Abstract
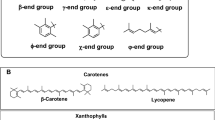
Cyanobacteria produce some carotenoids. We identified the molecular structures, including the stereochemistry, of all the carotenoids in the terrestrial cyanobacterium, Nostoc commune NIES-24 (IAM M-13). The major carotenoid was β-carotene. Its hydroxyl derivatives were (3R)-β-cryptoxanthin, (3R,3′R)-zeaxanthin, (2R,3R,3′R)-caloxanthin, and (2R,3R,2′R,3′R)-nostoxanthin, and its keto derivatives were echinenone and canthaxanthin. The unique myxol glycosides were (3R,2′S)-myxol 2′-fucoside and (2R,3R,2′S)-2-hydroxymyxol 2′-fucoside. This is only the second species found to contain 2-hydroxymyxol. We propose possible carotenogenesis pathways based on our identification of the carotenoids: the hydroxyl pathway produced nostoxanthin via zeaxanthin from β-carotene, the keto pathway produced canthaxanthin from β-carotene, and the myxol pathway produced 2-hydroxymyxol 2′-fucoside via myxol 2′-fucoside. This cyanobacterium was found to contain many kinds of carotenoids and also displayed many carotenogenesis pathways, while other cyanobacteria lack some carotenoids and a part of carotenogenesis pathways compared with this cyanobacterium.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Britton G, Liaaen-Jensen S, Pfander H (2004) Carotenoids handbook. Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel
Buchecker R, Liaaen-Jensen S, Borch G, Siegelman HW (1976) Carotenoids of Anacystis nidulans, structures of caloxanthin and nostoxanthin. Phytochemistry 15:1015–1018
Cunningham FX Jr, Sun Z, Chamovitz D, Hirschberg J, Gantt E (1994) Molecular structure and enzymatic function of lycopene cyclase from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp strain PCC7942. Plant Cell 6:1107–1121
Goodwin TW (1957) The nature and distribution of carotenoids in some blue-green algae. J Gen Microbiol 17:467–473
Goodwin TW (1980) The biochemistry of the carotenoids, vol 1: Plants, 2nd edn. Chapman and Hall, London
Graham JE, Bryant DA (2009) The biosynthetic pathway for myxol 2′-fucoside (myxoxanthophyll) in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7002. J Bacteriol 191:3292–3300
Hirschberg J, Chamovitz D (1994) Carotenoids in cyanobacteria. In: Bryant DA (ed) The molecular biology of cyanobacteria. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 559–579
Iwai M, Maoka T, Ikeuchi M, Takaichi S (2008) 2,2′-Hydoxylase (CrtG) is involved in carotenogenesis of both nostoxanthin and 2-hydroxymyxol 2′-fucoside in Thermosynechococcus elongatus strain BP-1. Plant Cell Physiol 49:1678–1687
Linden H, Vioque A, Sandmann G (1993) Isolation of a carotenoid biosynthesis gene coding for ζ-carotene desaturase from Anabaena PCC 7120 by heterologous complementation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 106:99–104
Makino T, Harada H, Ikenaga H, Matsuda S, Takaichi S, Shindo K, Sandmann G, Ogata T, Misawa N (2009) Characterization of cyanobacterial carotenoid ketolase CrtW and hydroxylase CrtR by complementation analysis in Escherichia coli. Plant Cell Physiol 50:1867–1878
Maresca JA, Graham JE, Wu M, Eisen JA, Bryant DA (2007) Identification of a forth family of lycopene cyclases in photosynthetic bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11784–11789
Mochimaru M, Masukawa H, Takaichi S (2005) The cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 has two distinct β-carotene ketolases: CrtO for echinenone and CrtW for ketomyxol synthesis. FEBS Lett 579:6111–6114
Mochimaru M, Masukawa H, Maoka T, Mohamed HE, Vermaas WFJ, Takaichi S (2008) Substrate specificities and availability of fucosyltransferase and β-carotene hydroxylase for myxol 2′-fucoside synthesis in Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 compared with Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. J Bacteriol 190:6726–6733
