Abstract
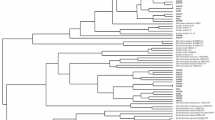
A total of eight strains of bacteria were isolated from the root nodule of Vicia faba on the selective media of Rhizobium. Two of these strains produced phenotypically distinct mucoid colonies (one slow growing and the other fast growing) and were examined using a polyphasic approach for taxonomic identification. The two strains (MTCC 7405 and MTCC 7406) turned out to be new strains of biovar 1 Agrobacterium rather than Rhizobium, as they showed growth on alkaline medium as well as on 2% NaCl and neither catabolized lactose as the carbon source nor oxidized Tween-80. The distinctness between the two strains was marked with respect to their growth on dextrose and the production of lysine dihydrolase, ornithine decarboxylase and DNA G + C content. 16S rDNA sequencing and their comparison with the 16S rDNA sequences of previously described agrobacteria as well as rhizobia strains confirmed the novelty of the two strains. Both of the strains clustered with strains of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in the 16S rDNA-based phylogenetic tree. The phenotypic and biochemical properties of the two strains differed from those of the recognized biovar of A. tumefaciens. It is proposed that the strains MTCC 7405 and MTCC 7406 be classified as novel biovar of the species A. tumefaciens (Type strains MTCC 7405 = DQ383275 and MTCC 7406 = DQ383276).

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The GenBank accession numbers for the 16S rRNA gene sequences of the two biovar deposited in NCBI, Bethesda, MD, USA is DQ383275 for MTCC7405 and DQ383276 for MTCC 7406, which canbe found online at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. The sequence is also available in EMBL in Europe and the DNA Data Bank of Japan.
References
Allen EK, Allen ON (1958) Biological aspects of symbiotic nitrogen fixation. In: Rubland W (ed) Hand buch der Pflanzenphysiologie, Vol. B. Springer-Verlag, Berlin pp 48–118
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, et al. (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Atlas RM, Brown AE, Dobra KW, et al. (1973) Experimental microbiology: fundamentals and applications. Macmillan, New York
Bouzar H, Jones JB, Hodge NC (1993) Differential characterization of Agrobacterium species using carbon source utilization pattern and fatty acid profiles. Phytopathology 83:733–739
Bouzar H, Moore LW (1987) Isolation of different Agrobacterium biovar from a natural oak savanna and tallgrass prairie. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:717–721
Brosius J, Palmer ML, Kennedy PJ, et al. (1978) Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:4801–4805
Dessaux Y, Petit A, Tempé J (1992) Opines in Agrobacterium biology. In Verma DPS (ed) Molecular signals in plant-microbe communication, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL pp 109–136
Farrand SK, van Berkum P, Oger P (2003) Agrobacterium is a definable genus of the family Rhizobiaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1681–1687
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenetics: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, et al. (1994) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC
Holmes B (1988) The taxonomy of Agrobacterium. Acta Hortic (The Hague) 225:47–52
Holmes B, Roberts P (1981) The classification, identification and nomenclature of agrobacteria. Incorporating revised descriptions for each of Agrobacterium tumefaciens (Smith & Townsend) Conn 1942, Agrobacterium rhizogenes (Ricker et al.) Conn 1942, and Agrobacterium rubi (Hildebrand) Starr & Weiss 1943. J Appl Bacteriol 50:443–467
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PHA, et al. (1993) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 9th ed. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Juke TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism, Vol. 3, Academic Press, New York, pp 21–132
Keane PJ, Kerr A, New PB (1970) Crown gall of stone fruit. II. Identification and nomenclature of Agrobacterium isolates. Aust J Biol Sci 23:585–595
Kersters K, De Ley J, Sneath PHA, et al. (1973) Numerical taxonomic analysis of Agrobacterium. J Gen Micrbiol 78:227–239
Kersters K, De Ley J (1984) Genus III. Agrobacterium Conn 1942. In: Krieg NR, Holt JG (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, Vol. 1. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 244–254
Mandel M, Marmur J (1968) Use of ultraviolet absorbance-temperature profile for determining the guanine plus cytosine content of DNA. Methods Enzymol 12B:195–206
Moore LW, Bouzar H, Burr T (1988) Agrobacterium. In: Schaad NW (ed) Laboratory Guide for identification of plant pathogenic bacteria, 2nd ed. APS Press, St Paul, MN, pp 16–36
Mougel C, Cournoyer B, Nesme X (2001) Novel tellurite-ammended media and specific chromosomal and Ti plasmid probes for direct analysis of soil populations of Agrobacterium biovars 1 and 2. Appl Env Microbiol 67:65–74
Ophel K, Kerr A (1990) Agrobacterium vitis sp. nov. for strains of Agrobacterium biovars 3 from grapevines. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 40:236–241
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbour-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 44:406–425
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, et al. (1997) The clustalx windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Van de Peer Y, De Wachter R (1994) TREECON for Windows: a software package for the construction and drawing of evolutionary trees for the Microsoft Windows environment. Comput Appl Biosci 10:569–570
Vincent GM (1970) A manual for the practical study of the root nodule bacteria. IBH Handbook No. 15. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Winans SC (1992) Two-way chemical signaling in Agrobacterium–plant interactions. Microbiol Rev 56:12–31
Woese CR, Stackebrandt E, Weisburg WG, et al. (1984) The phylogeny of purple bacteria: the alpha subdivision. Syst Appl Microbiol 5:315–326
Wong LL, Wong ET, Liu J, et al. (2006) Endophytic occupation of root nodules and root of Melilotus dentatus by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Microbial Ecol 52:436–443
Young JM, Bull CT, De Boer SH, et al. (2001) Classification, nomenclature and plant pathogenic bacteria: a clarification. Phytopathology 91:617–620
Young JM, Kuykendall LD, Martinez-Romero E, et al. (2003) Classification and nomenclature of Agrobacterium and Rhizobium: a reply to Farrand et al. (2003). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1689–1695
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Research Grant No. BT/PR-4191/PID/06/182/2003 (Microbial Biodiversity Consortium Network of Bihar) from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India. We thank Ms. Vartika Joshi of the Institute of Microbial Technology, Chandigarh for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiwary, B.N., Prasad, B., Ghosh, A. et al. Characterization of Two Novel Biovar of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Isolated from Root Nodules of Vicia faba . Curr Microbiol 55, 328–333 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-007-0182-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-007-0182-2