streptomyces chitinase promoters that are subject to carbon catabolite control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89(5):1885–1889
Ding XZ, Luo ZH, Xia LQ, Gao B, Sun YJ, Zhang YM (2008) Improving the insecticidal activity by expression of a recombinant cry1Ac gene with chitinase-encoding gene in acrystalliferous Bacillus thuringiensis. Curr Microbiol 56(5):442–446
Driss F, Kallassy-Awad M, Zouari N, Jaoua S (2005) Molecular characterization of a novel chitinase from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. J Appl Microbiol 99(4):945–953
Driss F, Rouis S, Azzouz H, Tounsi S, Zouari N, Jaoua S (2011) Integration of a recombinant chitinase into Bacillus thuringiensis parasporal insecticidal crystal. Curr Microbiol 62(1):281–288
Fujita Y (2009) Carbon catabolite control of the metabolic network in Bacillus subtilis. Biosci Biotech Bioch 73(2):245–259
Hirata H, Negoro S, Okada H (1984) Molecular basis of isozyme formation of beta-galactosidases in Bacillus stearothermophilus: isolation of two beta-galactosidase genes, bgaA and bgaB. J Bacteriol 160(1):9–14
Honeyman AL, Cote CK, Curtiss R 3rd (2002) Construction of transcriptional and translational lacZ gene reporter plasmids for use in Streptococcus mutans. J Microbiol Methods 49(2):163–171
Huang CJ, Wang TK, Chung SC, Chen CY (2005) Identification of an antifungal chitinase from a potential biocontrol agent, Bacillus cereus 28-9. J Biochem Mol Biol 38(1):82–88
Hu SB, Liu P, Ding XZ, Yan L, Sun YJ, Zhang YM, Li WP, Xia LQ (2009) Efficient constitutive expression of chitinase in the mother cell of Bacillus thuringiensis and its potential to enhance the toxicity of Cry1Ac protoxin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82(6):1157–1167
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6(13):3901–3907
Kraus A, Hueck C, Gartner D, Hillen W (1994) Catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis xyl operon involves a cis element functional in the context of an unrelated sequence, and glucose exerts additional xylR-dependent repression. J Bacteriol 176(6):1738–1745
Lecadet MM, Chaufaux J, Ribier J, Lereclus D (1992) Construction of novel Bacillus thuringiensis strains with different insecticidal activities by transduction and transformation. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(3):840–849
Lin Y, Xiong G (2004) Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the chitinase gene from Bacillus thuringiensis serovar alesti. Biotechnol Lett 26(8):635–639
Liu D, Cai J, Xie CC, Liu C, Chen YH (2010) Purification and partial characterization of a 36-kDa chitinase from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp colmeri, and its biocontrol potential. Enzyme Microb Tech 46(3–4):252–256
Ni X, Westpheling J (1997) Direct repeat sequences in the Streptomyces chitinase-63 promoter direct both glucose repression and chitin induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(24):13116–13121
Prasher DC, Eckenrode VK, Ward WW, Prendergast FG, Cormier MJ (1992) Primary structure of the Aequorea victoria green-fluorescent protein. Gene 111(2):229–233
Reyes-Ramirez A, Escudero-Abarca BI, Aguilar-Uscanga G, Hayward-Jones PM, Barboza-Corona JE (2004) Antifungal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis chitinase and its potential for the biocontrol of phytopathogenic fungi in soybean seeds. J Food Sci 69(5):M131–M134
Santos PM, Di Bartolo I, Blatny JM, Zennaro E, Valla S (2001) New broad-host-range promoter probe vectors based on the plasmid RK2 replicon. FEMS Microbiol Lett 195(1):91–96
Seo JW, Ohnishi Y, Hirata A, Horinouchi S (2002) ATP-binding cassette transport system involved in regulation of morphological differentiation in response to glucose in Streptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol 184(1):91–103
Thamthiankul S, Suan-Ngay S, Tantimavanich S, Panbangred W (2001) Chitinase from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. pakistani. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56(3–4):395–401
van der Vossen JM, Kok J, Venema G (1985) Construction of cloning, promoter-screening, and terminator-screening shuttle vectors for Bacillus subtilis and Streptococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 50(2):540–542
Vriesema AJ, Brinkman R, Kok J, Dankert J, Zaat SA (2000) Broad-host-range shuttle vectors for screening of regulated promoter activity in viridans group streptococci: isolation of a pH-regulated promoter. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(2):535–542
Wang SY, Wu SJ, Thottappilly G, Locy RD, Singh NK (2001) Molecular cloning and structural analysis of the gene encoding Bacillus cereus exochitinase Chi36. J Biosci Bioeng 92(1):59–66
Xie C, Chen Y, Cai J, Liu C (2010) Essential expression and inducible synthesis polymorphism of chitinase in Bacillus thuringiensis. Chin J Biotechnol 26(11):1532–1538
Xie CC, Jia HY, Chen YH (2011) Regulation of chitinase genes expression in bacteria. Yi chuan 33(10):1029–1038
Yuan G, Wong SL (1995) Regulation of groE expression in Bacillus subtilis: the involvement of the sigma A-like promoter and the roles of the inverted repeat sequence (CIRCE). J Bacteriol 177(19):5427–5433
Zhong WF, Fang JC, Cai PZ, Yan WZ, Wu J, Guo HF (2005) Cloning of the Bacillus thuringiensis serovar sotto chitinase (Schi) gene and characterization of its protein. Genet Mol Biol 28(4):821–826
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30971957), the Development Program of China (863 program) (No. 2011AA10A203) and the Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (No. 11JCYBJC08300 and 2012-2014). The authors thank Prof. Wei Chen at Jiangnan University of China for the gift of the plasmid pBSK-bgaB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, CC., Luo, Y., Chen, YH. et al. Construction of a Promoter-probe Vector for Bacillus thuringiensis: the Identification of cis-acting Elements of the chiA Locus. Curr Microbiol 64, 492–500 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0100-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0100-0