Nishida Y, Adachi K, Kasai H, Shizuri Y, Shindo K, Sawabe A, Komemushi S, Miki W, Misawa N (2005) Elucidation of a carotenoid biosynthesis gene cluster encoding a novel enzyme, 2,2′-β-hydroxylase, from Brevundimonas sp. strain SD212 and combinatorial biosynthesis of new or rare xanthophylls. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4286–4296
Rippka R, Castenholz RW, Herdman M (2001) Subsection IV. (Formerly Nostocales Castenholz 1989b sensu Rippka, Deruelles, Waterbury, Herdman and Stanier 1979). In: Boone DR, Castenholz RW (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 562–566
Sakamoto T, Yoshida T, Arima H, Hatanaka Y, Takani Y, Tamaru Y (2009) Accumulation of trehalose in response to desiccation and salt stress in the terrestrial cyanobacterium Nostoc commune. Phycol Res 57:66–73
Shindo K, Kikuta K, Suzuki A, Katsuta A, Kasai H, Yasumoto-Hirose M, Matuo Y, Misawa N, Takaichi S (2007) Rare carotenoids, (3R)-saproxanthin and (3R,2′S)-myxol, isolated from novel marine bacteria (Flavobacteriaceae) and their antioxidative activities. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:1350–1357
Steiger S, Sandmann G (2004) Cloning of two carotenoid ketolase genes from Nostoc punctiforme for the heterogous production of canthaxanthin and astaxanthin. Biotechnol Lett 26:813–817
Stickforth P, Steiger S, Hess WR, Sandmann G (2003) A novel type of lycopene ε-cyclase in the marine cyanobacterium Prochlorococcus marinus MED4. Arch Microbiol 179:409–415
Stransky H, Hager A (1970) The carotenoid pattern and the occurrence of the light induced xanthophylls cycle in various classes of algae. IV. Cyanophyceae and Rhodophyceae. Arch Mikrobiol 72:84–96
Takaichi S, Shimada K (1992) Characterization of carotenoids in photosynthetic bacteria. Methods Enzymol 213:374–385
Takaichi S, Mochimaru M (2007) Carotenoids and carotenogenesis in cyanobacteria: unique ketocarotenoids and carotenoid glycosides. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:2607–2619
Takaichi S, Mochimaru M (2009) Carotenoids, their diversity and carotenogenesis in cyanobacteria. In: Gault PM, Marler HJ (eds), Handbook of cyanobacteria: biochemistry, biotechnology and applications. Nova Science Publishers, New York, in press (https://www.novapublishers.com/catalog/product_info.php?products_id=9524)
Takaichi S, Maoka T, Masamoto K (2001) Myxoxanthophyll in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 is myxol 2′-dimethyl-fucoside, (3R,2′S)-myxol 2′-(2,4-di-O-methyl-α-L-fucoside), not rhamnoside. Plant Cell Physiol 42:756–762
Takaichi S, Mochimaru M, Maoka T, Katoh H (2005) Myxol and 4-ketomyxol 2′-fucosides, not rhamnosides, from Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 and Nostoc punctiforme PCC 73102, and proposal for the biosynthetic pathway of carotenoids. Plant Cell Physiol 46:497–504
Takaichi S, Mochimaru M, Maoka T (2006) Presence of free myxol and 4-hydroxymyxol and absence of myxol glycosides in Anabaena variabilis ATCC 29413, and proposal of a biosynthetic pathway of carotenoids. Plant Cell Physiol 47:211–216
Tao L, Rouvière PE, Cheng Q (2006) A carotenoid synthesis gene cluster from a non-marine Brevundimonas that synthesizes hydroxylated astaxanthin. Gene 379:101–108
Yokoyama A, Miki W (1995) Isolation of myxol from a marine bacterium Flavobacterium sp. associated with a marine sponge. Fish Sci 61:684–686
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Professors M. Tanaka and T. Sanji, Tokyo Institute of technology, for their help in measuring CD spectra, and Dr. T. Sakamoto, Kanazawa University, for his gift of N. commune natural field sample.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takaichi, S., Maoka, T. & Mochimaru, M. Unique Carotenoids in the Terrestrial Cyanobacterium Nostoc commune NIES-24: 2-Hydroxymyxol 2′-Fucoside, Nostoxanthin and Canthaxanthin. Curr Microbiol 59, 413–419 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-009-9453-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-009-9453-4